Tiger Bone
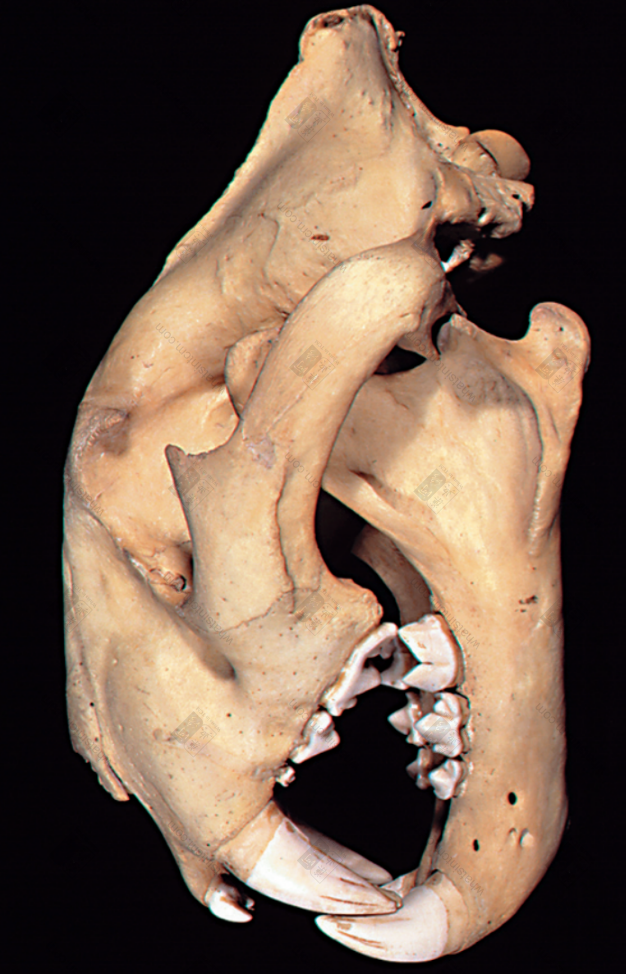
Tiger bone (Tiger skull) (Shallow groove on the forehead, posterior ridge of the parietal bone, molars shaped like the Chinese character ‘山’) Tiger
Tiger Tiger skin
