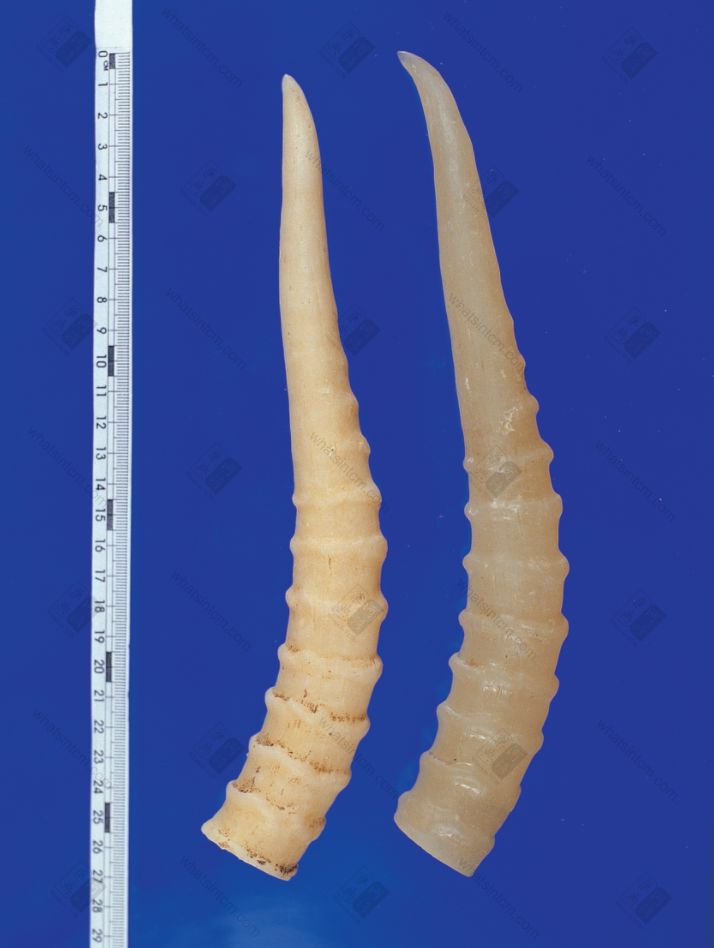
Antelope Horn
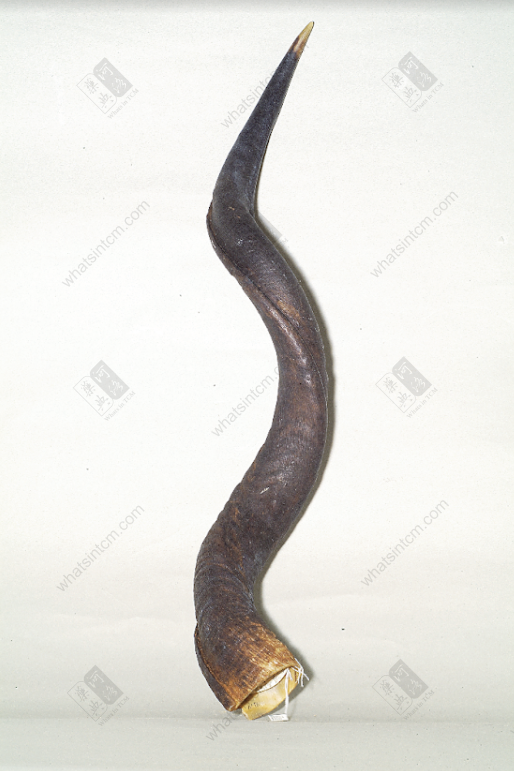
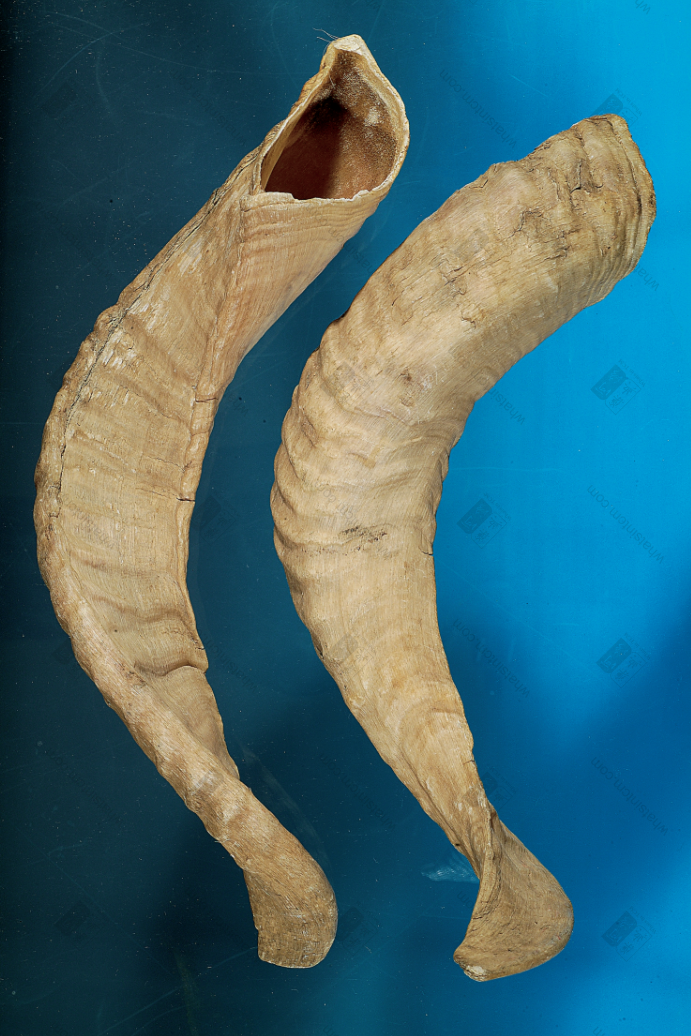
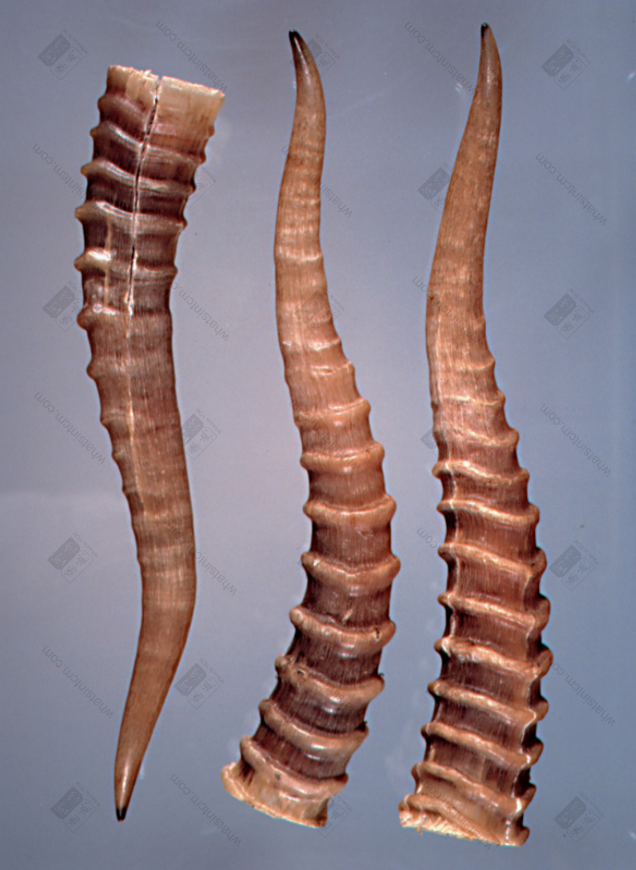 Antelope Horn (Slender cone, curved, yellowish-white, black at the top, ringed sections at the bottom, hard)
Antelope Horn (Slender cone, curved, yellowish-white, black at the top, ringed sections at the bottom, hard)
