American Ginseng
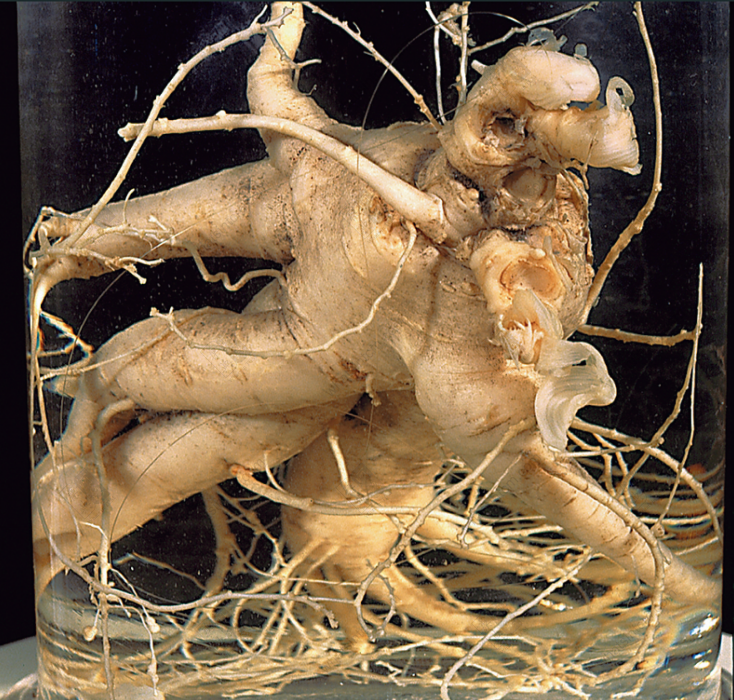

Fresh Wild American Ginseng
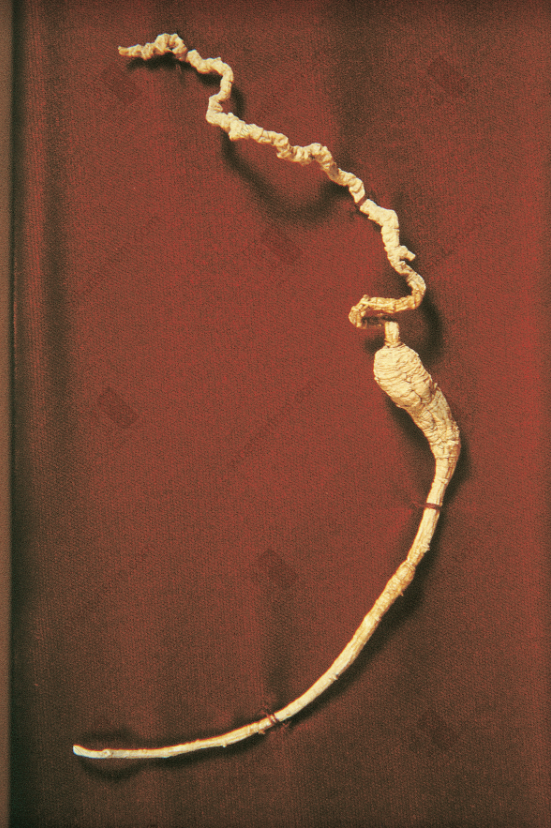

Wild American Ginseng, Year 112 (Collectible)
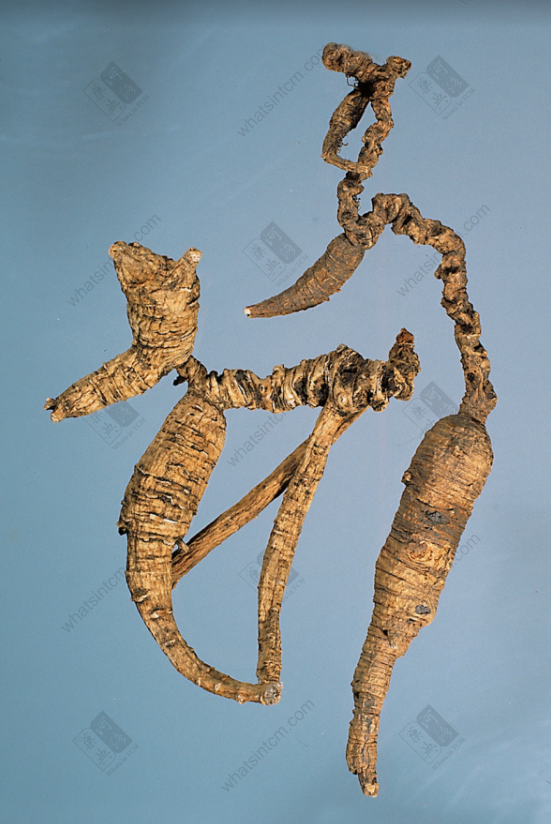
Decades-Old Wild American Ginseng (Black Line Texture)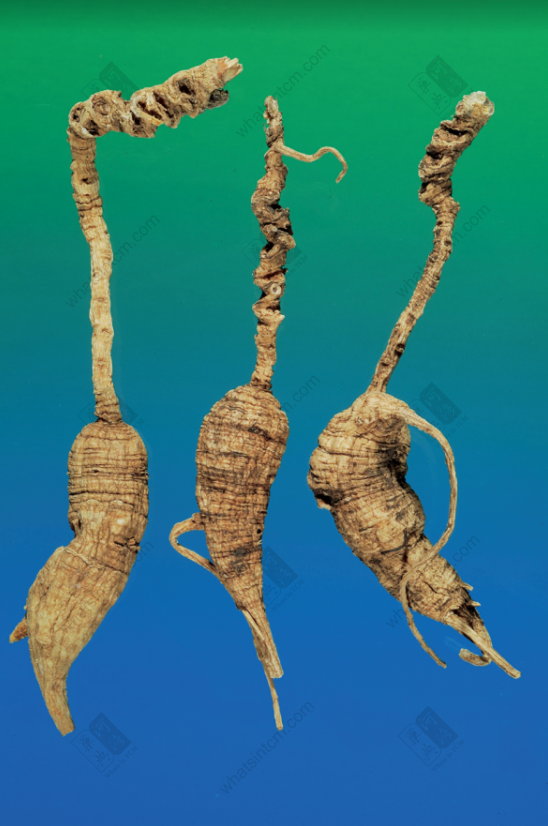
Decades-Old Wild American Ginseng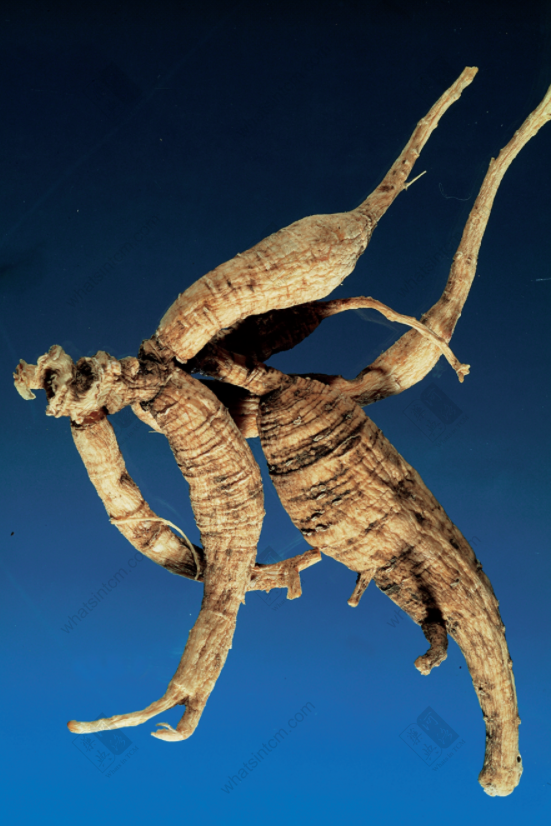
Generations-Old Wild American Ginseng (Human Shape)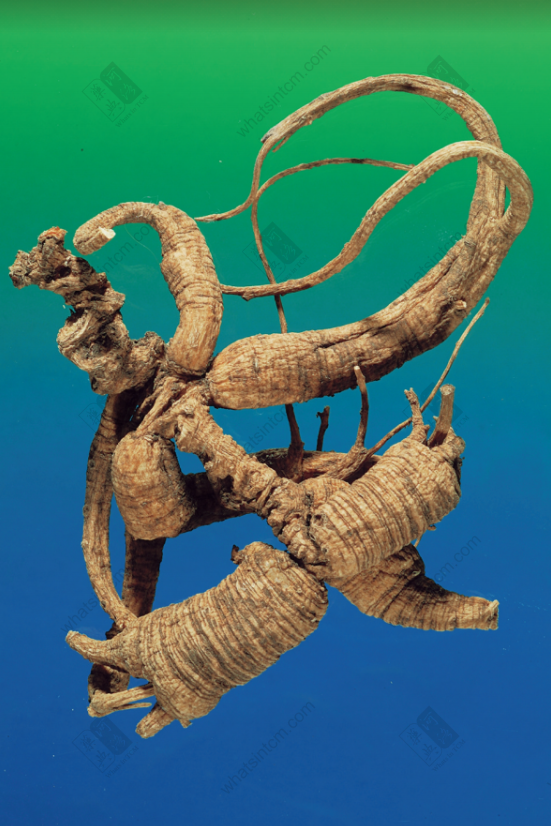
Generations-Old Wild American Ginseng (Black Line Texture)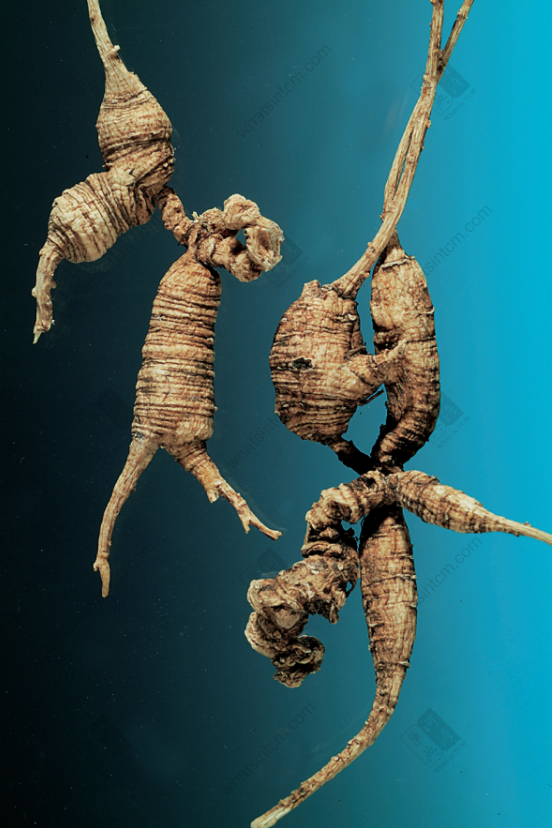
Generations-Old Wild American Ginseng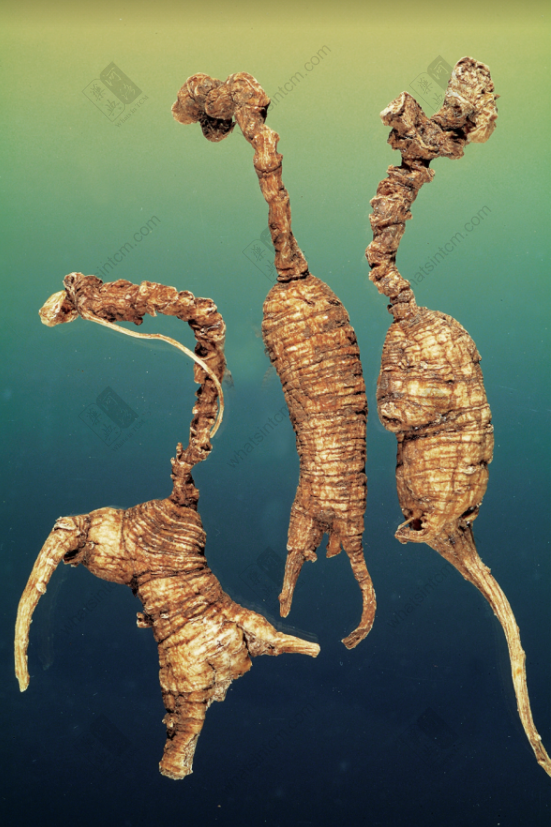
Virgin Forest Wild American Ginseng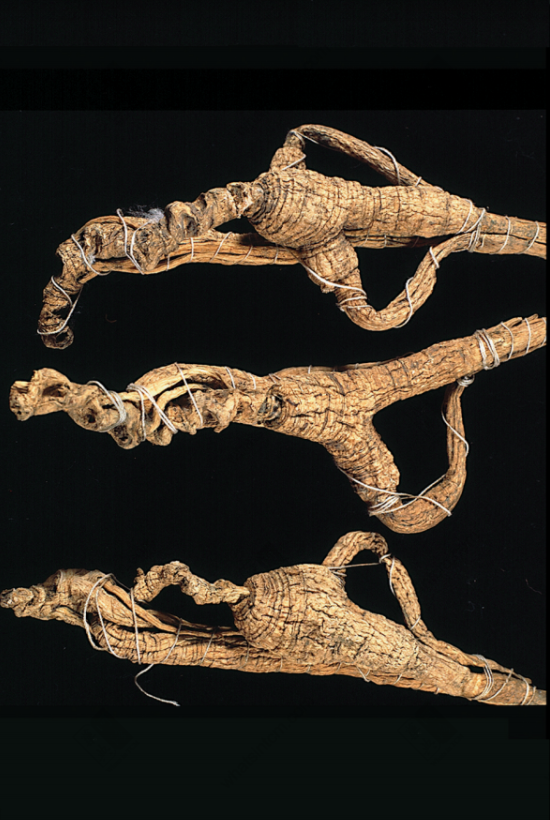
Premium Wild American Ginseng
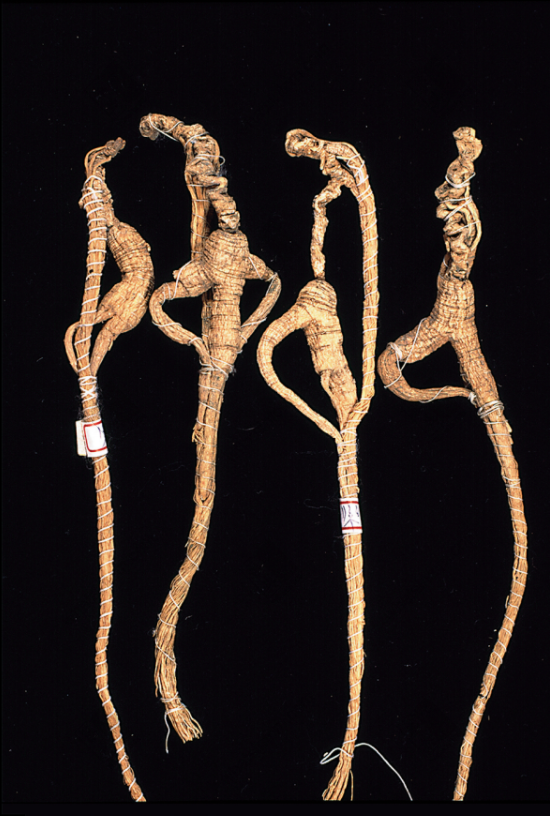
Premium Wild American Ginseng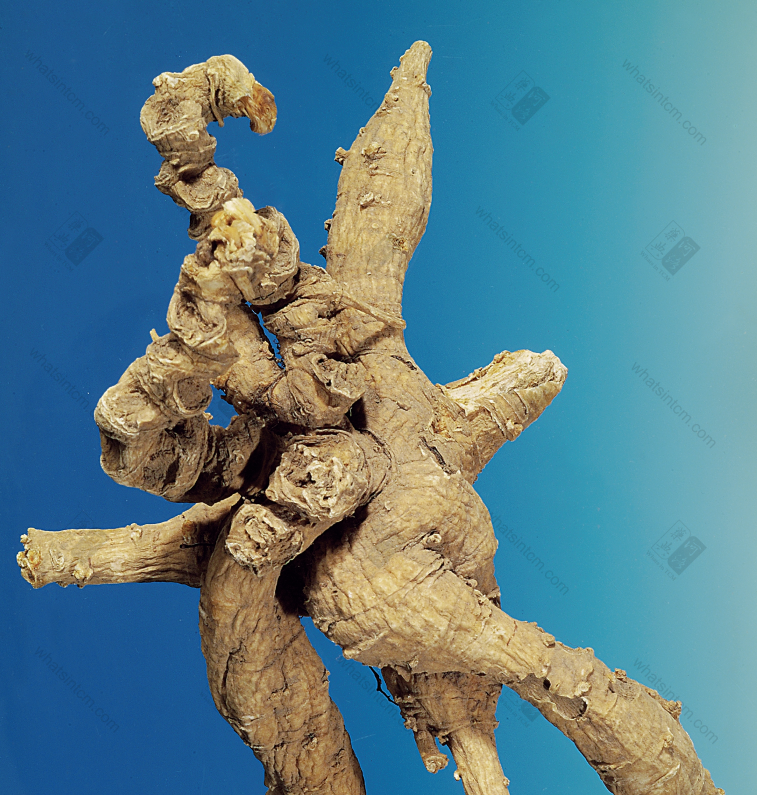
Special Wild Bubble
Top Grade Wild American Ginseng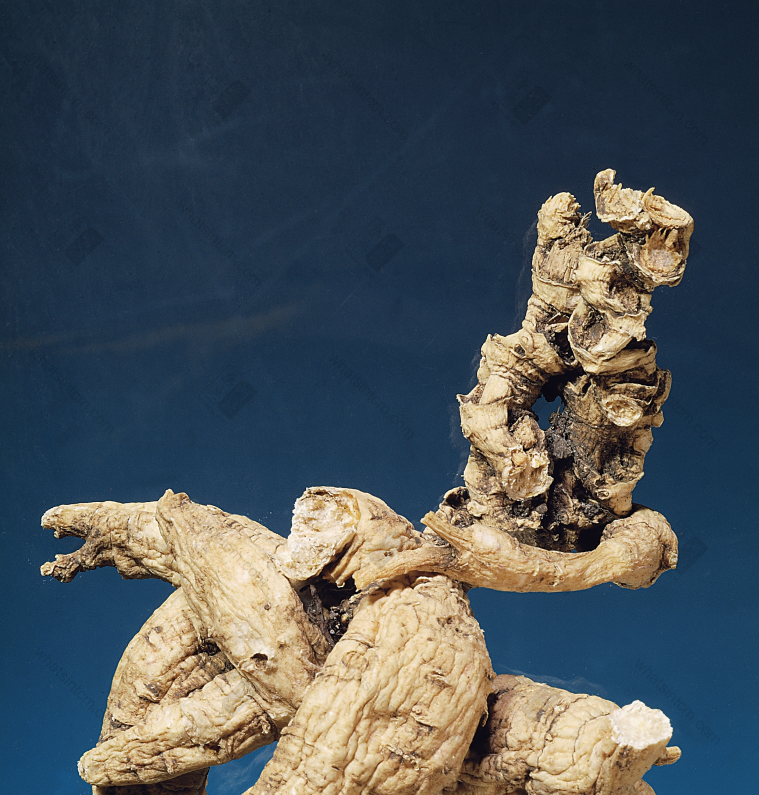
Top Grade Wild American Ginseng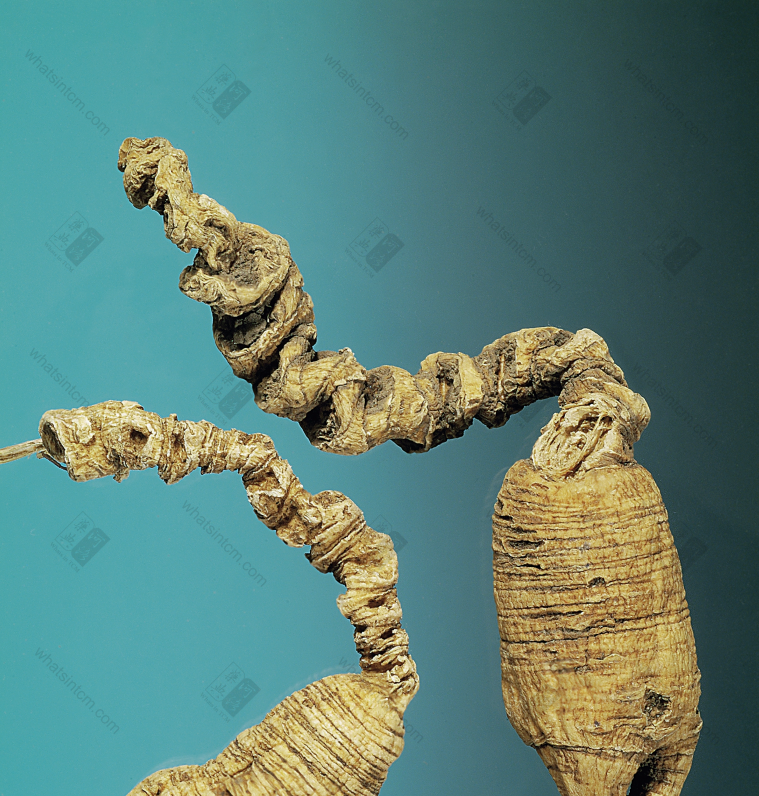
Special Wild Bubble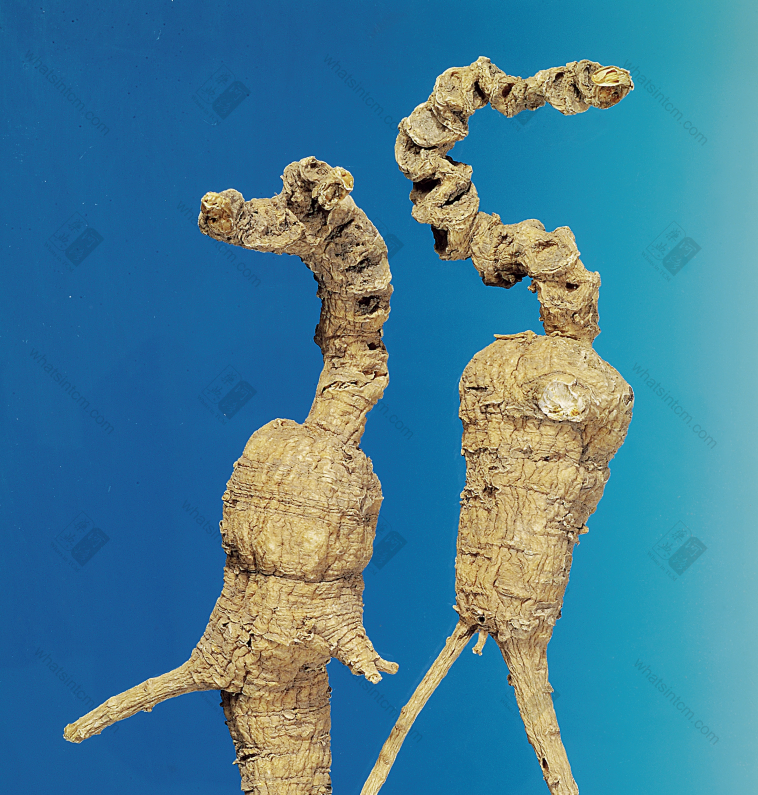
Special Wild Bubble

Extra Large Wild American Ginseng (Two Generations)(Loose and Porous)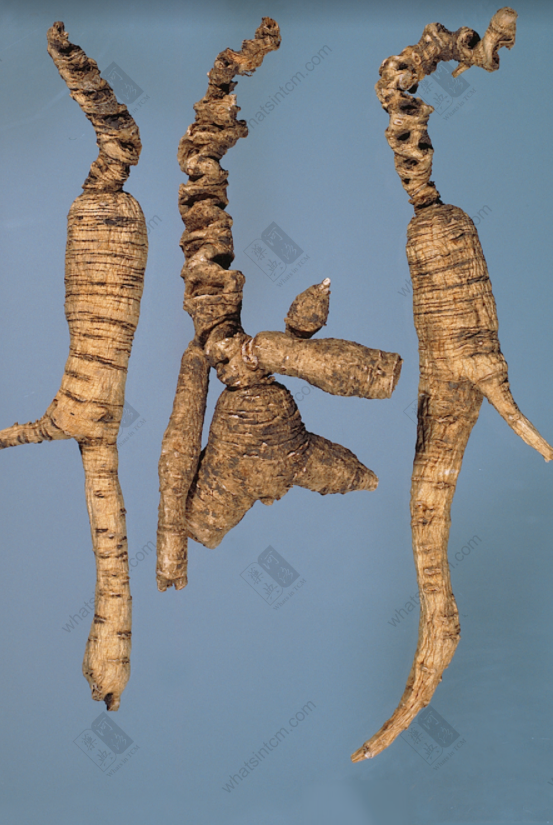 Extra Large Wild American Ginsengnn
Extra Large Wild American Ginsengnn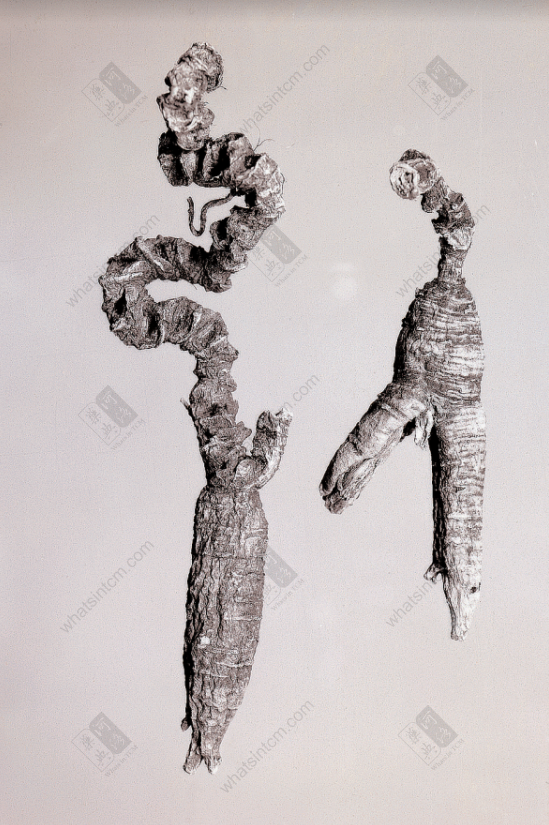 Wild American Ginseng (1984 Chinese Herbal Medicine Atlas Black and White Photo)nn
Wild American Ginseng (1984 Chinese Herbal Medicine Atlas Black and White Photo)nn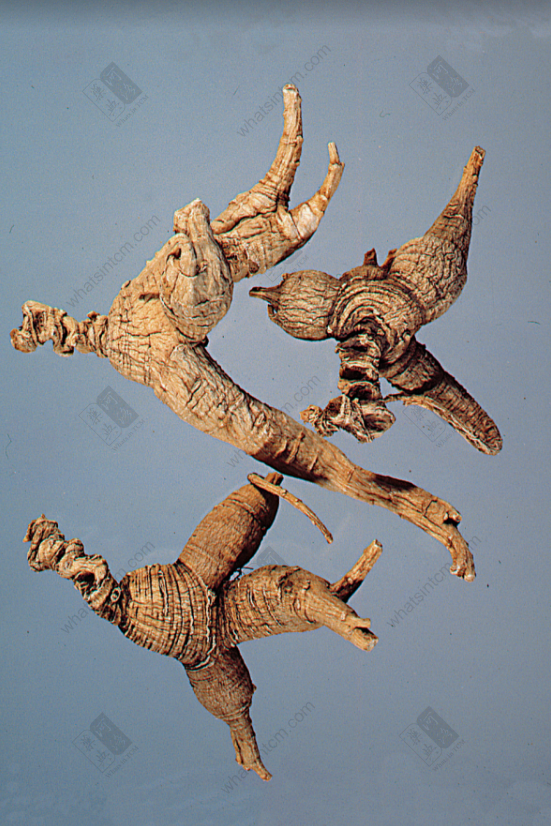 Wild American Ginseng, First Grade (Human Shape)nn
