Yin Chai Hu (Stellaria)
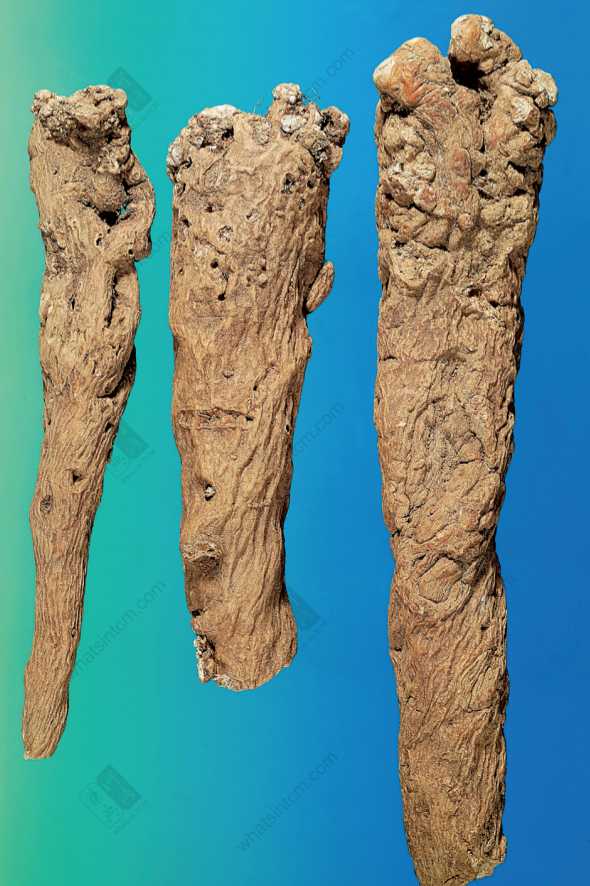 Yin Chai Hu (Lion’s head) (Cylindrical, few branches, light yellow)
Yin Chai Hu (Lion’s head) (Cylindrical, few branches, light yellow)
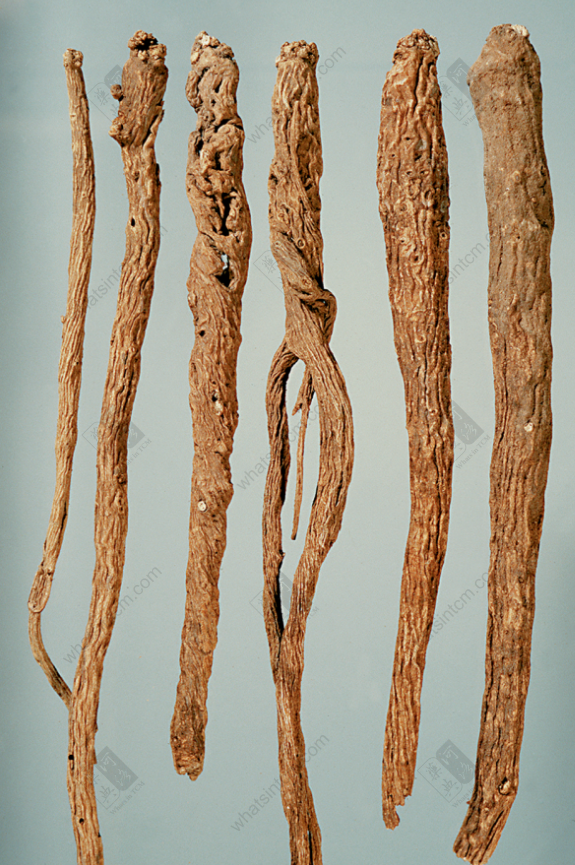 Yin Chai Hu (Pearl disk head, sandy eyes)
Yin Chai Hu (Pearl disk head, sandy eyes)
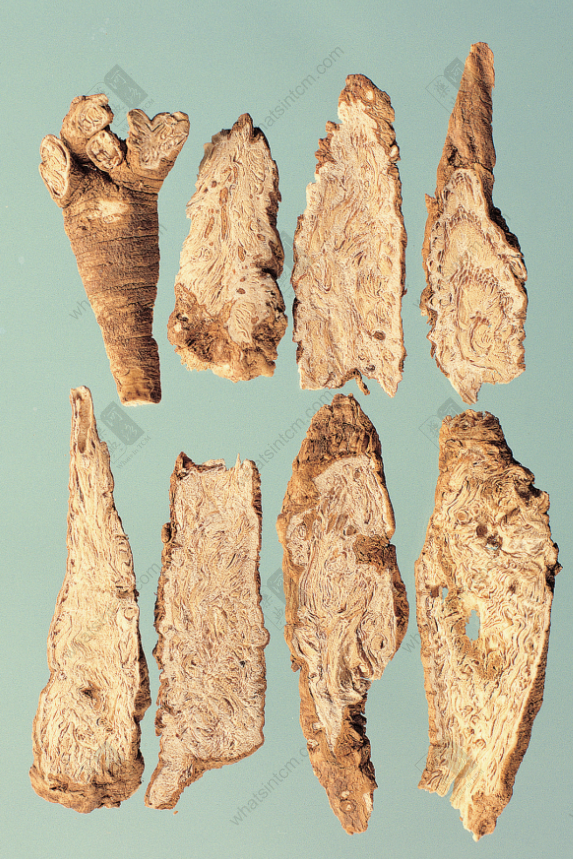 Yin Chai Hu slices (Radial texture)
Yin Chai Hu slices (Radial texture)
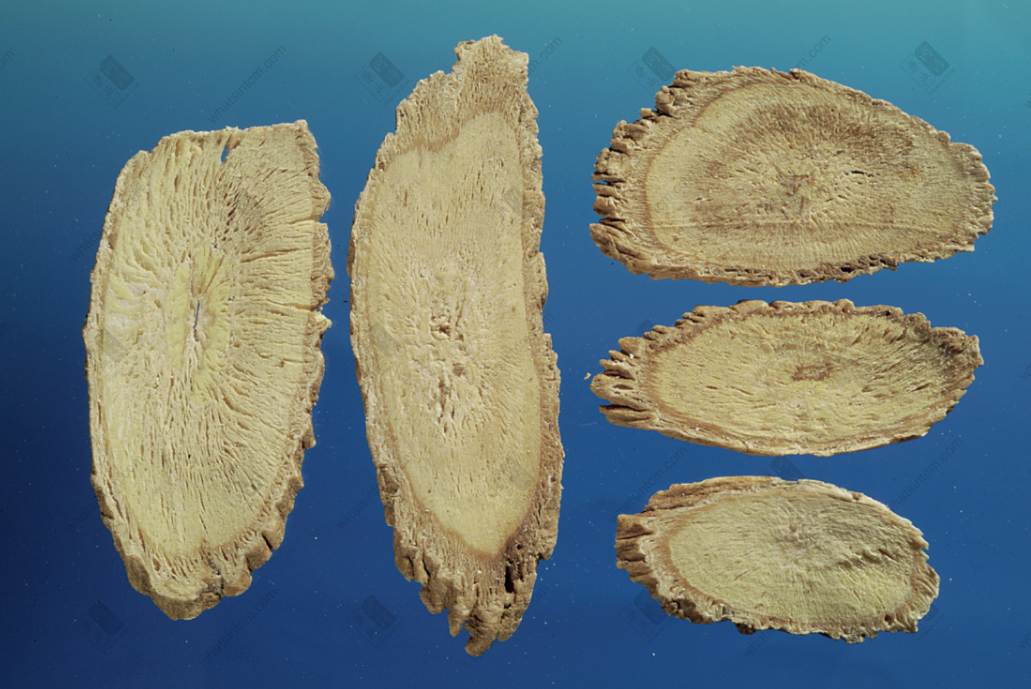 Yin Chai Hu slices
Yin Chai Hu slices
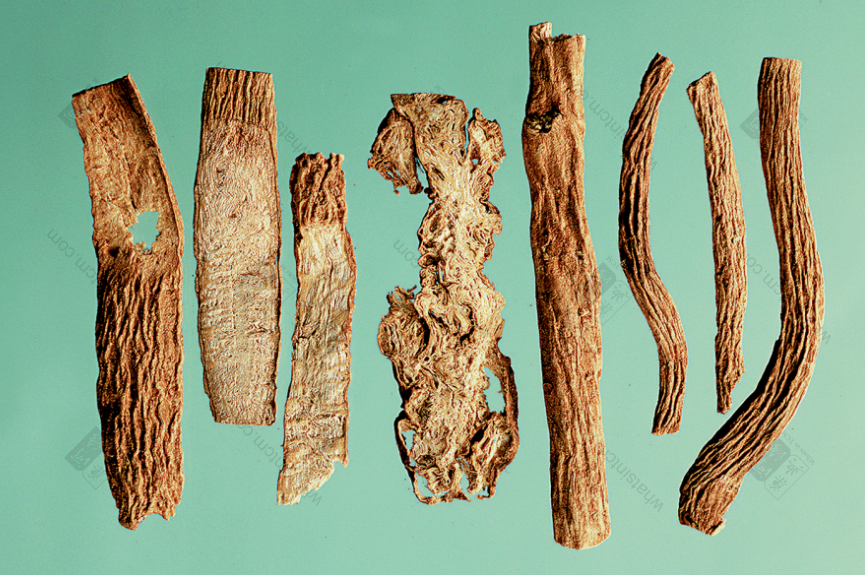 Yin Chai Hu slices
Yin Chai Hu slices
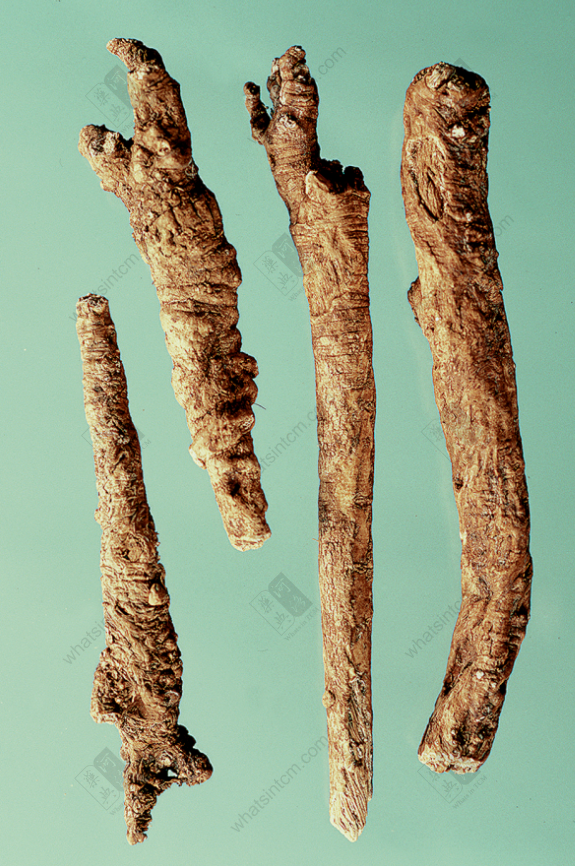 Tu Yin Chai Hu
Tu Yin Chai Hu
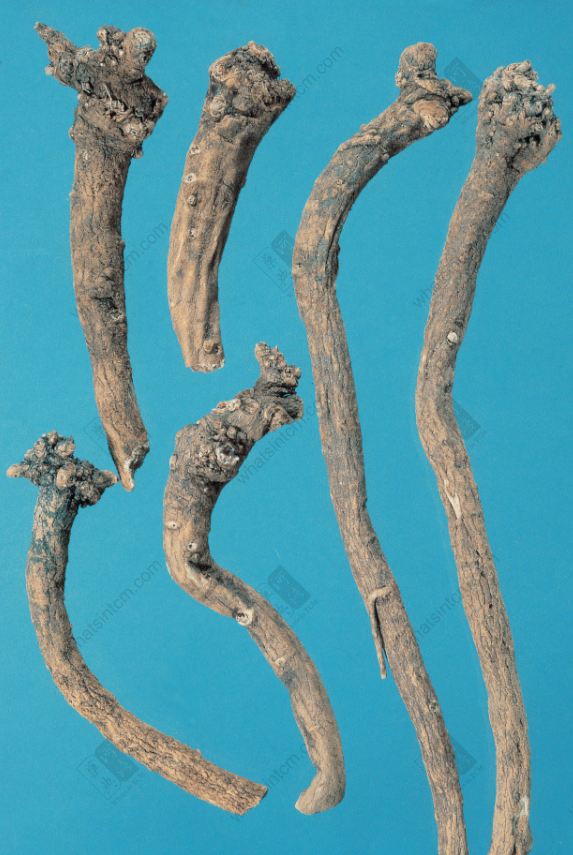 Tu Yin Chai Hu
Tu Yin Chai Hu
【Name】
Yin Chai Hu
【Source】
Compendium of Materia Medica
【Common Usage Level】
E
【Botanical Origin】
The root of Stellaria dichotoma L. var. lanceolata Bunge., of the Caryophyllaceae family.
【Characteristics】