 Antelope Horn (Top left, young) (Dark cloud covering the top, water ripple pattern, annular ridges, gear-like pattern, bone plug)
Antelope Horn (Top left, young) (Dark cloud covering the top, water ripple pattern, annular ridges, gear-like pattern, bone plug)
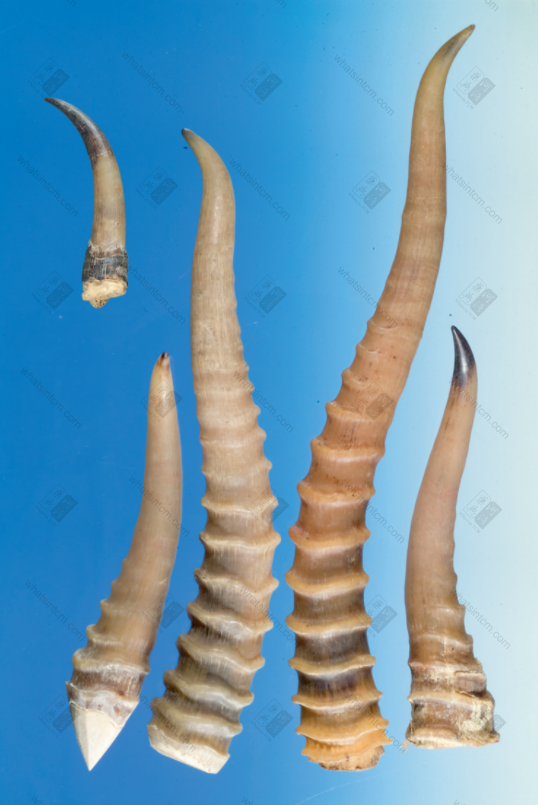
 Inferior Antelope Horn
Inferior Antelope Horn
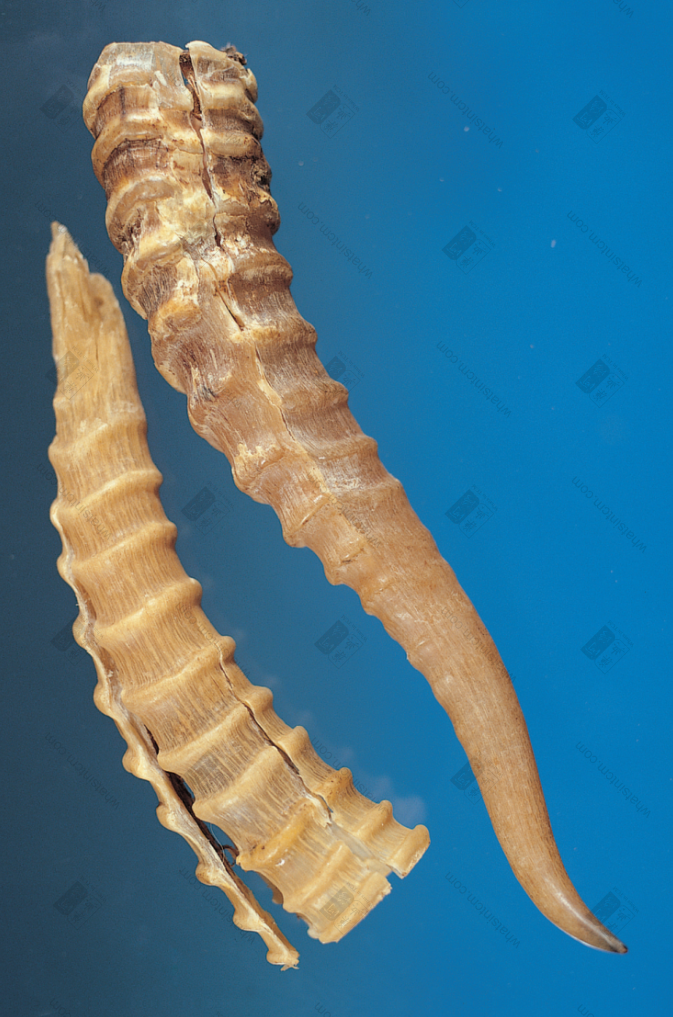