Wild American Ginseng, First Grade (Human Shape)nn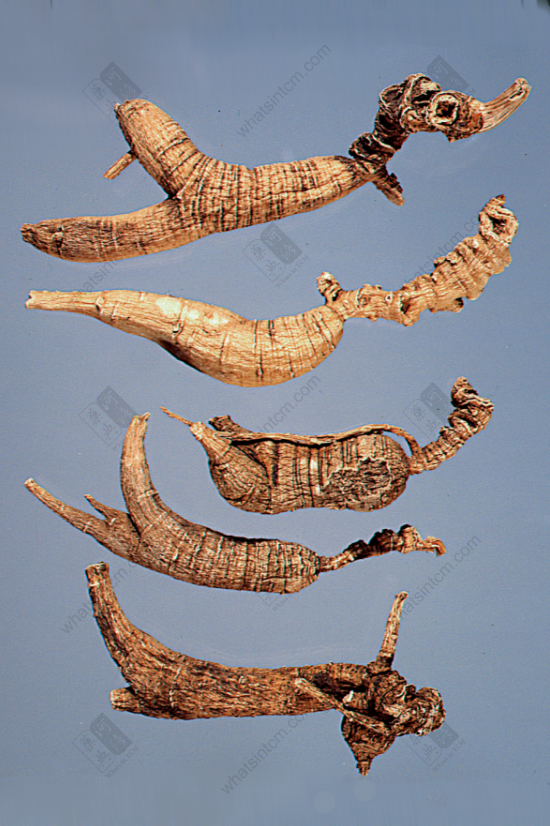 Wild American Ginseng, Second Gradenn
Wild American Ginseng, Second Gradenn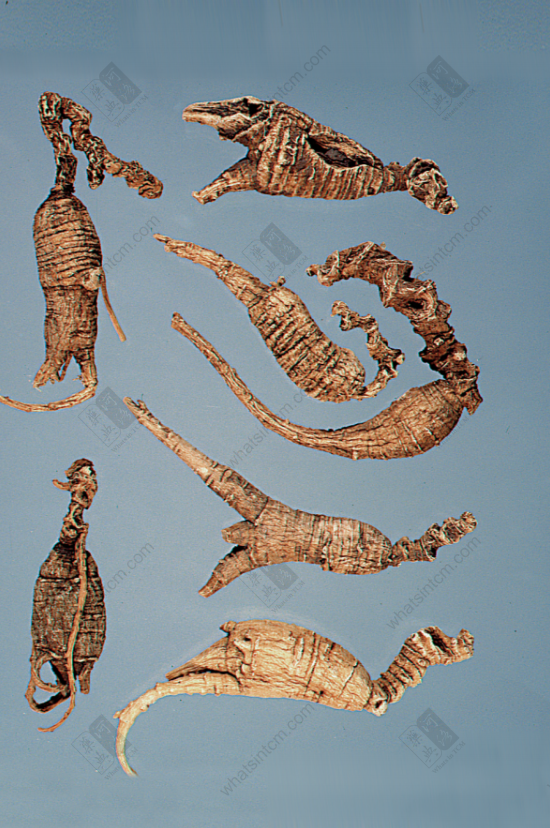 Wild American Ginseng, Third Gradenn
Wild American Ginseng, Third Gradenn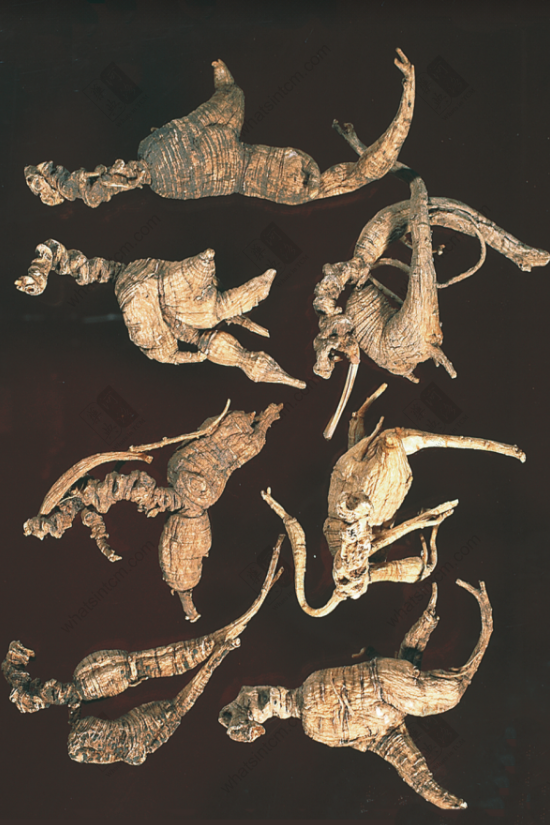 Wild American Ginseng, Third Gradenn
Wild American Ginseng, Third Gradenn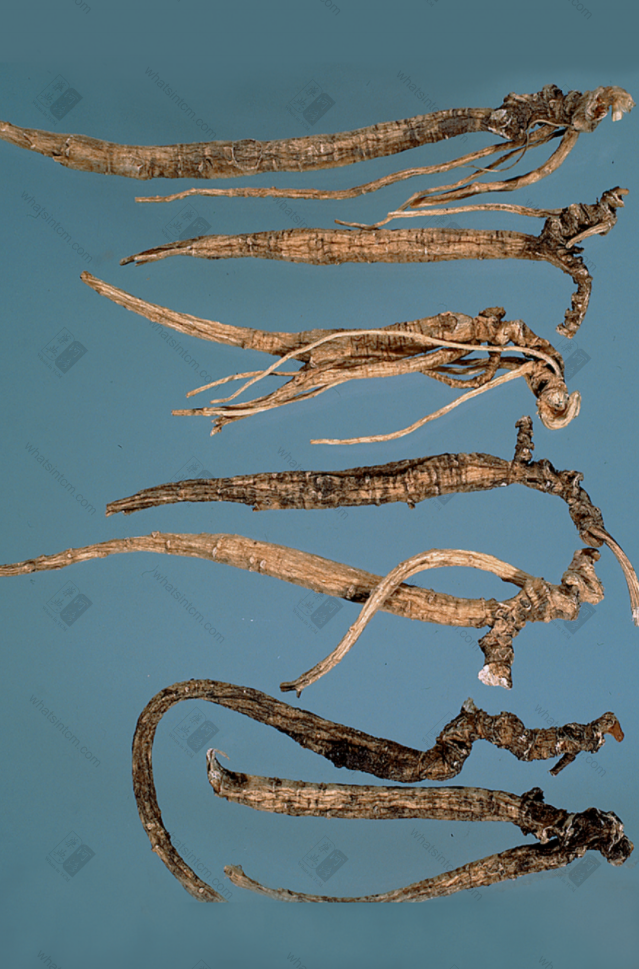 Wild American Ginseng, Fourth Gradenn
Wild American Ginseng, Fourth Gradenn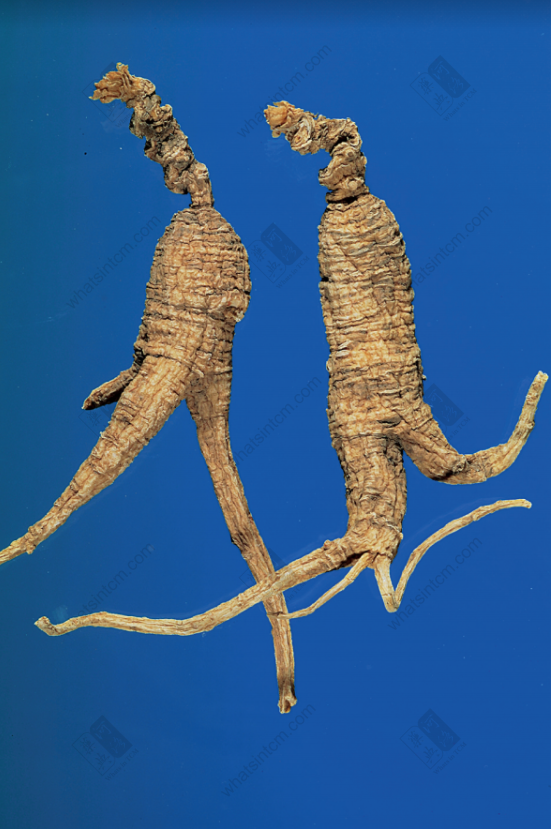 Semi-Wild (Artificially Planted in Forest, Left to Grow Wild)nn
Semi-Wild (Artificially Planted in Forest, Left to Grow Wild)nn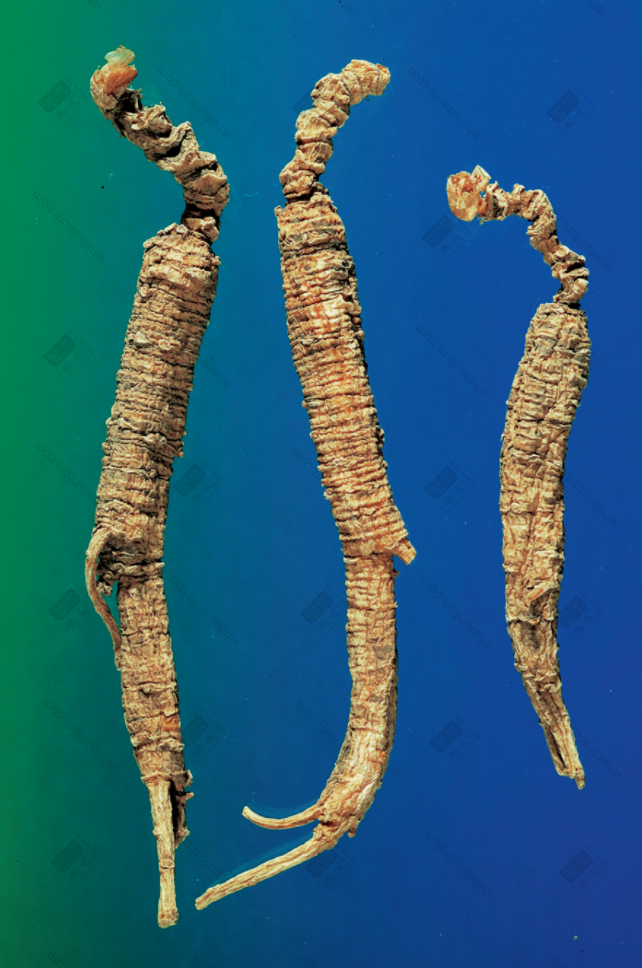 Semi-Wild American Ginseng (Silkworm Shape)(Artificially Planted in Forest, Left to Grow Wild)nn
Semi-Wild American Ginseng (Silkworm Shape)(Artificially Planted in Forest, Left to Grow Wild)nn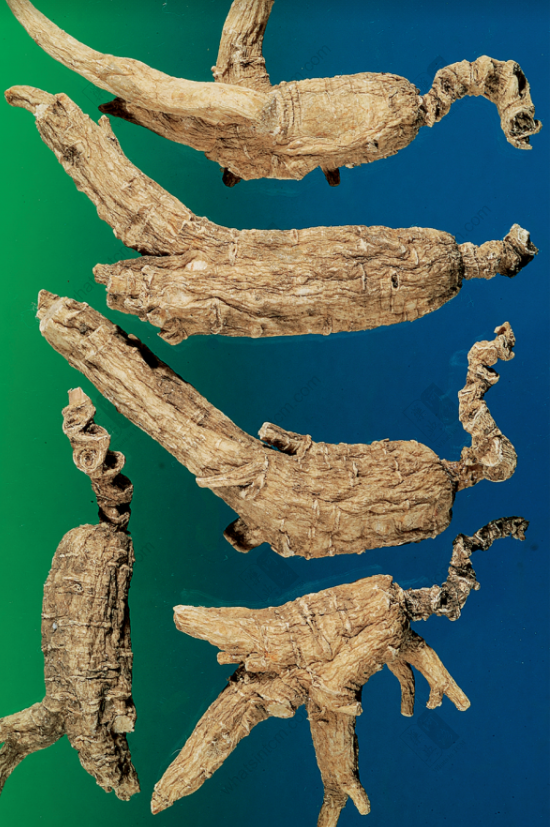 Semi-Wild American Ginseng (Full Body, No Spiral Texture)nn
Semi-Wild American Ginseng (Full Body, No Spiral Texture)nn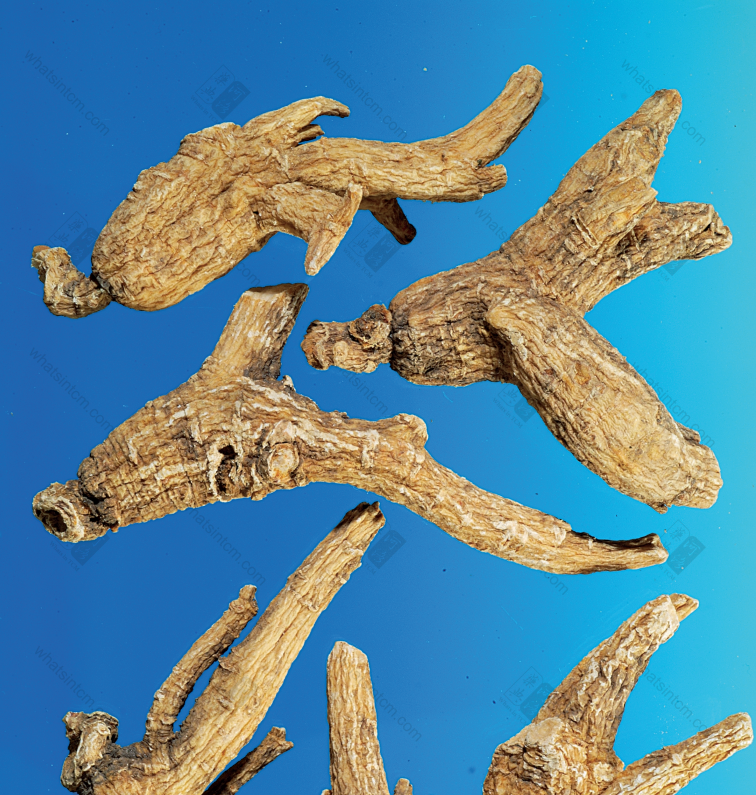 Semi-Wild American Ginsengnn
Semi-Wild American Ginsengnn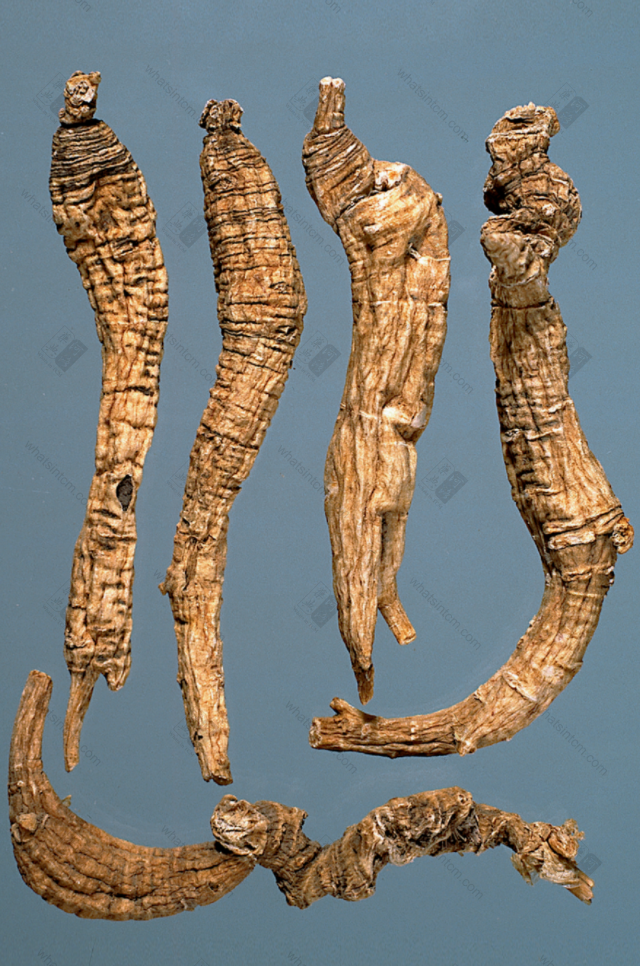 Secondary American Ginseng (Silkworm Shape)(Top 4 Cultivated, Bottom 1 Wild)nn
Secondary American Ginseng (Silkworm Shape)(Top 4 Cultivated, Bottom 1 Wild)nn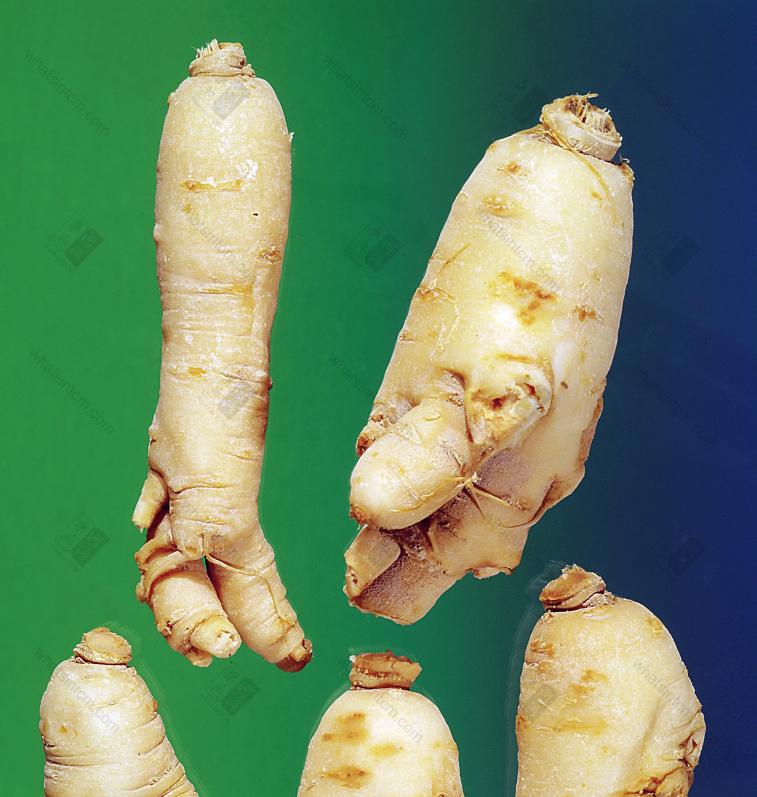 American Ginseng (Fresh Product)nn
American Ginseng (Fresh Product)nn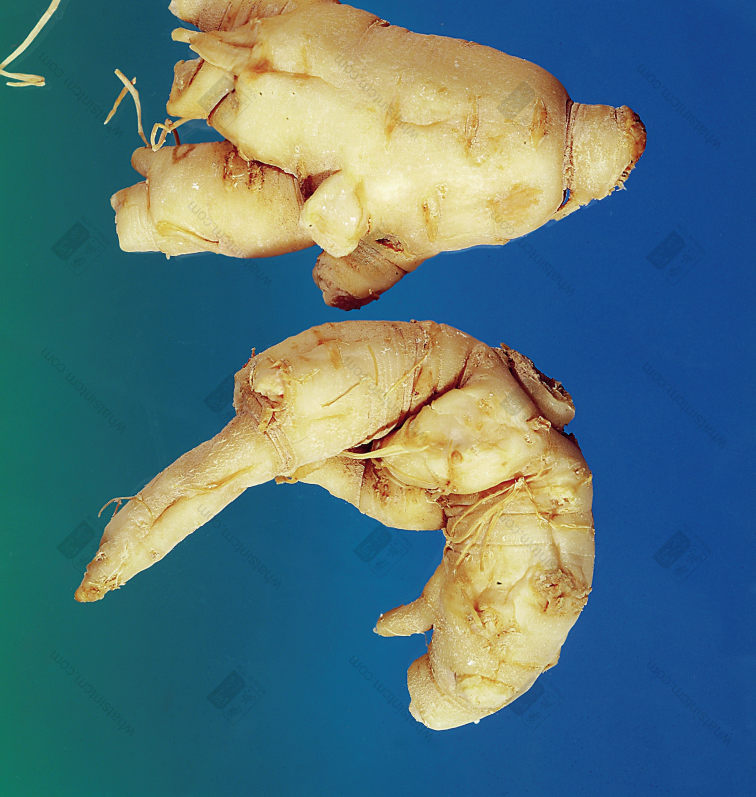 American Ginseng (Fresh Product)nn
