During the Beginning of Summer, Rose Tea is Often Used to Soothe the Liver and Regulate Qi. Be Careful Not to Buy the Wrong Kind to Avoid Harming Your Health.
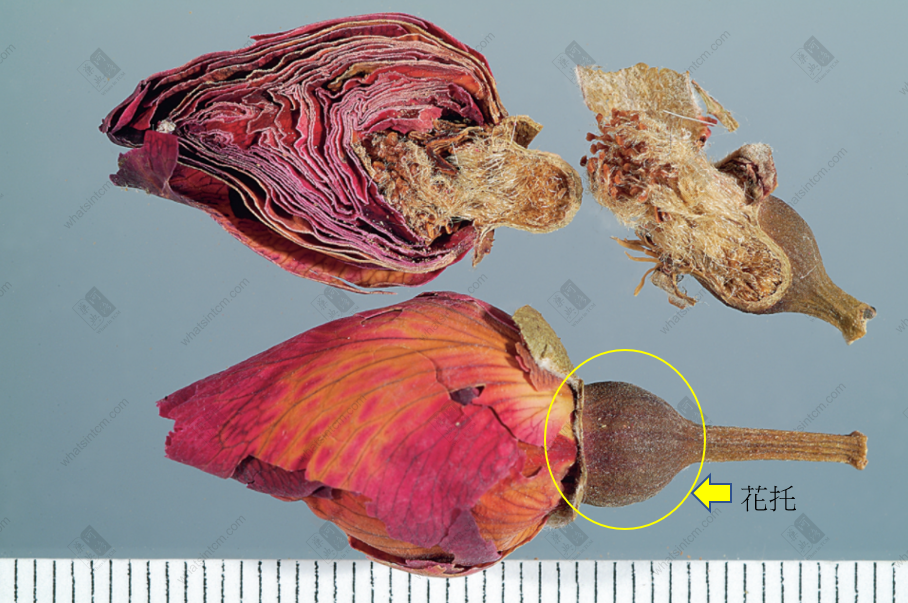 Rose: The receptacle is hemispherical and purplish-red. The sepals are connate at the base, and the petals are shriveled and imbricated, with a light and crisp texture.
Rose: The receptacle is hemispherical and purplish-red. The sepals are connate at the base, and the petals are shriveled and imbricated, with a light and crisp texture.
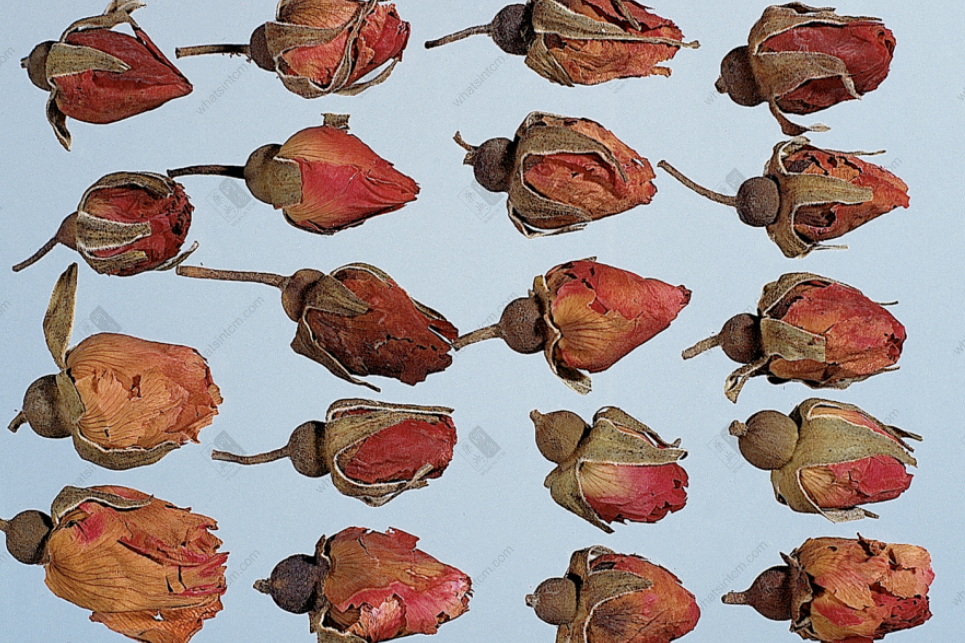 Rose
Rose
“Not related to the name of the month rose, nor shares lineage with the wild rose. Thousands of green leaves connect, one flower displays two colors, light and deep red. Each has its own unique charm and fragrance, as if blessed by nature’s grace. Yet, its inherent floral scent cannot be captured, and poets infuse it into their incense.