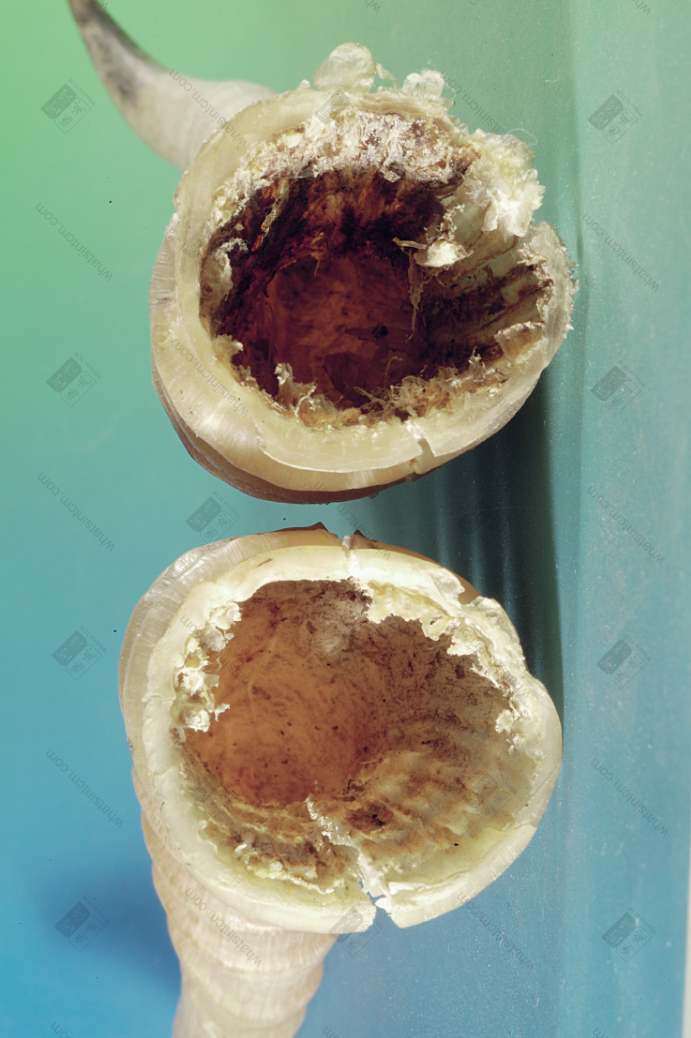 Antelope Horn (Sky-piercing eye) (The sky-piercing eye, a channel going straight to the tip of the horn, can be seen when held to the light)
Antelope Horn (Sky-piercing eye) (The sky-piercing eye, a channel going straight to the tip of the horn, can be seen when held to the light)
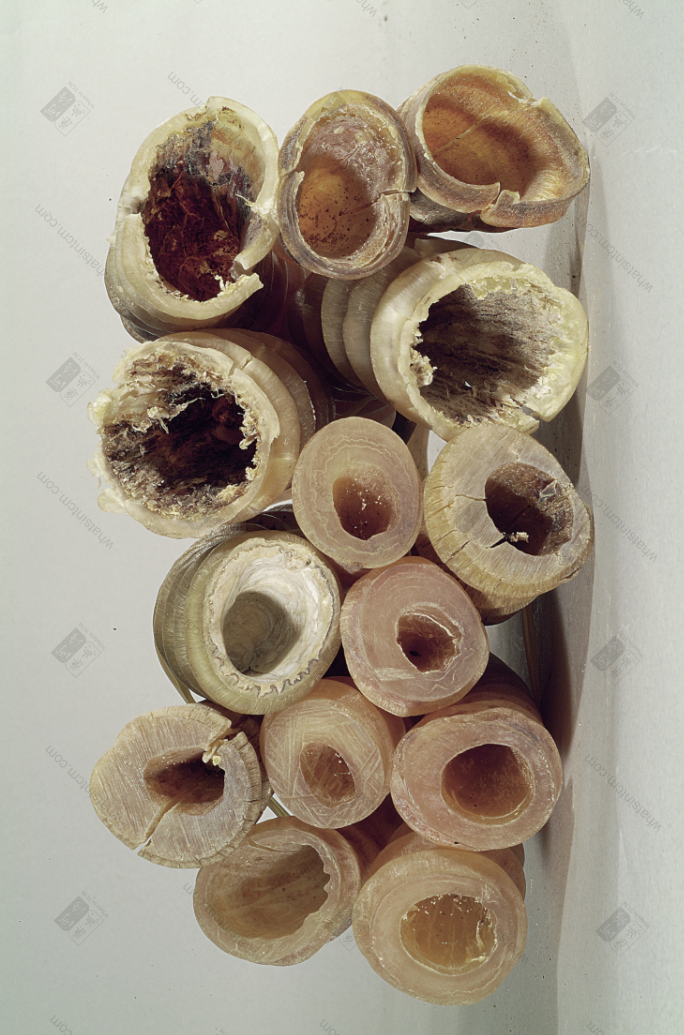 Base hole of Antelope Horn
Base hole of Antelope Horn
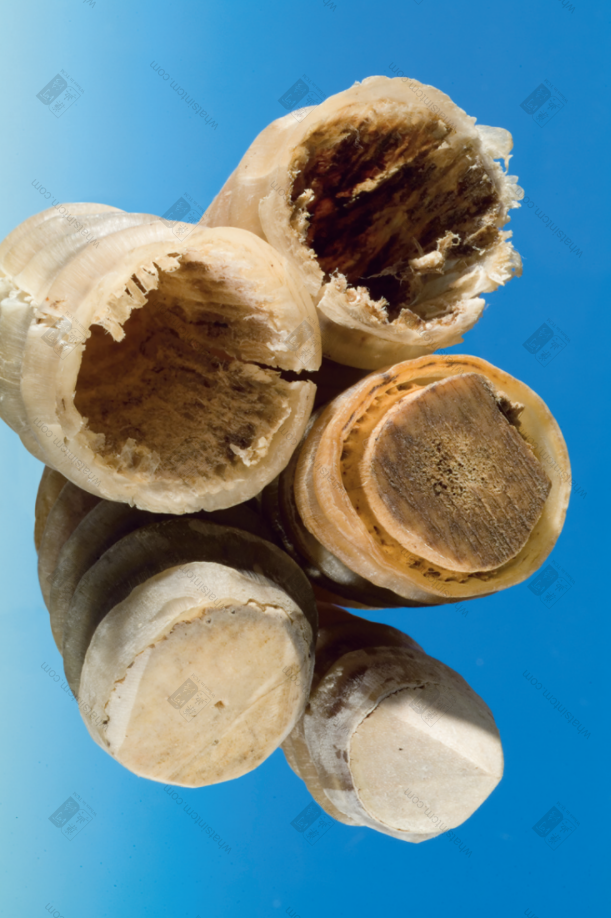 Antelope Horn Horn plug