American Ginseng (Fresh Product)nn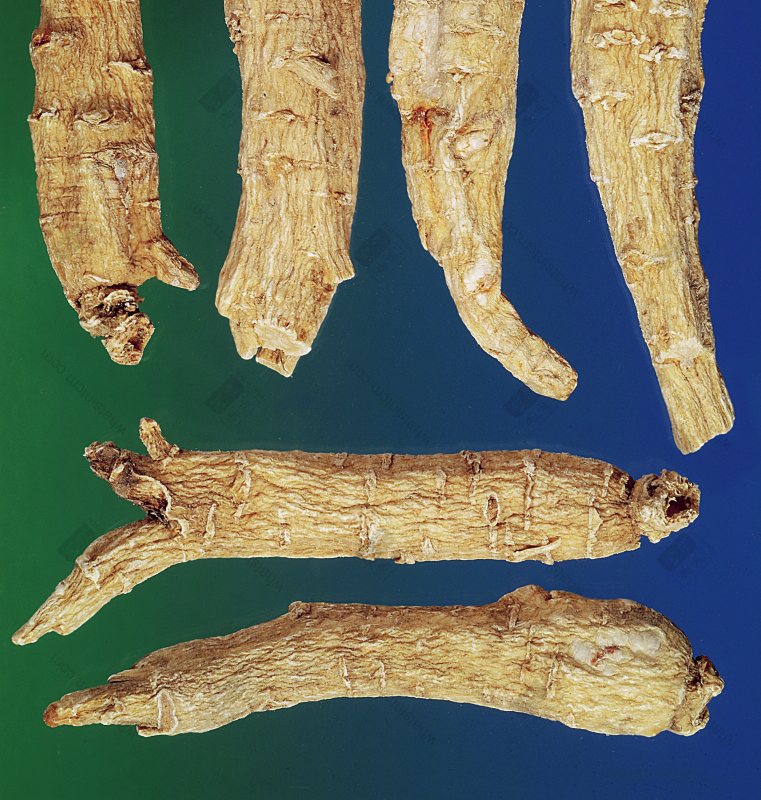 Tribute Tip (Right 3), Special Tip (Left 1, Bottom 2)nn
Tribute Tip (Right 3), Special Tip (Left 1, Bottom 2)nn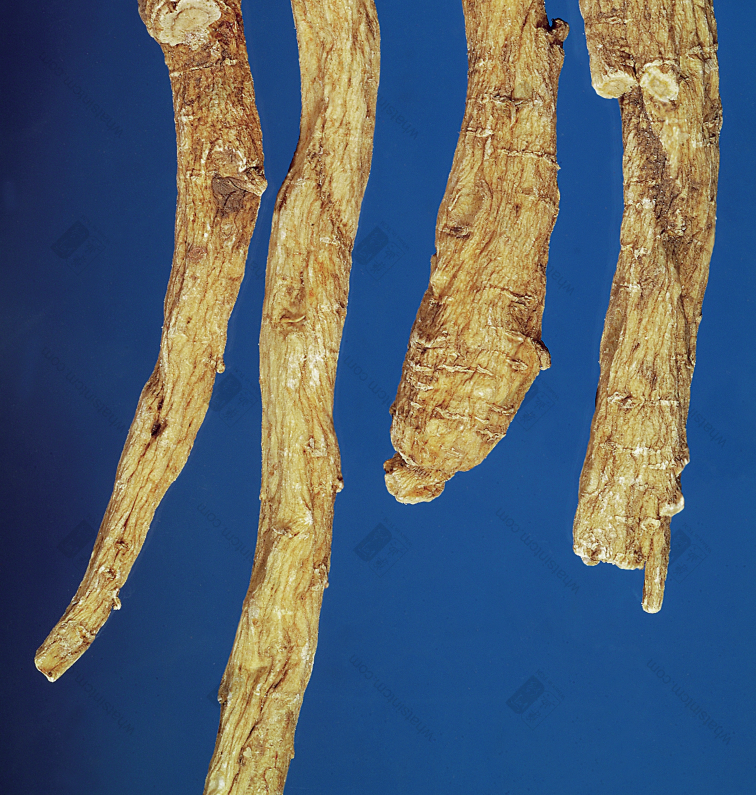 Extra Long Tip (Right 2), Large Long Tip (Left Long 2)nn
Extra Long Tip (Right 2), Large Long Tip (Left Long 2)nn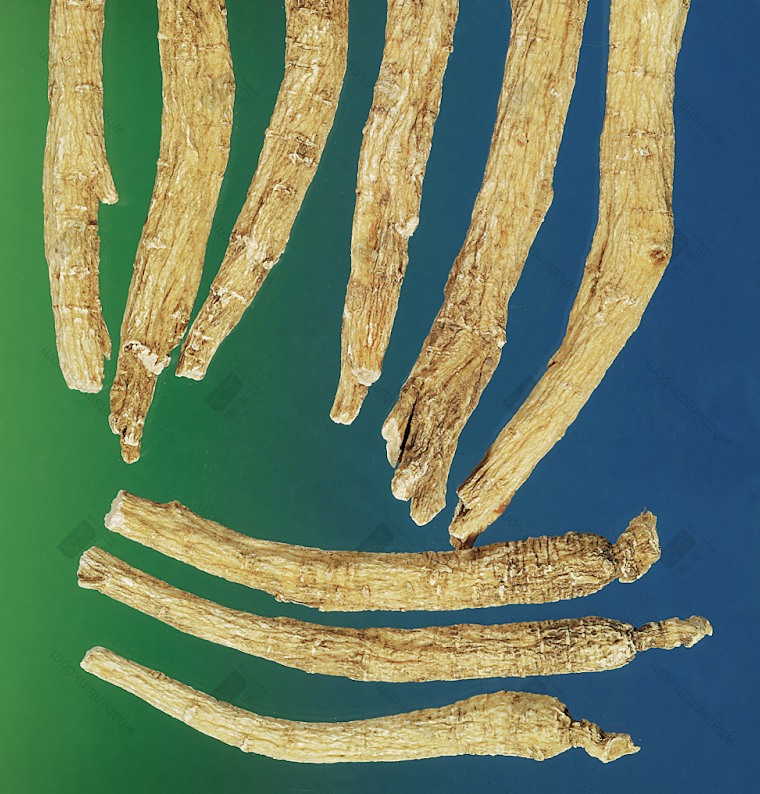 Medium Long Tip (Right 3), Small (Left 3), Tiny (Bottom 3)nn
Medium Long Tip (Right 3), Small (Left 3), Tiny (Bottom 3)nn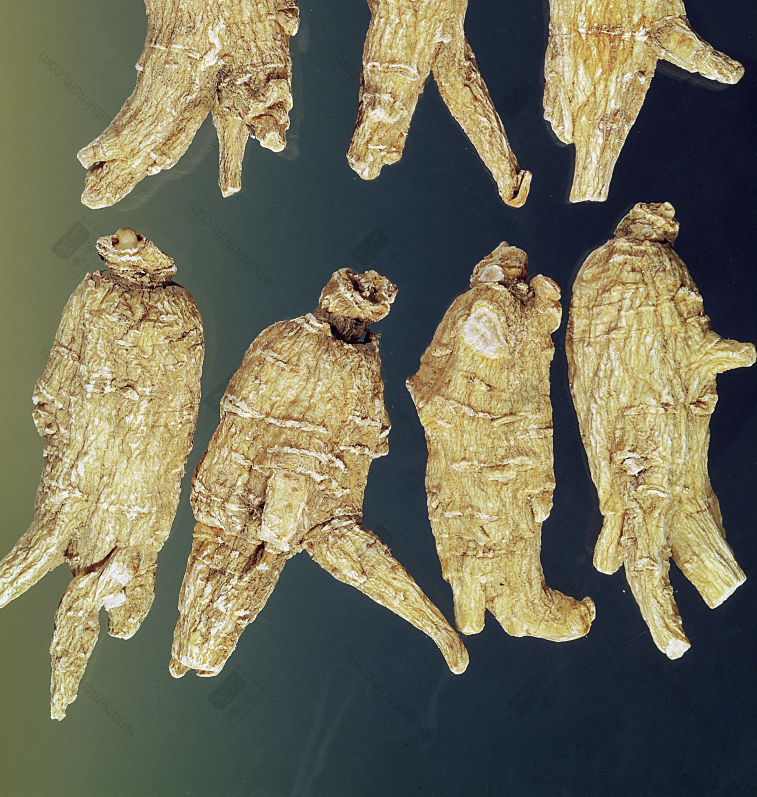 Original Tail Flag (Top 3 Special, Bottom 4 Large Bubble)nn
Original Tail Flag (Top 3 Special, Bottom 4 Large Bubble)nn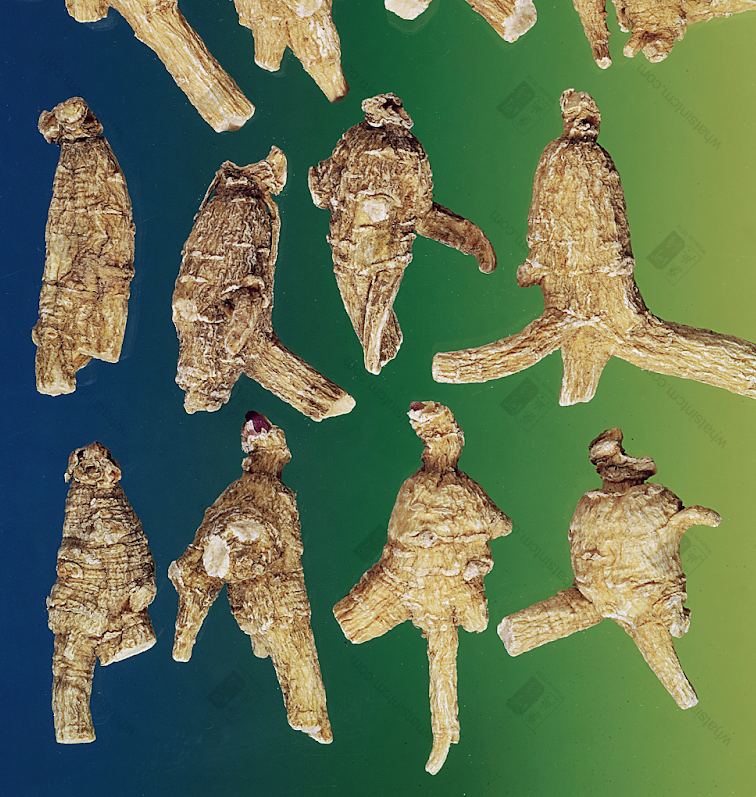 Original Tail Flag Bubble (Top 4, Middle 4 Small, Bottom 4 Tiny)nn
Original Tail Flag Bubble (Top 4, Middle 4 Small, Bottom 4 Tiny)nn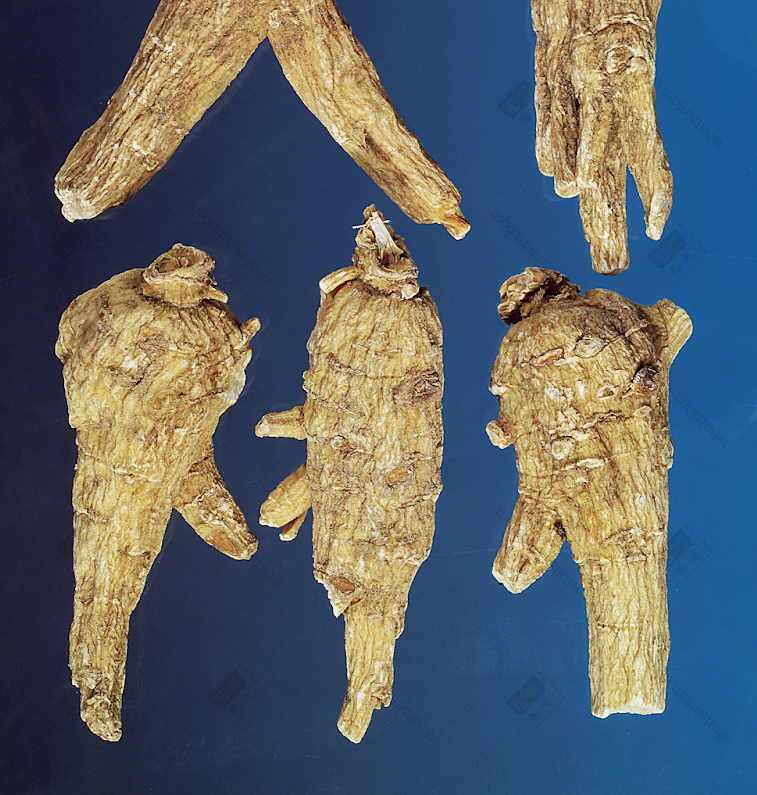 Original Tail Flag (Top 2 Special, Bottom 3 Large)nn
Original Tail Flag (Top 2 Special, Bottom 3 Large)nn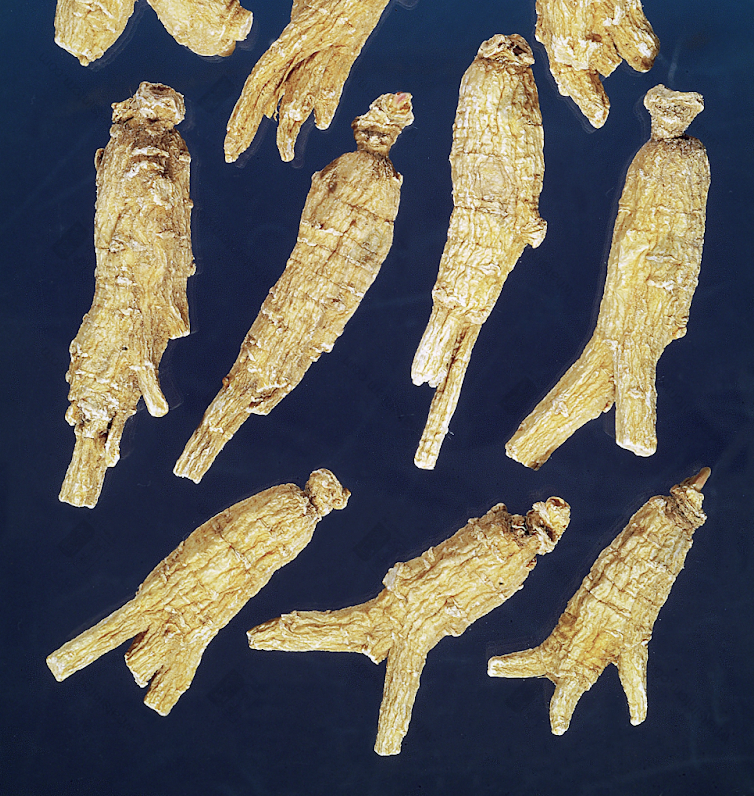 Original Tail Flag (Top 3, Middle 4 Small, Bottom 3 Tiny)nn
Original Tail Flag (Top 3, Middle 4 Small, Bottom 3 Tiny)nn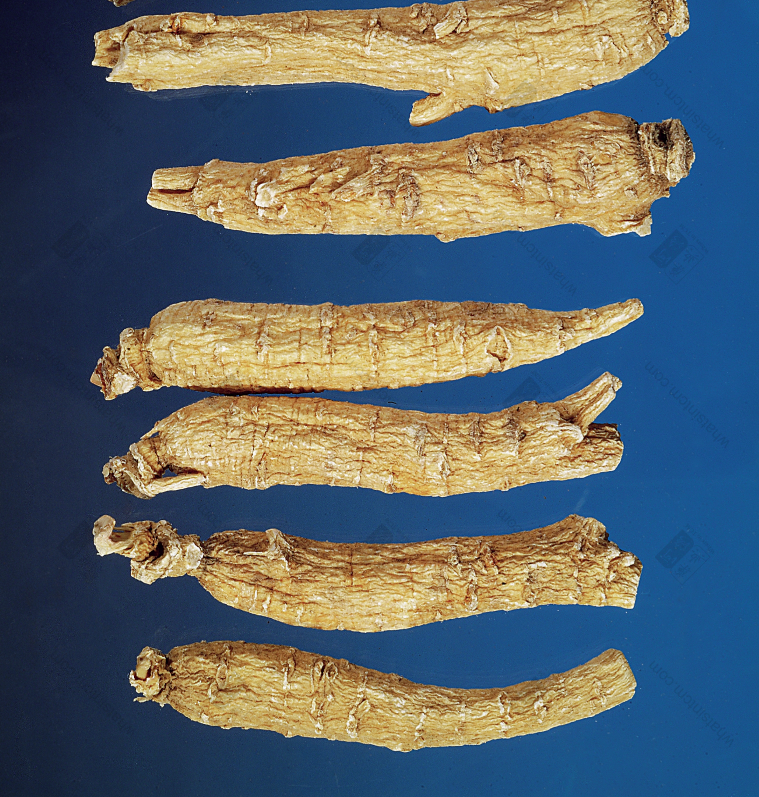 Large Tip (Top 4), Medium Tip (Bottom 4)nn
Large Tip (Top 4), Medium Tip (Bottom 4)nn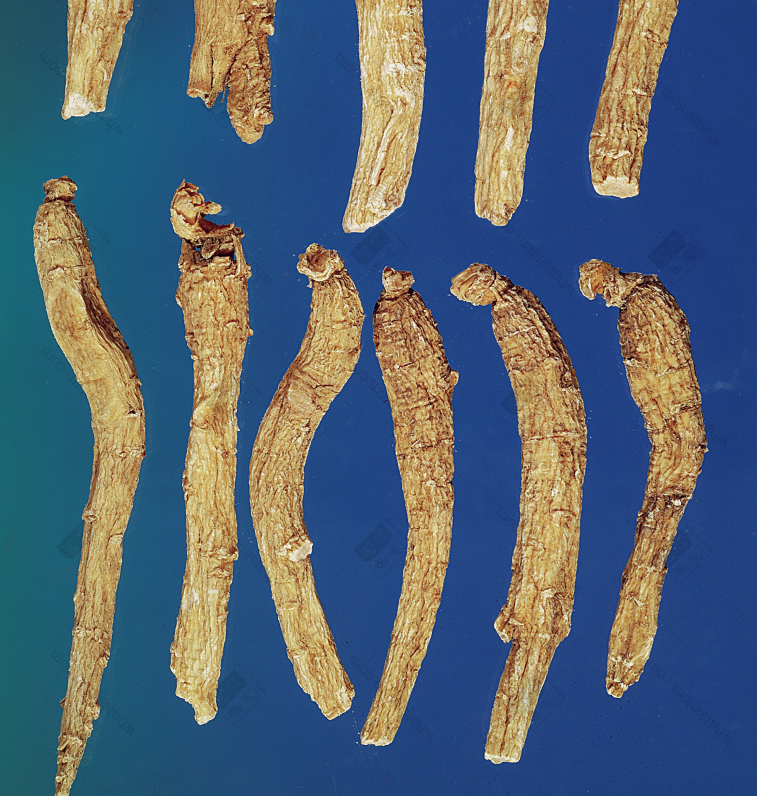 Small Tip (Top 5), Tiny Tip (Bottom 6)nn
Small Tip (Top 5), Tiny Tip (Bottom 6)nn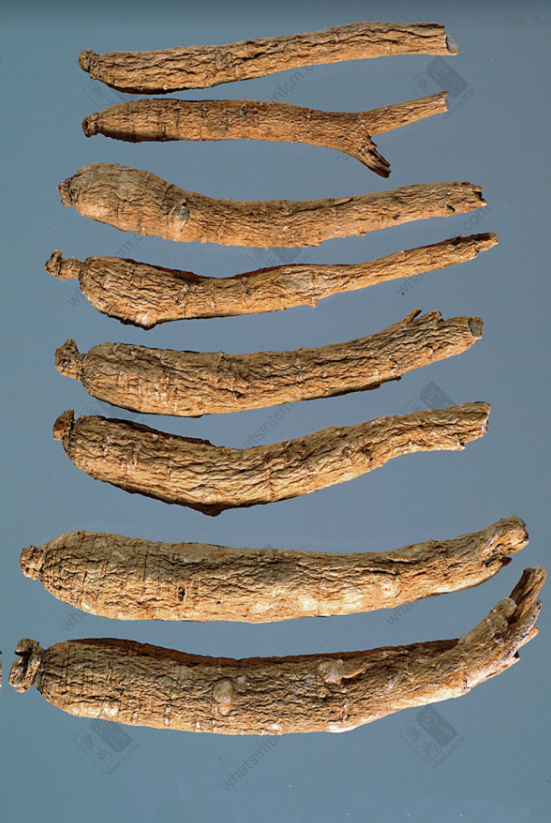 Long Flagnn
Long Flagnn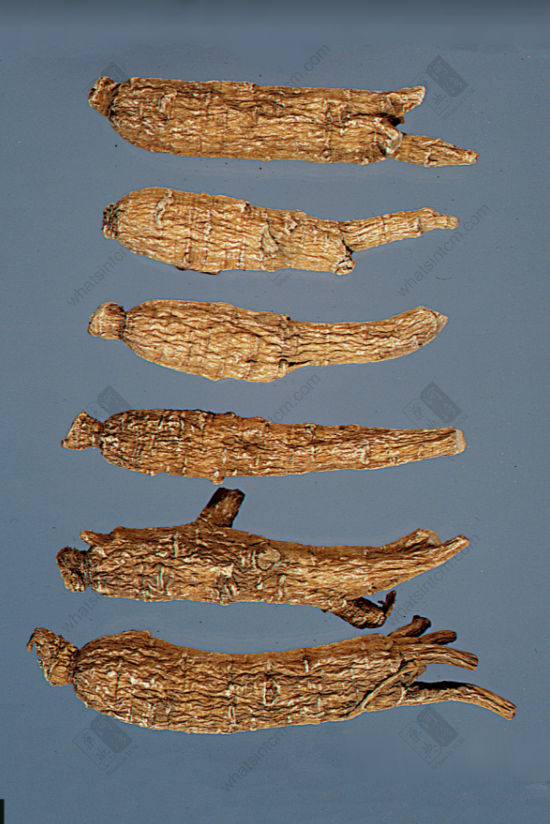 Large Tip Tail Flag Ginseng (Top 3 American, Bottom 3 Canadian)nn
Large Tip Tail Flag Ginseng (Top 3 American, Bottom 3 Canadian)nn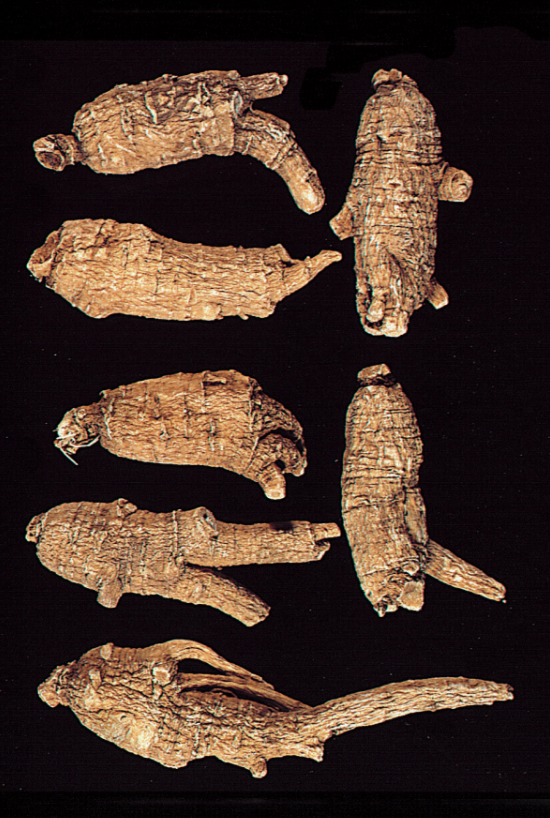 Large Round Grain Flag Ginsengnn