Cylindrical, 15-40cm long, 1-2.5cm in diameter. The top of the root has many small wart-like protrusions (pearl-like head growing at the top), which are traces of above-ground stems, densely white, called “pearl disk”. The surface is yellowish-brown or grayish-brown, with longitudinally wrinkled striations twisted to the left and traces of branch roots, and numerous round, concave brown dotted small holes can be seen, commonly called “sand eyes” (rust-colored sand eye epidermis remains), especially near the root head. The texture is loose and brittle, and dust flies out when broken (powder flies out from the fracture surface).
The surface of the prepared slices is yellowish-brown and gray, with slightly twisted longitudinal lines, and numerous circular small cavities are called sand eyes, especially near the root head. When cut off from the sand eye, brown patterns can be seen. The cut surface is rough, powdery, and has gaps. The center is slightly flat and has a yellow-white chrysanthemum heart with radial lines. It has a slight fragrance and a sweet and slightly bitter taste.
【Preparation】
1. Cut into thick slices and dry in the sun. 2. Stir-fried Yin Chai Hu 3. Yin Chai Hu prepared with blood
【Identification】
The best quality has uniform and long strips, a pearl disk (stem trace) at the root top, thin skin, soft texture, no sandy eyes and black heart, and a white fracture surface. The quality is lower if the strips are uneven in thickness, with sandy eyes and a black heart.
【Identification Terminology】
1. Pearl disk, pearl disk head: refers to the white wart-like protrusions formed by numerous residual stem bases and buds densely packed at the head of root-type medicinal materials, which appear silvery-white, shaped like inlaid pearl disks, such as Yin Chai Hu, which are the traces left after the above-ground stems (growing in clusters) fall off.
2. Sand eye: The upper and middle parts of Yin Chai Hu (especially near the root head) have numerous irregular round small concave holes, which often accumulate sediment. These are called sand eyes, which are actually concave branch root traces.
3. Lion’s head: refers to the enlarged head of roots and rhizomes with numerous wart-like protruding stem traces, shaped like a lion’s head, such as Yin Chai Hu.
【Section】
Roots