Antelope Horn Horn plug
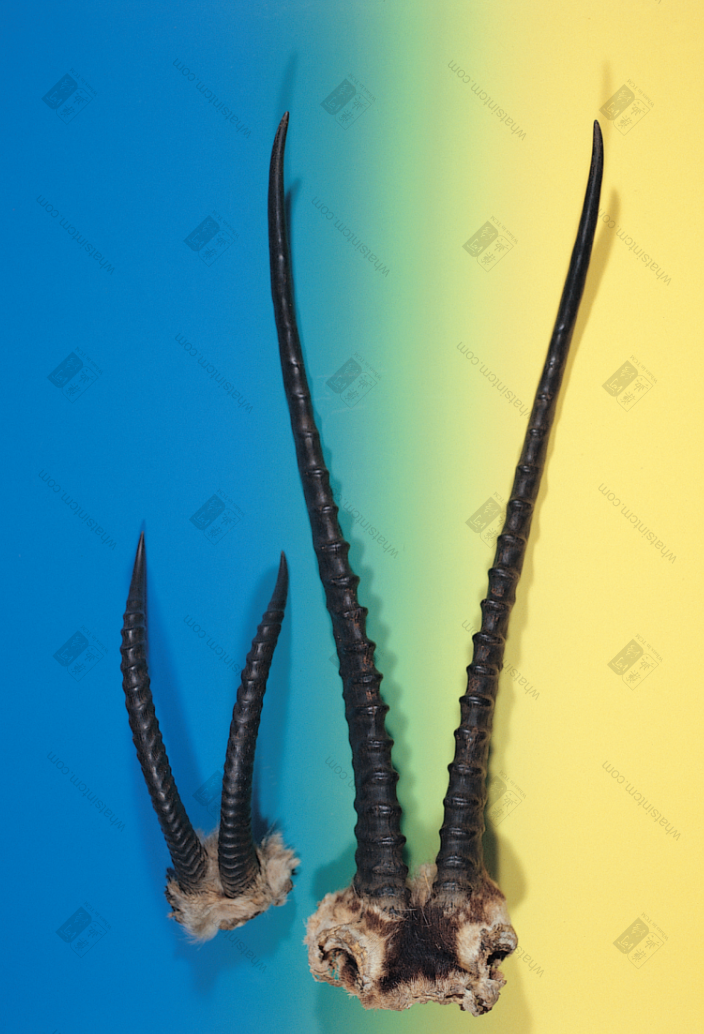 Tibetan Antelope (Left small Tibetan Antelope)
Tibetan Antelope (Left small Tibetan Antelope)
 Small Tibetan Antelope
Small Tibetan Antelope
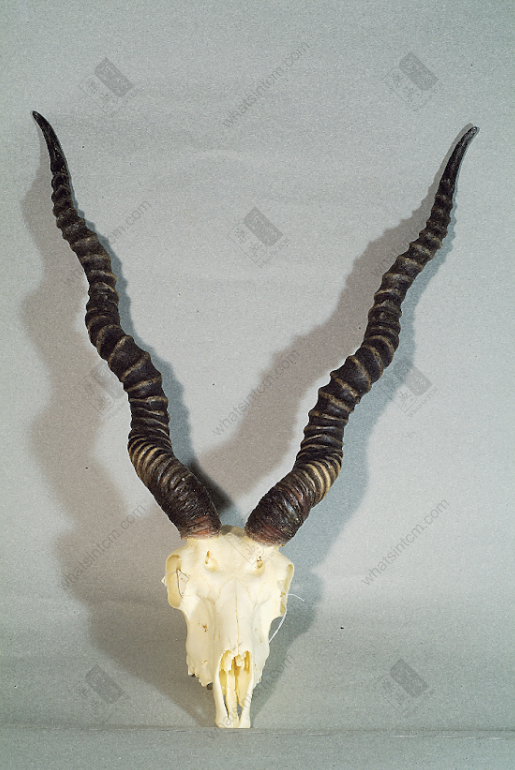
 African Eland
African Eland
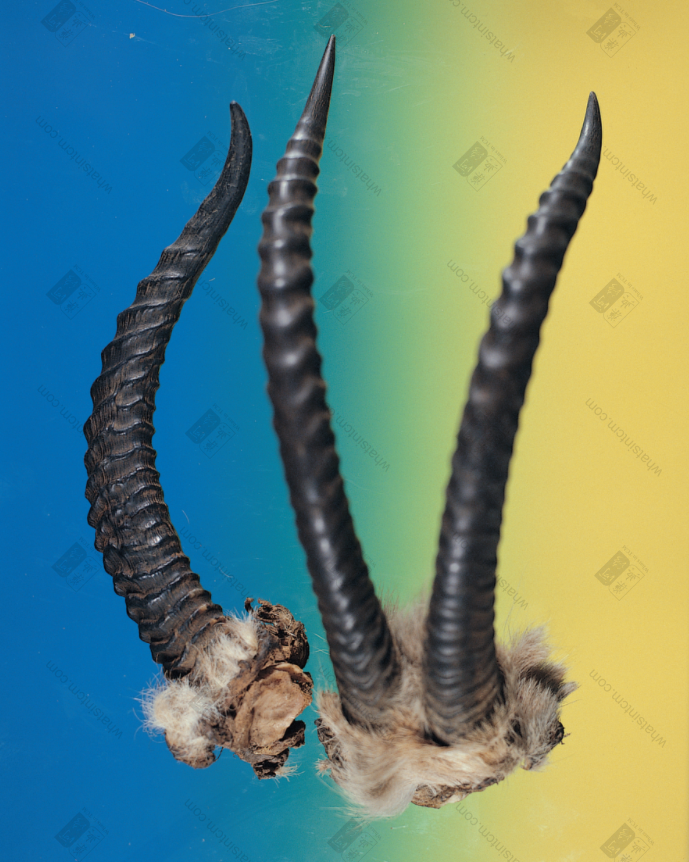
 African Antelope
African Antelope
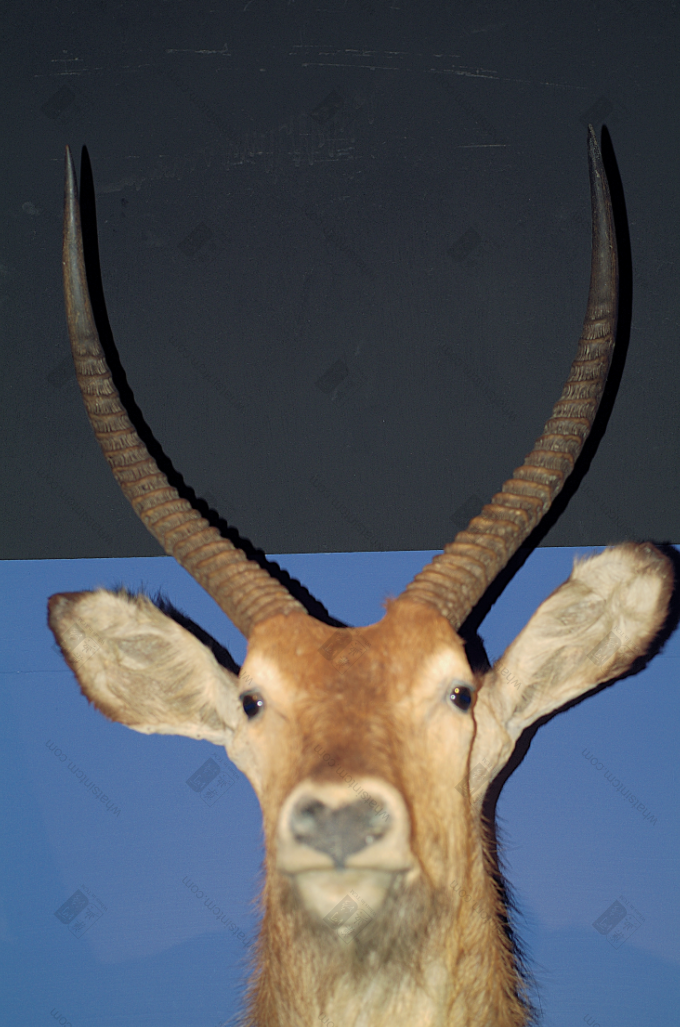
 Sable Antelope
Sable Antelope