Tiger skin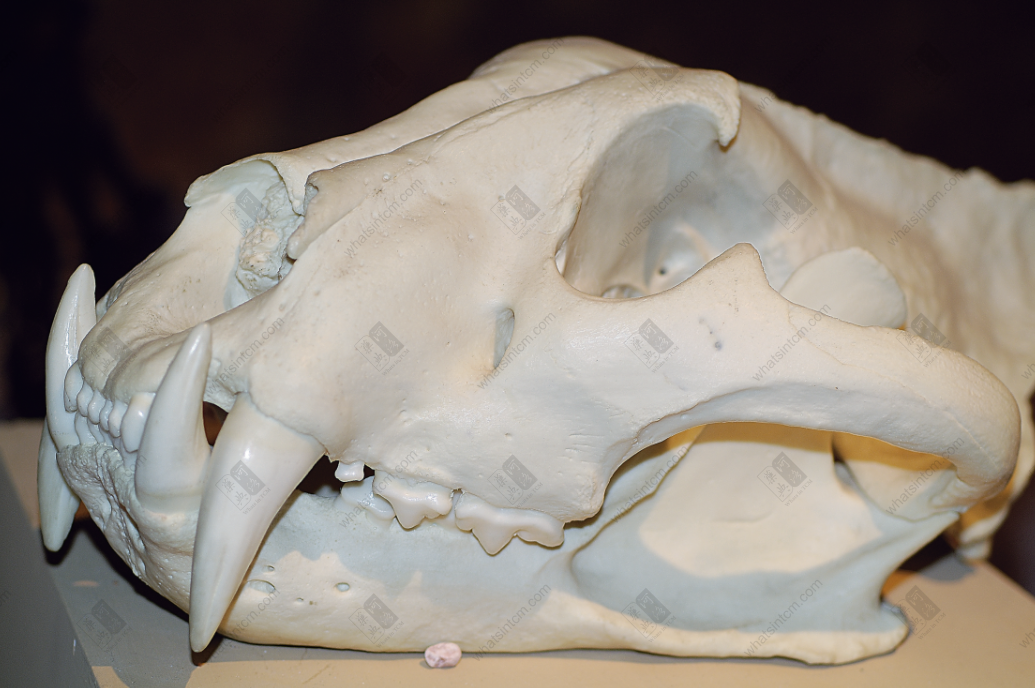 Northeast tiger skull
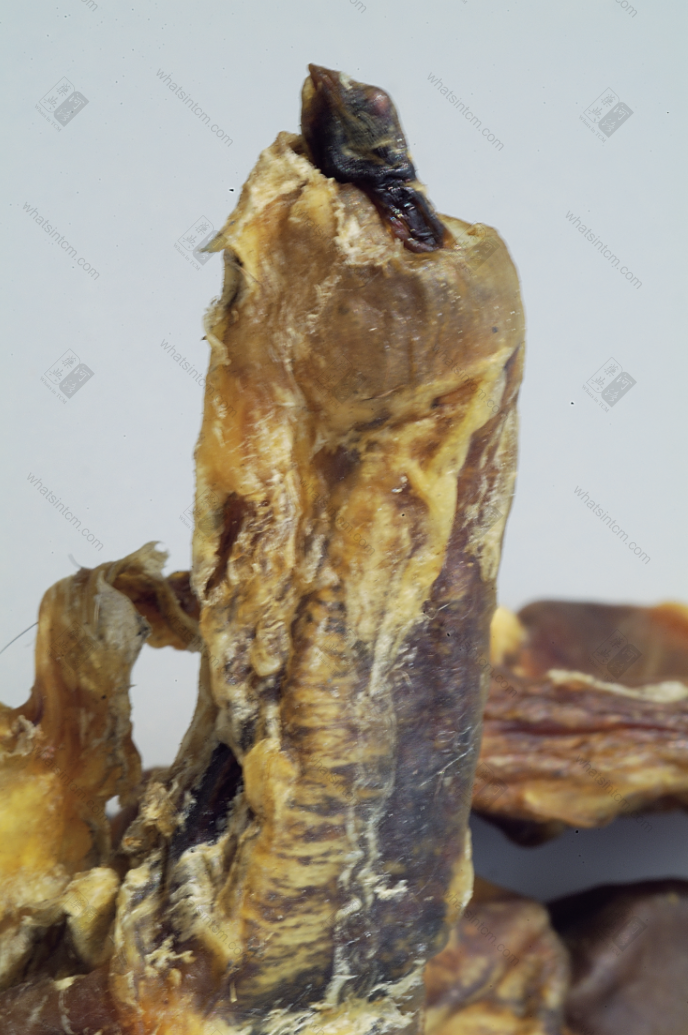
Northeast tiger skull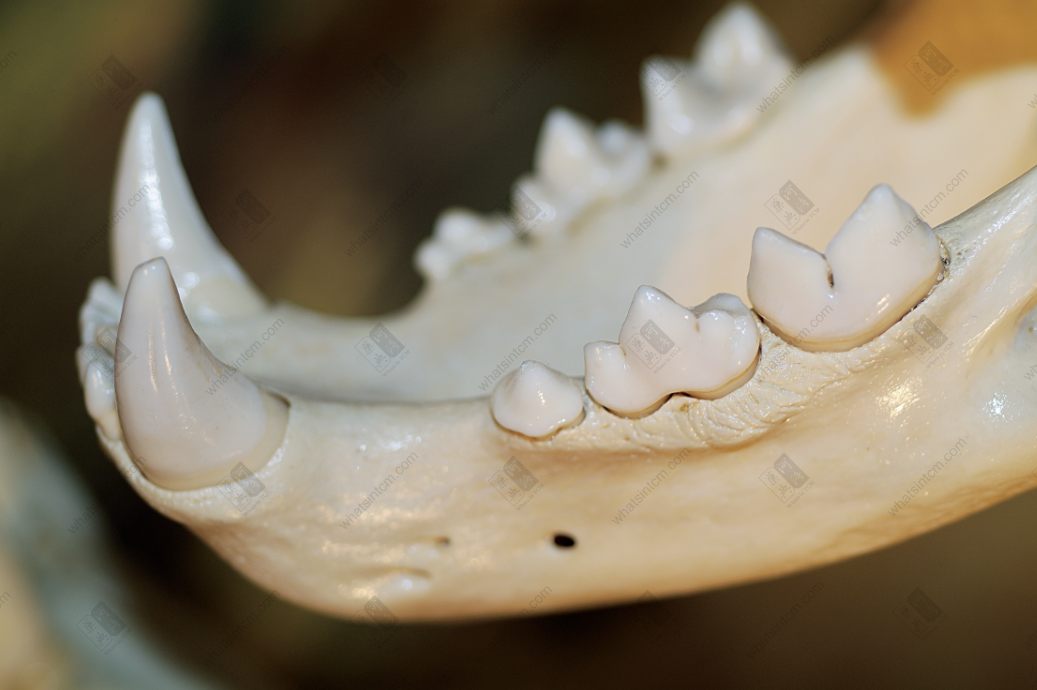 Tiger canine tooth (Mountain-shaped tooth)