Large Round Grain Flag Ginsengnn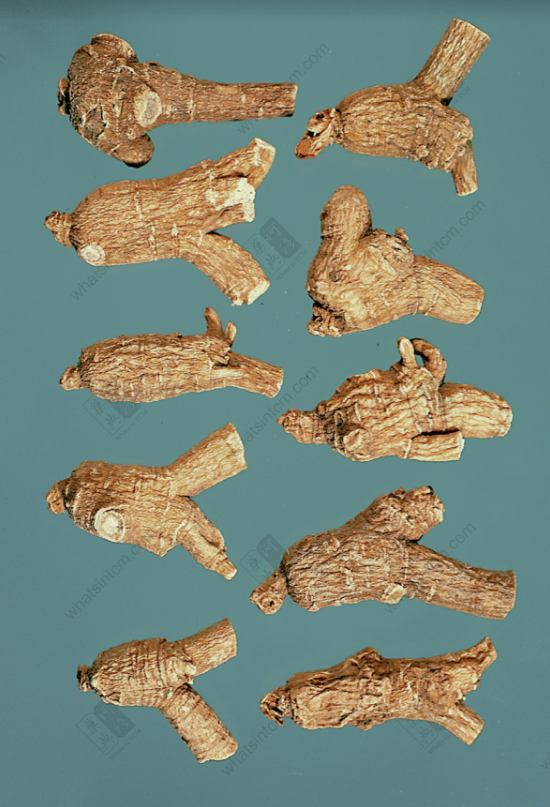 Large Round Grain Flag Ginsengnn
Large Round Grain Flag Ginsengnn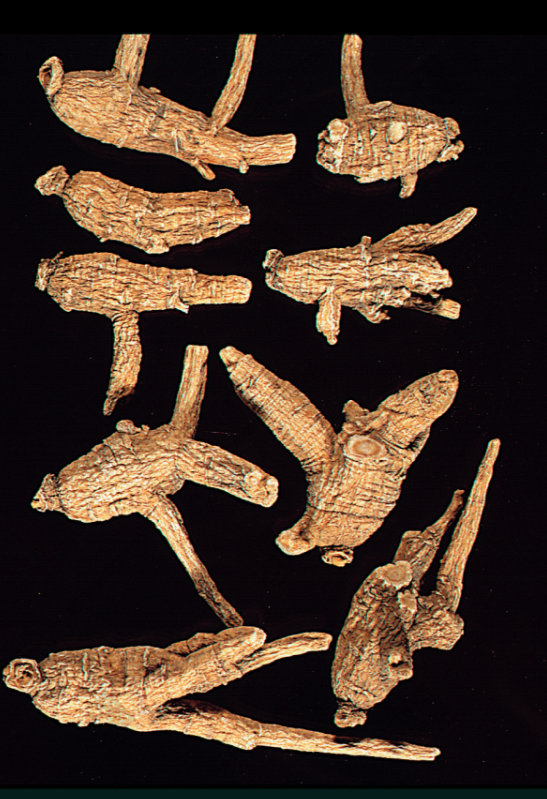 Flag Ginseng (Top 5 Small Round Grain, Bottom 4 Medium Round Grain)nn
Flag Ginseng (Top 5 Small Round Grain, Bottom 4 Medium Round Grain)nn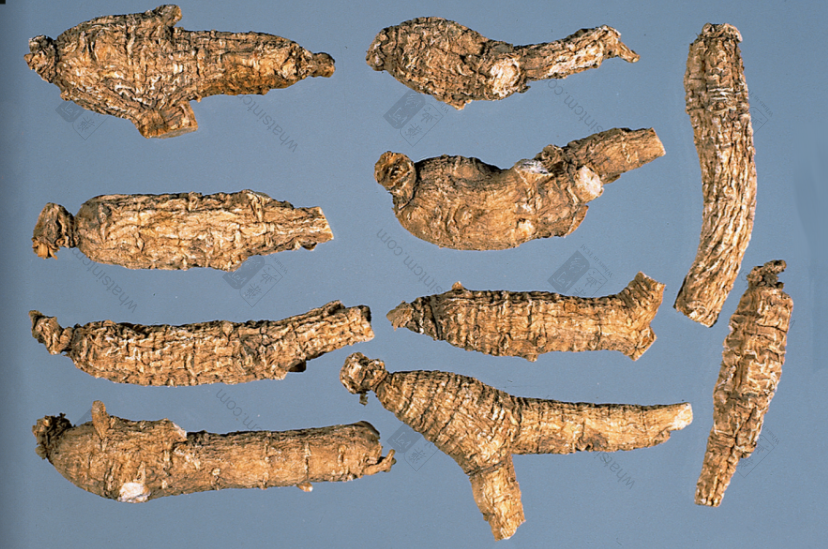 Small Flagnn
Small Flagnn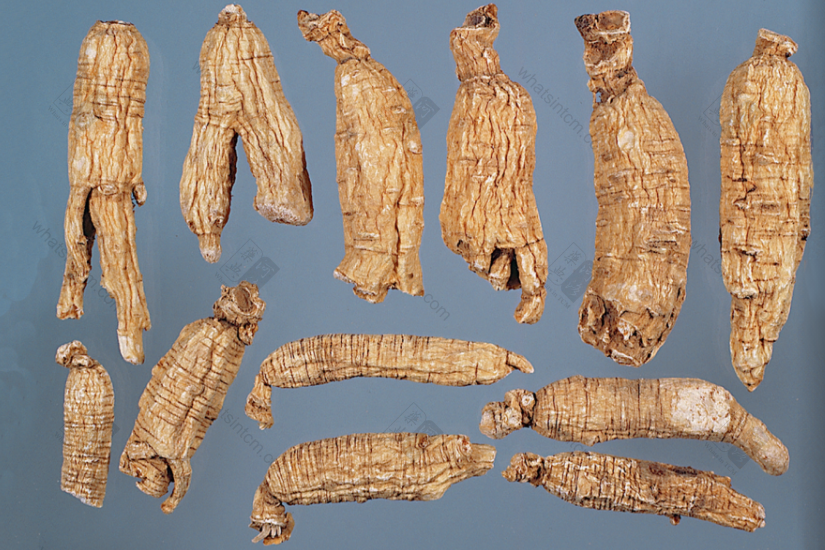 Small Flagnn
Small Flagnn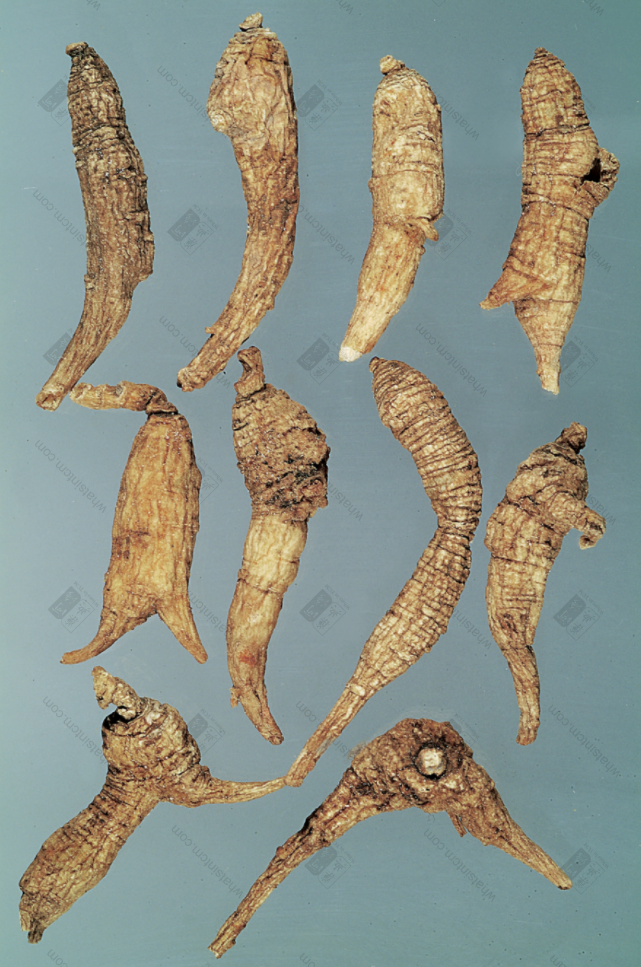 Secondary American Ginseng (No Long Reed Head)nn
Secondary American Ginseng (No Long Reed Head)nn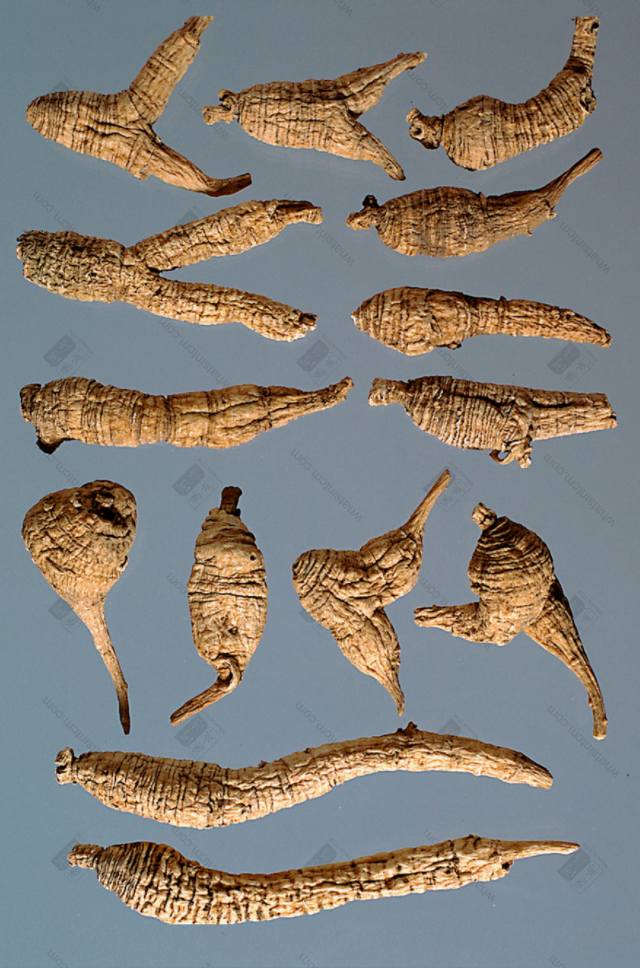 Secondary Three American Ginsengnn
Secondary Three American Ginsengnn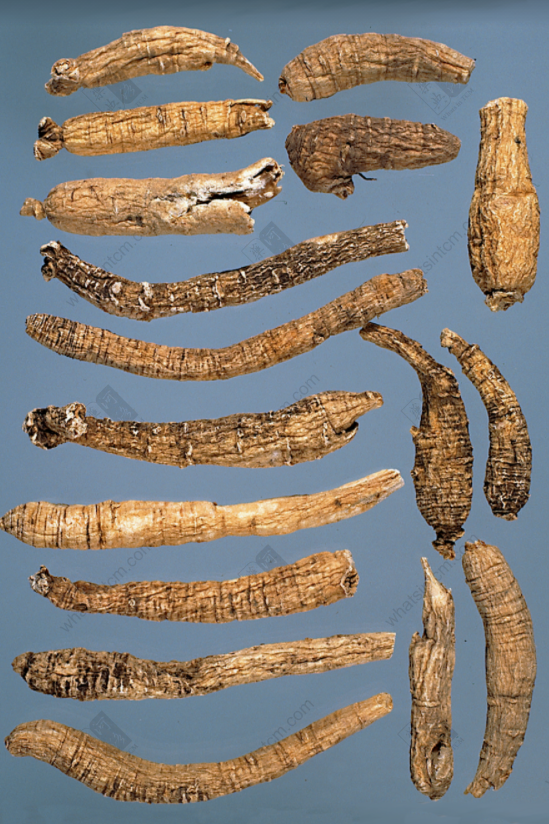 Secondary Three/Four American Ginsengnn
Secondary Three/Four American Ginsengnn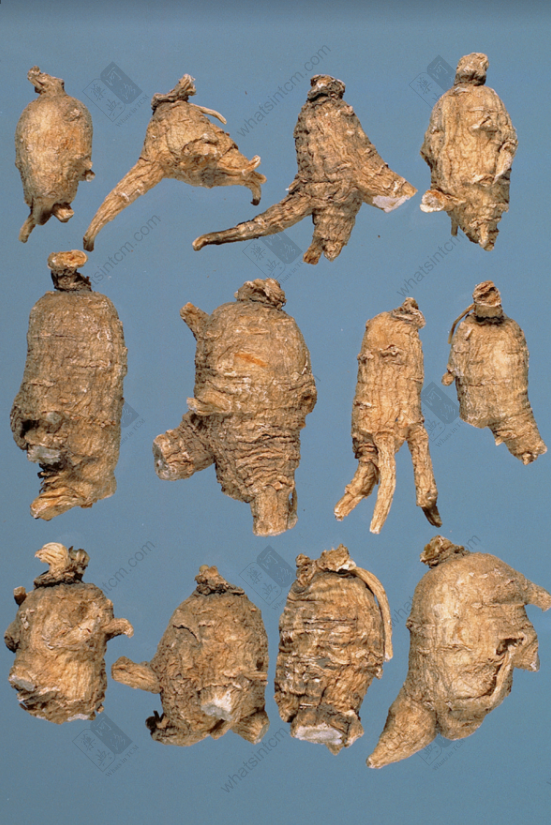 Pearl Grain American Ginsengnn
Pearl Grain American Ginsengnn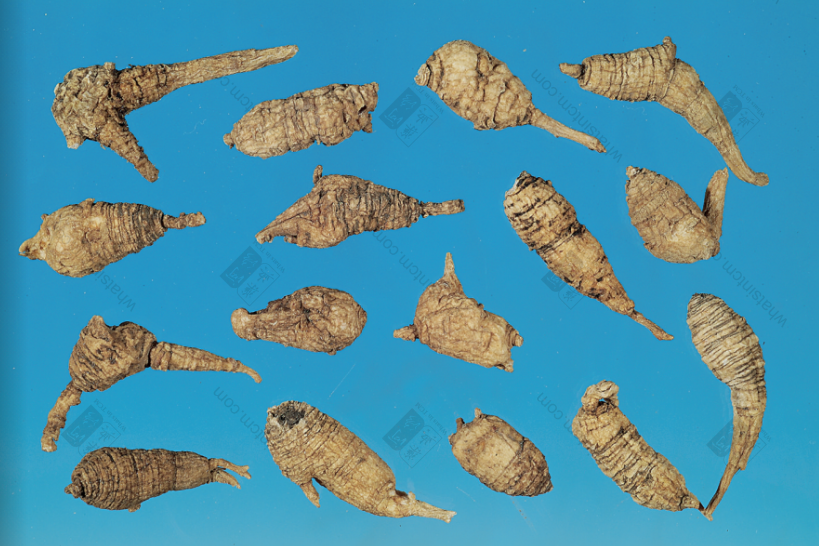 Pearl Grain American Ginsengnn
Pearl Grain American Ginsengnn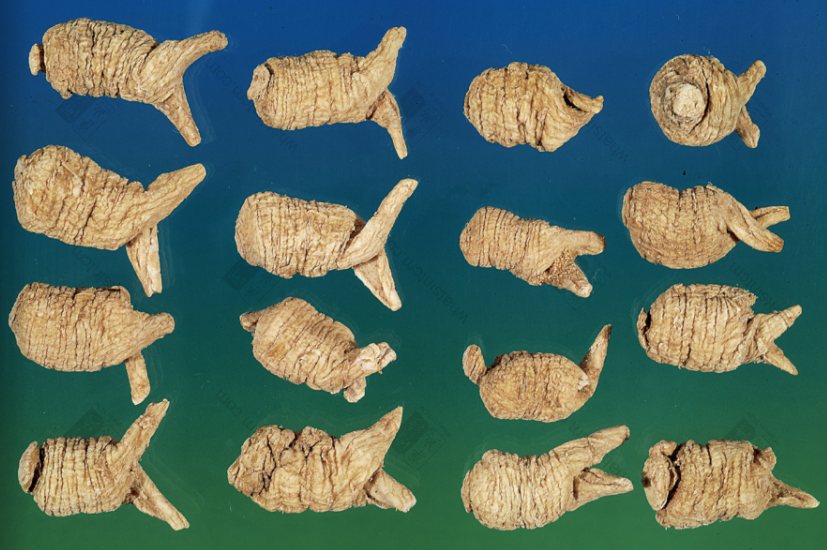 Craft Secondary American Ginseng (Transplanted, Compressed, Processed)nn
Craft Secondary American Ginseng (Transplanted, Compressed, Processed)nn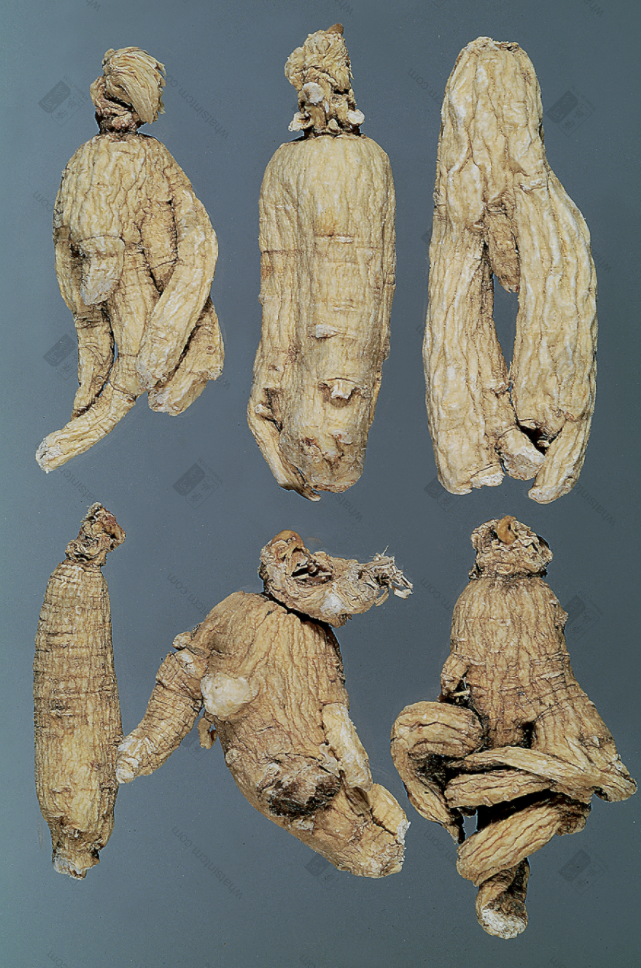 Northeast Cultivated American Ginsengnn
Northeast Cultivated American Ginsengnn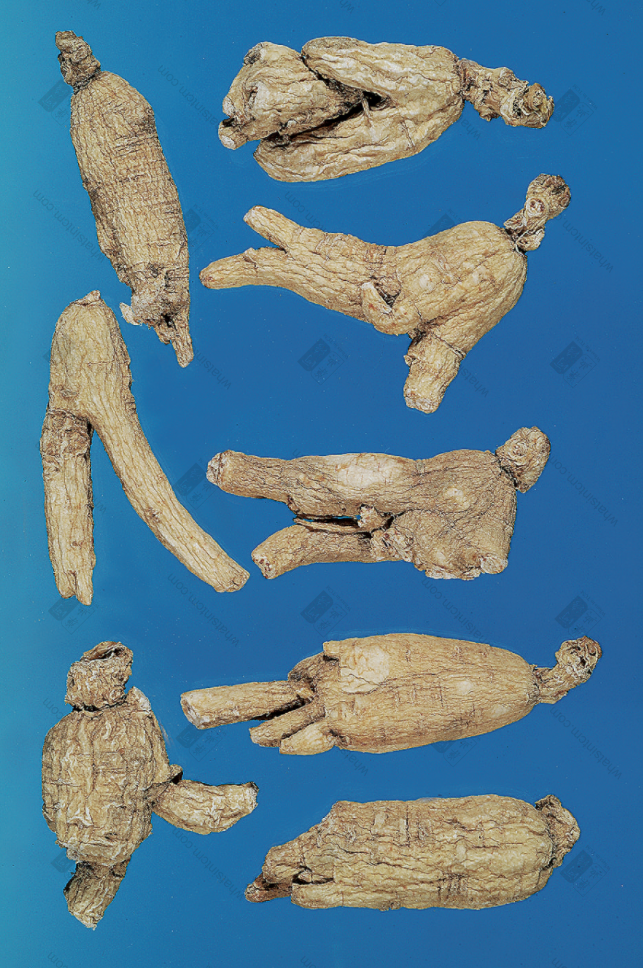 Northeast Cultivated American Ginsengnn
Northeast Cultivated American Ginsengnn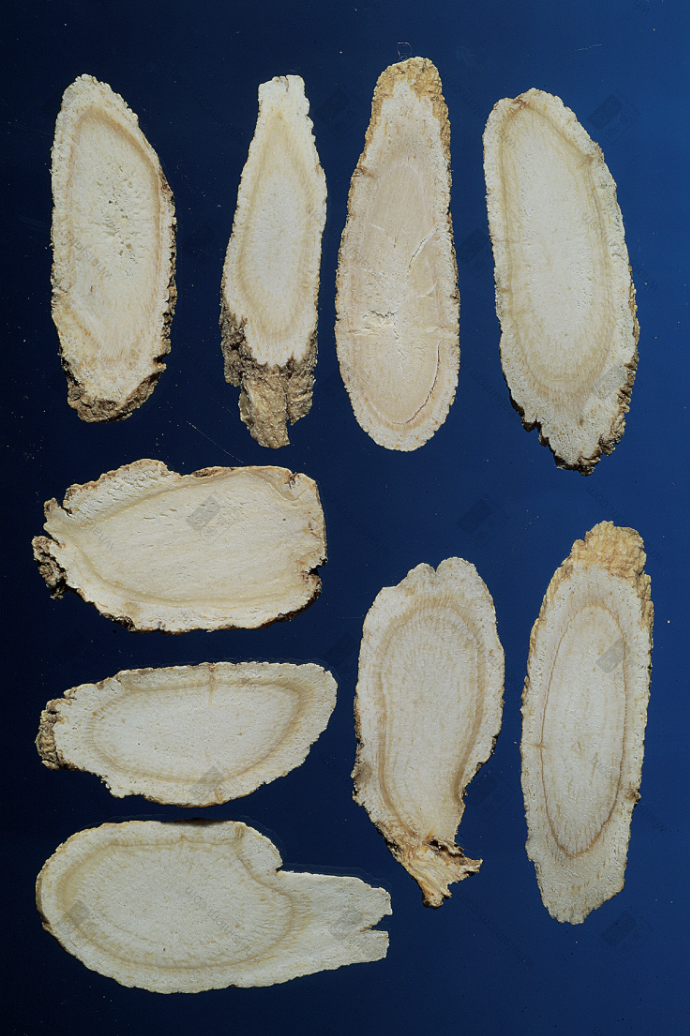 American American Ginseng Slices (Powder White and Shiny)nn