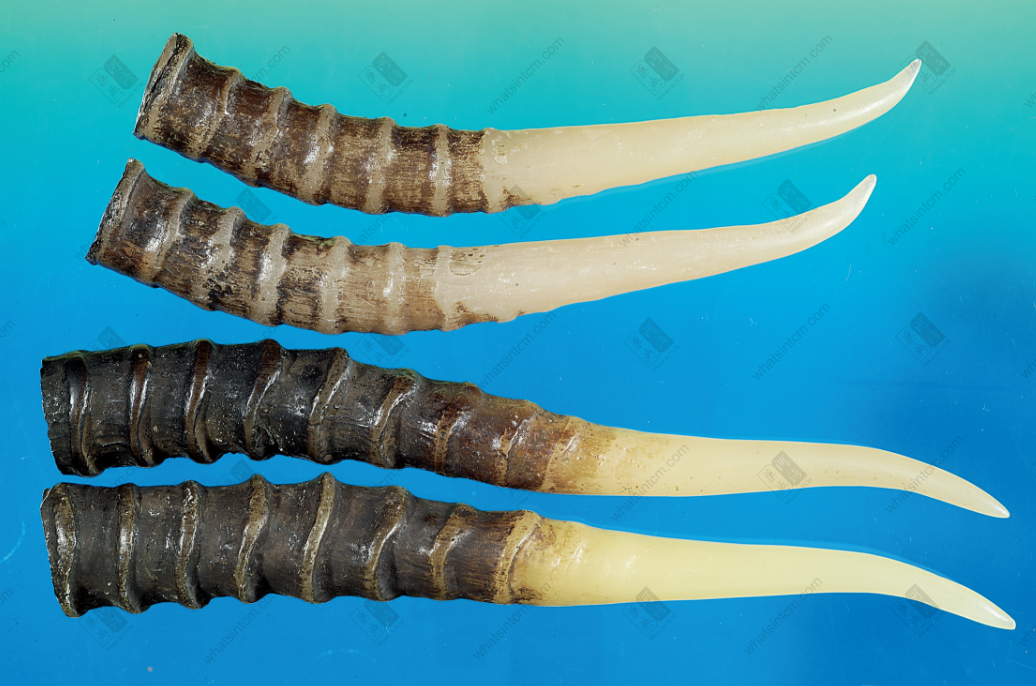
 Argali Sheep Horn (Falsely used as Antelope Horn)
Argali Sheep Horn (Falsely used as Antelope Horn)
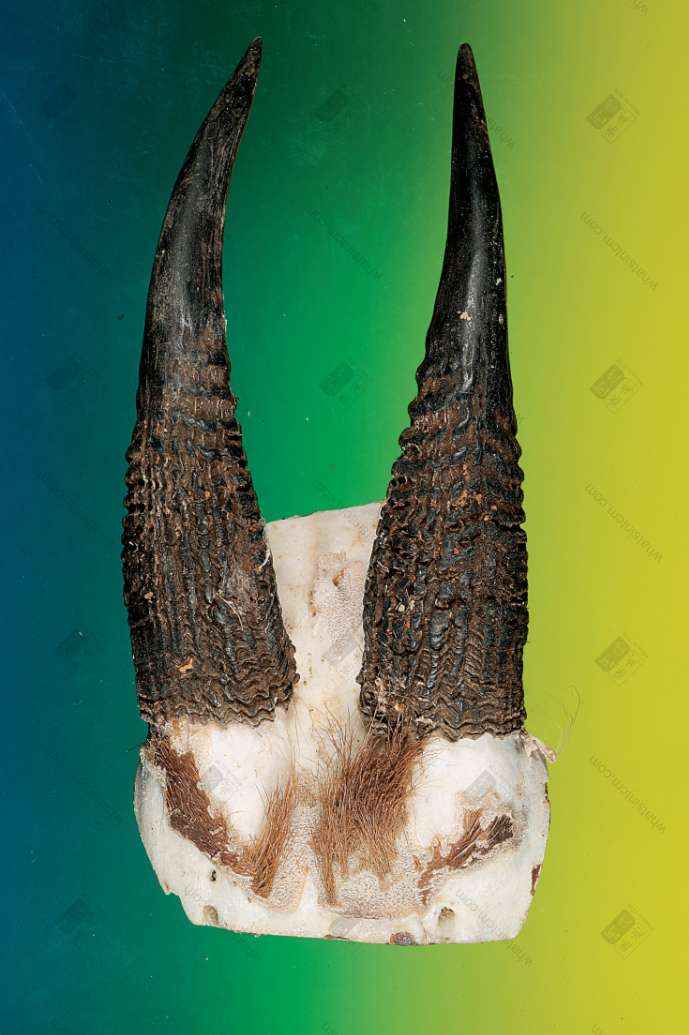 Goat Horn
Goat Horn
 Plastic Fake Antelope Horn
Plastic Fake Antelope Horn
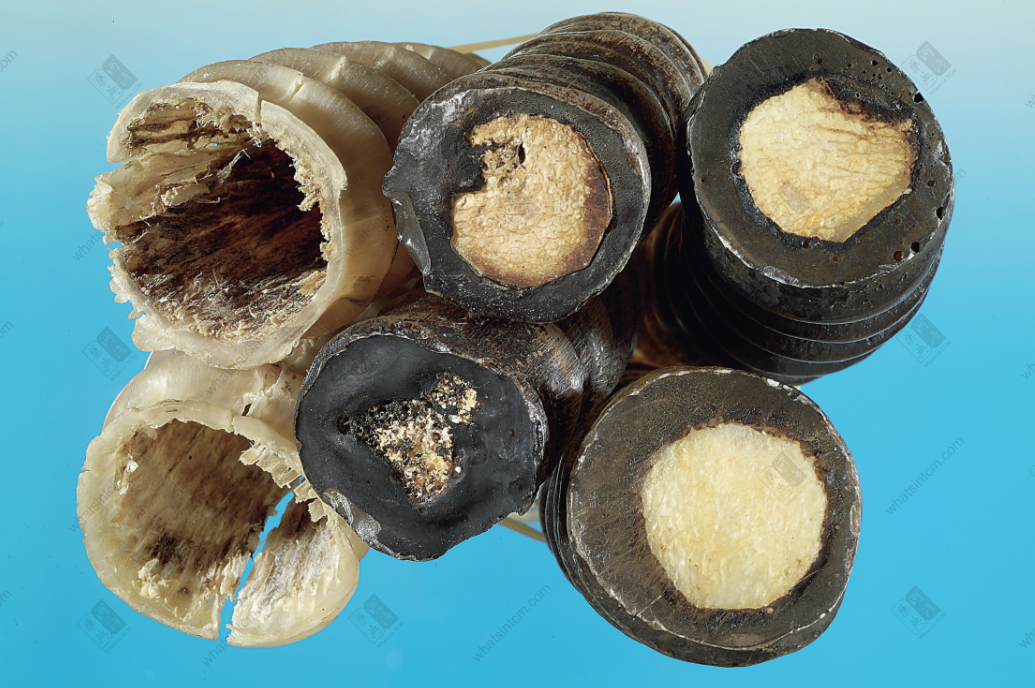 Comparison of Authentic and Fake Antelope Horn Base
Comparison of Authentic and Fake Antelope Horn Base
【Naming】
【Source】
Ben Jing (Shen Nong’s Herbal Classic)
【Common Usage Degree】
C
【Botanical Origin】
The horn of the Saiga antelope, Saiga tatarica L., family Bovidae.
【Characteristics】
Slender and curved, thick at the base and gradually thinning towards the tip. Generally about 30-40cm long, with a basal diameter of about 5-7cm. There are whorled annular segments slightly below the tip. The tip is translucent, like jade, with annular ridges. The inner surface of the base is slightly darker and opaque due to the presence of a bony “antelope plug”. There is a dark line shadow in the center of the horn, which is a fine channel that extends directly to the tip, called the “sky-piercing eye”. The bony “antelope plug” has protruding straight lines, which are tightly connected to the concave lines (i.e., grooves) of the horn. The junction is irregularly serrated.