Tiger canine tooth (Mountain-shaped tooth)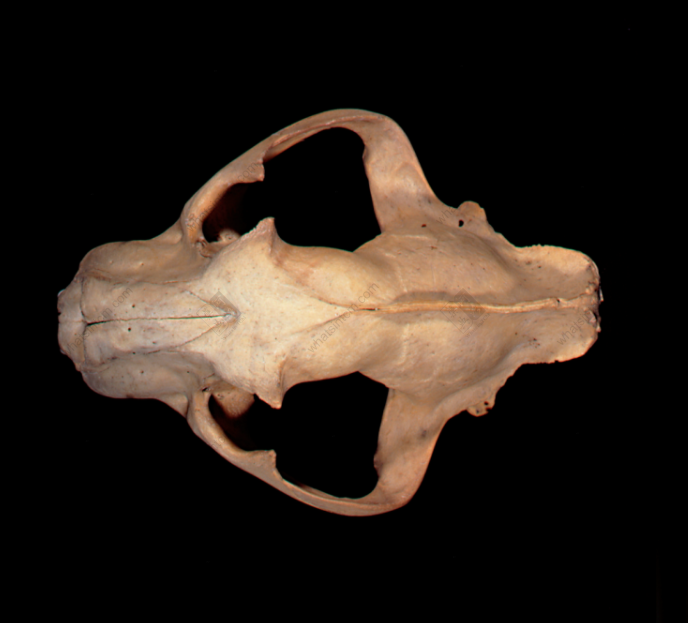
Tiger skull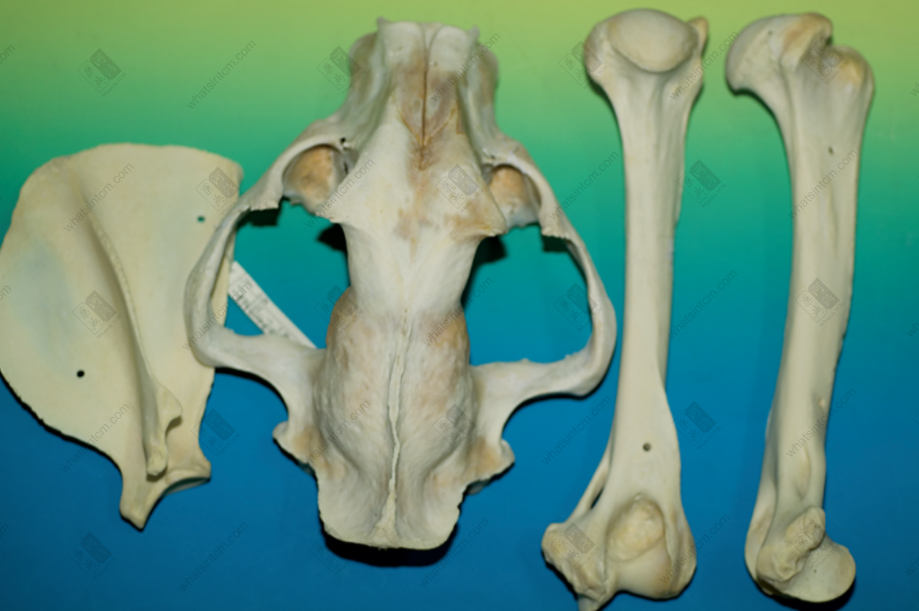 Tiger scapula, skull, humerus (The lower part of the tibia is thick and large, presenting