American American Ginseng Slices (Powder White and Shiny)nn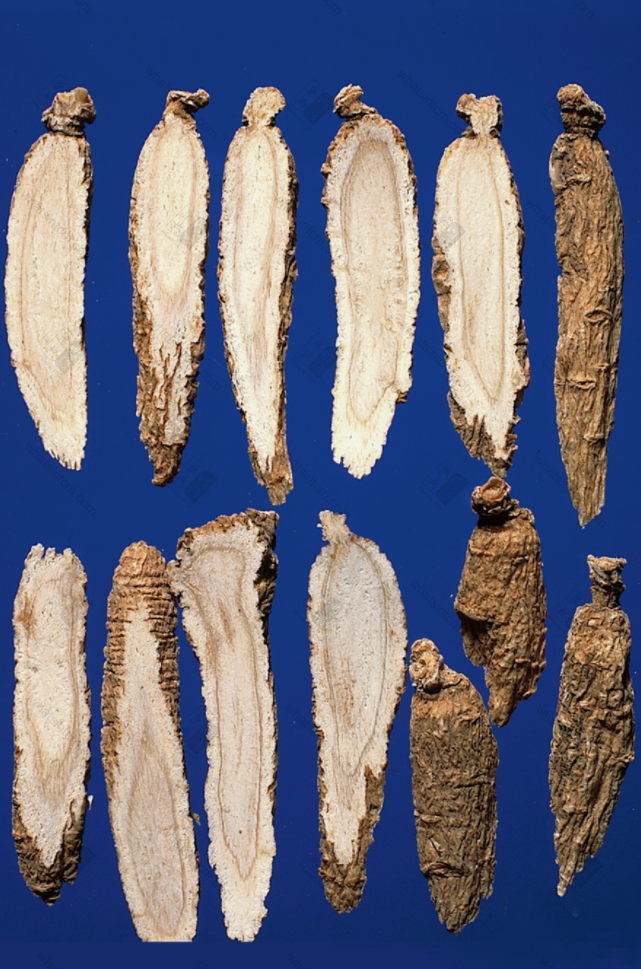 American American Ginseng Slicesnn
American American Ginseng Slicesnn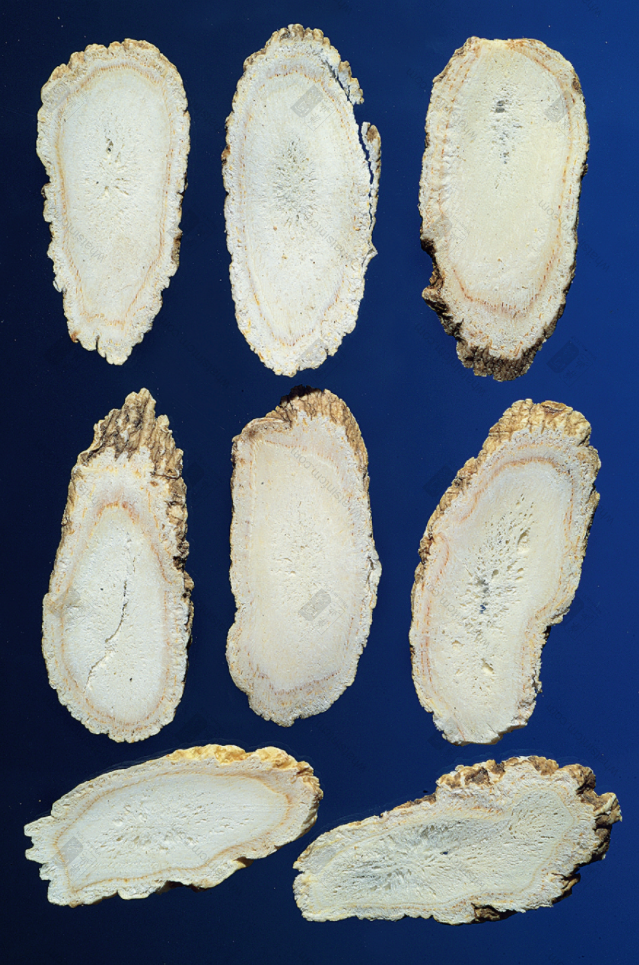 Northeast American Ginseng Slices (Light Formation Layer Color, Dark Yellow Cortex, Few Spots, Porous)nn
Northeast American Ginseng Slices (Light Formation Layer Color, Dark Yellow Cortex, Few Spots, Porous)nn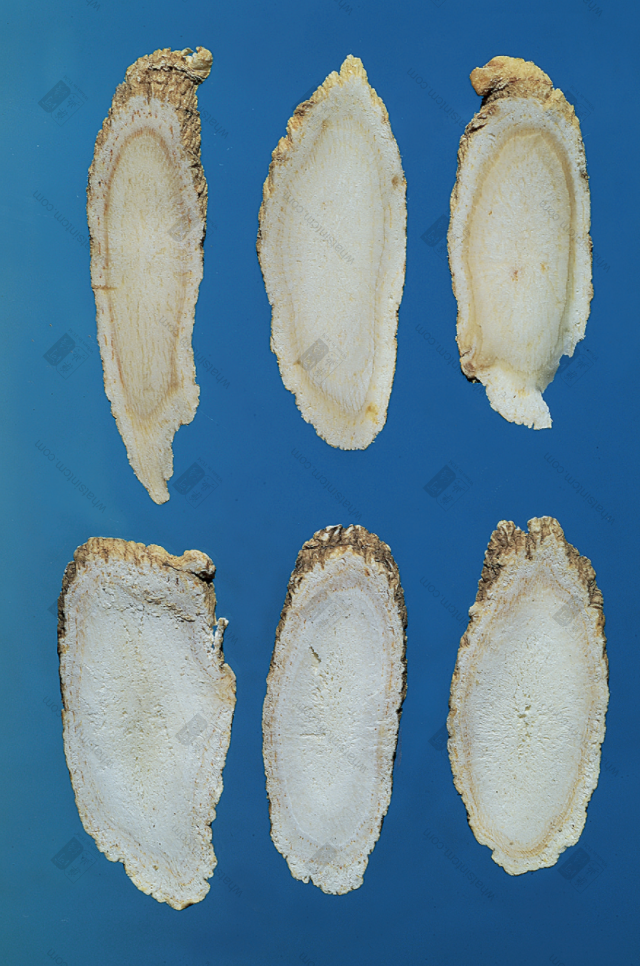 Top American, Bottom Northeast American Ginseng Slices (American Dense and Solid, Northeast Loose and Porous)nn
Top American, Bottom Northeast American Ginseng Slices (American Dense and Solid, Northeast Loose and Porous)nn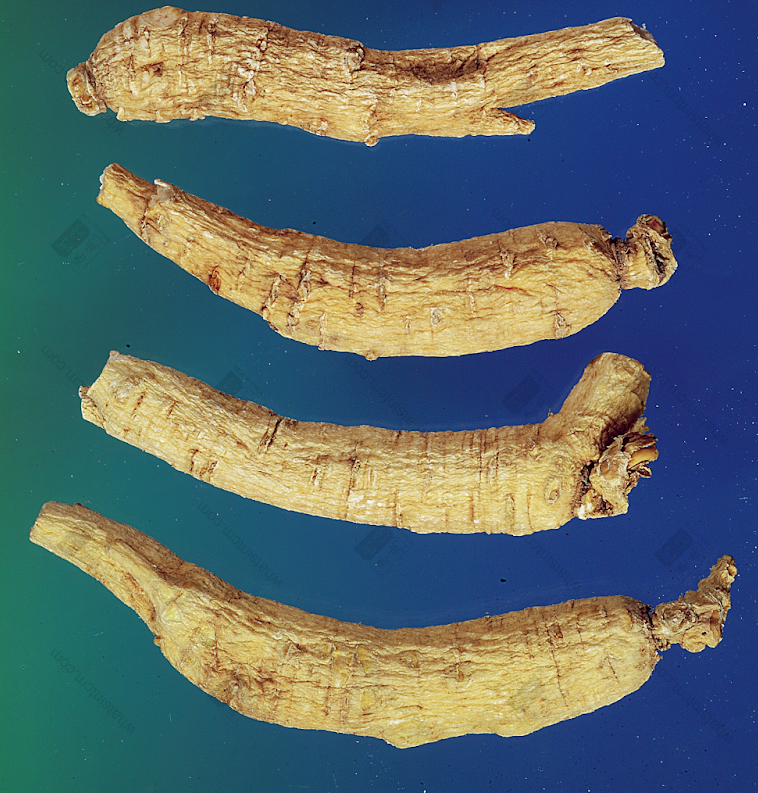 Toronto, Canada (Top), Northeast (Bottom)nn
Toronto, Canada (Top), Northeast (Bottom)nn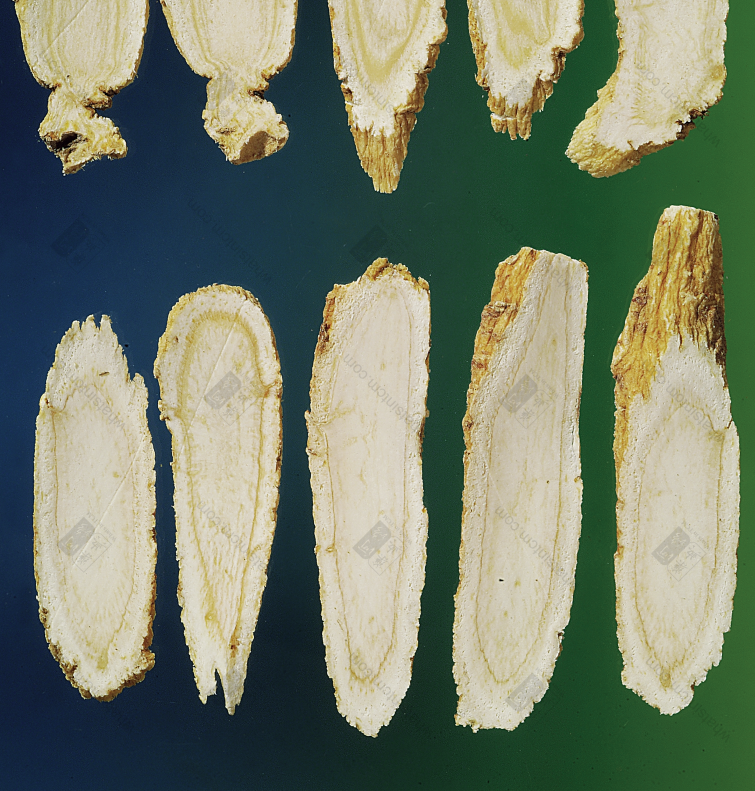 Toronto, Canada (Top), Northeast (Bottom)nn
Toronto, Canada (Top), Northeast (Bottom)nn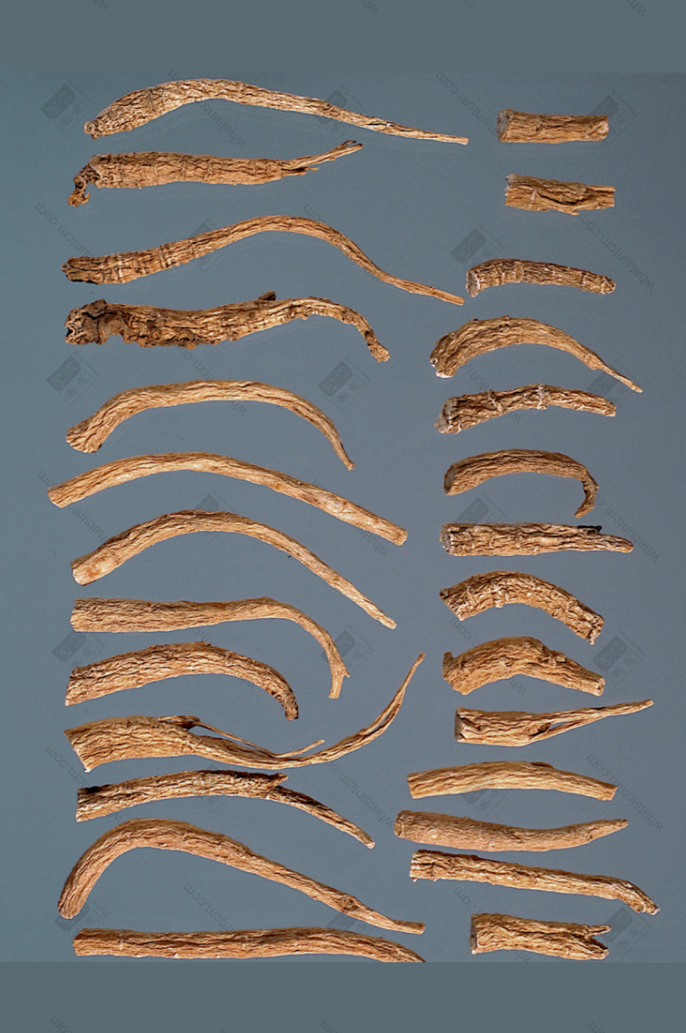 Left: Big Bi, Right: Small Binn
Left: Big Bi, Right: Small Binn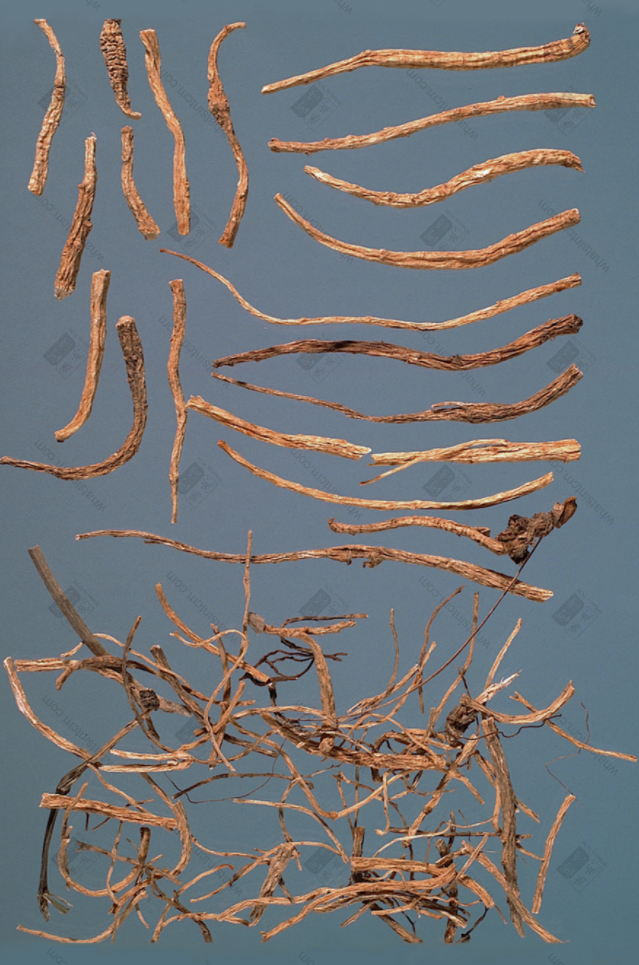 Eight Hundred Lightnn【Naming】n
Eight Hundred Lightnn【Naming】n
nn【Source】n
Essentials of Materia Medica
nn【Common Usage Level】n
A
nn【Botanical Origin】n
The dried root of Panax quinquefolium Li, of the Araliaceae family.
nn【Characteristics】n
This product is slightly cylindrical, and some are long spindle-shaped, 2-6 cm long and 0.5-1 cm in diameter. Cultivated ones have no reed head. Commercial products have their fibrous roots and branch roots removed. The surface of unpeeled ones is soil-yellow, and the surface of