“Red Rose” by Yang Wanli of the Song Dynasty
The poem mentions that although the monthly rose and the wild rose belong to the same Rosaceae family, they have many differences. Ancient people wore them, their colors were vibrant, and their fragrance filled the air like agarwood, making them irresistible.
According to the “Illustrated Identification Guide to Confusing Chinese Patent Medicines Sold in Taiwan” published by the Ministry of Health and Welfare, the source of rose (https://whatsintcm.com/dt_articles/%e7%8e%ab%e7%91%b0%e8%8a%b1/) is the dried flower buds of the rose plant *Rosa rugosa Thunb.* from the Rosaceae family. It is mainly produced in Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Anhui, Shandong, and Gansu. Pingyin County in Shandong, Yongdeng County in Gansu, and Miaofeng Mountain in Beijing are three very famous rose-producing areas in mainland China. In Taiwan, there are also rose plantings for ornamental and edible purposes in Nantou County and Taichung City in the central region, and Pingtung County in the south. Their quality has also been recognized in international competitions. According to the 2019 Taiwan Agricultural Statistics Annual Report, the total rose planting area in Taiwan was approximately 178.23 hectares. Because its stems have thorns, the rose is also called “ci mei” (刺玫). And because of its strong fragrance, people often linger around it, hence it is also called “pai hui hua” (徘迴花), meaning “lingering flower”. Together with the monthly rose and the wild rose, they are usually called the “three sisters of the rose family.” Due to the special nature of these three sisters, many countries around the world, such as the United Kingdom, the United States, Bulgaria, Iran, and Syria, have adopted it as their national flower. Rose buds are usually harvested in batches in late spring and early summer, just before they fully open. They are then promptly dried at low temperatures for preservation. Generally, the receptacle is slightly hemispherical, and the petals are purplish-red. They should feel light and crisp to the touch. They have a rich and fragrant aroma and a slightly bitter and astringent taste. Traditional selection experience favors large and intact flowers, with thicker petals, bright purple color, no visible stamens, and a strong fragrance. Rose entered the materia medica relatively late. The Qing Dynasty pharmacologist Zhao Xue-min (approximately 1719-1805) recorded in his “Supplement to the Compendium of Materia Medica” (《本草綱目拾遺》) that: “Rose, has a fragrant aroma and warm nature, sweet and slightly bitter taste, enters the Spleen and Liver meridians, harmonizes and invigorates blood, regulates qi and treats wind-dampness paralysis.” This shows its remarkable efficacy in regulating qi and invigorating blood. The book also mentions: “Treats dysentery with closed mouth: dried rose decocted and taken orally,” indicating its efficacy in treating dysentery.
There are several varieties that are easily confused in the market. The most common one is the monthly rose, which belongs to the same family. The main difference between rose and monthly rose is that the receptacle of the rose is typically urn-shaped or hemispherical, while the monthly rose is mainly obconical. The flower stalk of the rose is usually shorter or absent, while the monthly rose usually has a visible flower stalk. Furthermore, the sepals of the rose are usually lanceolate, yellowish-green or brownish-green, while the monthly rose sepals are ovate and dark green. Finally, by smelling them, one can usually detect that the rose has a stronger fragrance, while the monthly rose is typically more delicately fragrant. With the above methods, it is very easy to distinguish their differences.
Rose is not only used as a traditional Chinese medicine but also often used as food or for ornamental purposes. However, due to different usage methods, relevant authorities have different management regulations. Typically, pesticide standards for edible use and ornamental use have different detectable limits. According to Article 15 of the Act Governing Food Safety and Sanitation and the “Standard for Pesticide Residue Limits,” the quantitative limit for the pesticide salicin in edible roses is 0.05 ppm. Roses for general ornamental purposes will differ. Therefore, after purchasing roses from the flower market, the public should not put them in the bathtub for bathing, to avoid harming their health. If you wish to use them, you should purchase edible-grade roses. Due to their strong fragrance, roses are often used to extract essential oils or hydrosols. The taste and quality vary depending on the type of rose and the extraction method. Therefore, the prices sold on the market vary greatly. It is essential to choose reputable merchants before purchasing to ensure excellent quality.
【Images provided by】Professor Chang Xian-zhe, “Authentic Medicinal Material Illustrated Guide” https://whatsintcm.com