a triangular prism shape)nn
Tiger scapula, skull, humerus (The lower part of the tibia is thick and large, presenting a triangular prism shape)nn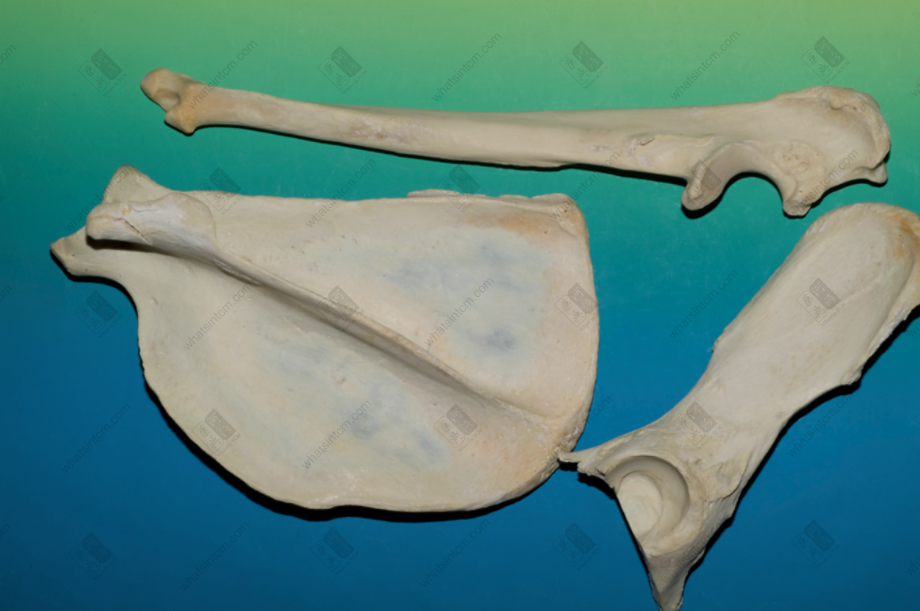 Tiger ulna, scapulann