peeled ones is white, with dense fine transverse lines on it. The lines at the top are more dense and ring-shaped. The fracture surface is flat, light yellowish-white, with a dark colored formation layer ring, and scattered with numerous reddish-brown resin tubes. It is light in texture, hard in body, and mucilaginous. It has a slight aroma and is slightly sweet and bitter. It can produce saliva when held in the mouth, and a thick, sweet and bitter taste is called “Ge Liang”. Chewing leaves a lasting taste in the mouth.nThe sliced form is an oblique slice with finely wavy edges. The cut surface is yellowish-white, with a brown ring, and the cortex has yellowish-brown or reddish-brown dots (resin ducts).
nn【Identification】n
It is identified by even strips, white color, and powdery surface (unpeeled ones have a yellowish-white surface and a white interior). The fine lines on the surface are dense and ring-shaped, the texture is hard, the body is light, and it can produce saliva in the mouth, “Ge Liang”.
nn【Identification Terms】n
1. Human Shape, Silkworm Shape: High-quality products are shaped like a human or a silkworm.n2. Eight Hundred Light: Small root, small strip goods, 1 catty has around 800 strips (7-900 strips).n3. Big Bi, Small Bi: The cut-off branch roots are called Bi, and they are distinguished by the size of the strips.n4. Bubble Ginseng (Wild Bubble): High-quality wild ginseng, the texture is loose and porous, and it feels light in weight when placed on the hand.n5. Flag Ginseng (Flag): The US flag has many patterns, and it was called Flag Ginseng during the Qing