【Identification】
《Xin Xiu Ben Cao (Newly Revised Materia Medica)》: “[Note] This antelope horn is best from the blue ram.”《Zheng Lei Ben Cao (Classified Materia Medica)》: “A true horn makes a ‘jiji’ sound when listened to near the ear is good”, “A horn from a one-horned antelope is superior.”《Ben Cao Yan Yi Bu Yi (Supplement to the Extended Materia Medica)》: “Antelope horns now and in the past were selected by the presence of hanging marks. It is said: Listen to the horn, if it makes a ‘jiji’ sound, it is good. This is a forced argument and has not been widely tested. Now, if you put other horns to the ear, they all make a ‘jiji’ sound. So the hanging mark method is the only correct way. However, many are fake, so you must be careful.”《Ben Cao Pin Hui Jing Yao (Essential Compendium of Materia Medica)》: “The white and crystal clear ones are the best.”《Ben Cao Bei Yao (Essentials of Materia Medica)》: “Comes from the western region, similar to a goat but larger, the horn has segments and is very strong. It can crush diamonds and tapir bones. At night, to prevent danger, it hangs its horns on trees to rest. Most have two horns, but one-horned ones are superior.”《Jing Yan Dan Fang Hui Bian (Collection of Proven Elixir Formulas)》: “For antelope horns, look for those that are pointed and slender in the curve of the horn and have hanging marks to be considered genuine; or listen near the ear for a ‘jiji’ sound to be considered good.”, “For antelope horns, look for those that are pointed and slender in the curve of the horn and have hanging marks to be considered genuine.”《Ben Cao Jian Yao Fang (Simple Formulas from Materia Medica)》: “It is best to cut the horn while it is still alive.”《Liang Lie Jian Bie (Identification of Good and Bad)》: “The top one or two inches of the tip is the best, followed by the outer shavings from the segmented area. The internal marrow should be the color of malt sugar to be considered superior.”
Look for horns that are energetic, with a fleshy or tender white color, emitting a treasure-like luster, with a blood heart inside. When held to the light, they should be translucent, with slight black spots at the tip. The center of the horn tip has a transparent point that gradually extends downwards (sky-piercing eye). When soaked in water, they should have a clear fragrance to be considered good.
【Identification Terms】
<span style="font-weight: 400;
1. Water Ripple Pattern: Refers to the 10-20 raised wave-like annular ridges on the Antelope Horn, excluding the smooth top portion. The distance between them is about 2cm, and it feels comfortable to hold.
2. Blood Streaks: Tender Antelope Horn has blood-red mottling when viewed under light.
3. Blood Groove (Blood Line): The part of the Antelope Horn surface where the raised straight lines closely match the concave straight lines inside the horn sheath.
4. Withered Horn: Refers to the withered horn of horned animals that have been around for a long time, or the dead horn left in the mountains after the death of wild animals.
5. Dark Cloud Covering the Top: The horn tip of the tender horn of the Antelope Horn is blackish-brown, commonly known as “Dark Cloud Covering the Top”.
6. Antelope Plug (Antelope Bone, Bone Plug): The bone plug in the lower half of the Antelope Horn. It is about one-half or one-third of the entire horn in length, and it is in the shape of a long cone with shallow longitudinal grooves on the surface. The bony plug connects the bone tissue to the blood socket, and the inlay is tight. The bony plug is white, and the base resembles a peach shape.
7. Sky-Piercing Eye (One-Line Connection, Piercing Eye): Remove the bone plug, it is hollow, and there is a thin triangular flat hole in the center of the Antelope Horn, which goes straight to the horn tip but does not penetrate the outside of the horn. When viewed under light, there is a thin hole in the center of the horn that goes straight to the top, called the “Sky-Piercing Eye”, which is a nerve hole.
8. Shadowless Pattern: The tip of the Antelope Horn is as smooth as jade, and the tender ones have blood streaks or purplish-black mottling in the center when viewed under light. There are no cracks, commonly known as “Shadowless Pattern”.
9. Silk Pattern: The color of the Antelope Horn is smooth and lustrous like jade, white and yellowish-white. In addition to the whorled segments, the surface also has fine silk patterns that are organized.
10. Gear Pattern: The antelope plug has longitudinal bone ridges around it, which are tightly meshed with the grooves (called blood grooves) on the horn wall, and it is very firm. The cross-section of the base is serrated around it, called “Gear Pattern”.
11. Annular Ridge (Annular Node): Refers specifically to the raised annular lines in the middle and lower part of the Antelope Horn. Until the horn is near the horn tip, there are about 10-20 of them. One side of the wheel joint is convex and the other is concave. The lines are sequentially annular, smooth and natural, and it feels comfortable to hold with your hand, commonly known as “Handy”. Annular ridges are often used to identify counterfeit Antelope Horns, such as yellow goat horns, which have 17-20 wheel ridges that are closely spaced and do not form a ring.
【Section】
Vertebrate Category