Dynasty and continues to be called that today.n6. Pearl Grain: Cultivated species, blunt, round, granular, hard, good goods.n7. American Ginseng: High quality ones, when cut open, the surface is powder-white and shiny, and the hand touches white powder, so American Ginseng is commonly called American Ginseng.n8. Genuine American Ginseng, Secondary American Ginseng: Wild ones are called genuine American Ginseng, and cultivated ones of good quality, when cut open, the surface is powder-shiny, are called secondary American Ginseng.n9. Ge Liang: High-quality ones, when chewed in the mouth, have a Ge Liang texture.n10. Loose and Porous: Refers to the medicinal material being light and loose in texture and easily broken when bent. Example: Bubble Ginseng.n11. Iron Wire Texture (Black Line Texture): High-quality wild products, the transverse lines on the outer skin of the upper part are black-brown or yellow-brown, obvious and clear, spiral, fine and deep.
nThe main differences between wild and cultivated are as follows:nWild Cultivatedn1 Reed Head Has layered reeds, the more the better. None, or short, small, no layered reeds.n2. Shape Uneven, human shape is best, silkworm moth shape is second best. Mostly cylindrical or spindle-shaped.n3. Outer Appearance Color Yellow-brown, rust-yellow. Soil-yellow, yellowish-white.n4. Ring Pattern The lines are tightly connected, fine, clear and obvious, the more lines, the darker the better. None, some ginseng bodies are smooth, and some have them, but the layer lines are widely spaced, and the lines are not obvious, seemingly there and seemingly not.n5. Quality Light weight, loose and porous flesh. Heavy weight, sticky flesh.n6. Texture Tough. The ginseng body is easy to break and the legs are easy to break off.n7. Slicing Fire Baking No need to heat with fire to cut it smoothly. It must be heated with fire to soften it before it can be cut smoothly.n8. Sliced Color White with powder (hence the name American Ginseng). The skin has dark brown spots. Yellow with light black, less powder.n9. Chewing Taste Bitter first, then sweet, and the ginseng residue after chewing is easily dissolved in saliva. It tastes slightly sweet at first, but turns sour and bitter after prolonged chewing.n10. Odor Clear fragrance, strong and mellow taste. The aroma is not mellow and does not last long.n11. Storage Less susceptible to insect infestation. More susceptible to insect infestation.nnThe differences in the characteristics of American Ginseng produced in the United States and Canada and American Ginseng produced in Northeast ChinanNamenItem American Ginseng produced in the US and Canada American Ginseng produced in Northeast ChinanShape The main root is long conical, spindle-shaped or cylindrical, with one to several residual broken lateral root marks visible in the middle and lower part of the main root, and a few upper fork-shaped branches. The columnar root is long cylindrical, long spindle-shaped or strip-shaped, oxtail-shaped, or nodular-shaped, with one to several residual broken lateral roots visible in the middle and lower part of the main root.nSize 3-12cm long, 0.5-2cm in diameter 3-15cm long, 0.5-2.5cm in diameter