Tiger ulna, scapulann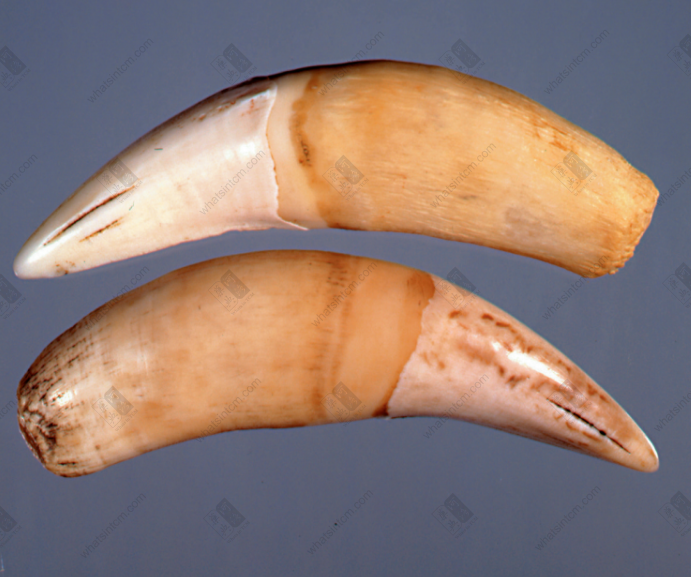 Tiger caninenn
Tiger caninenn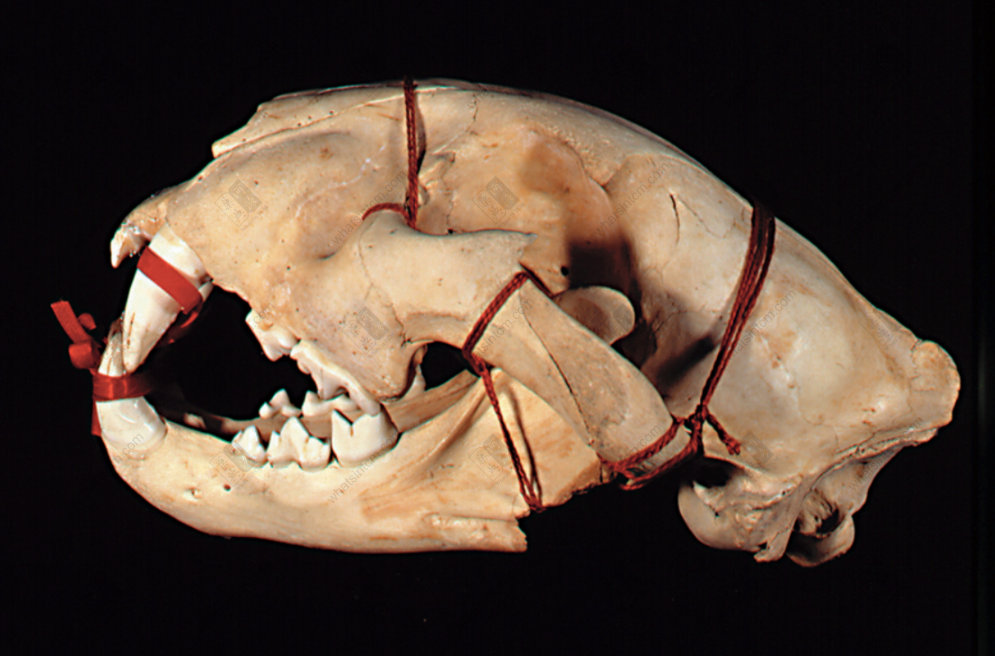 Lion skullnn
Lion skullnn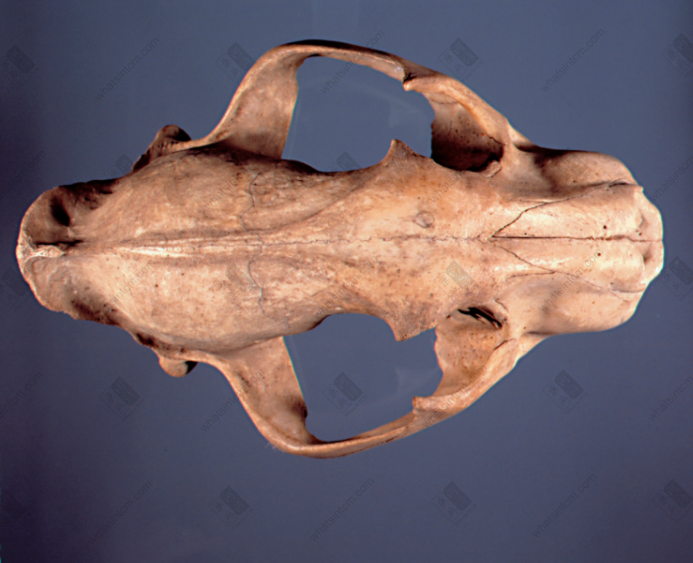 Lion skullnn
Lion skullnn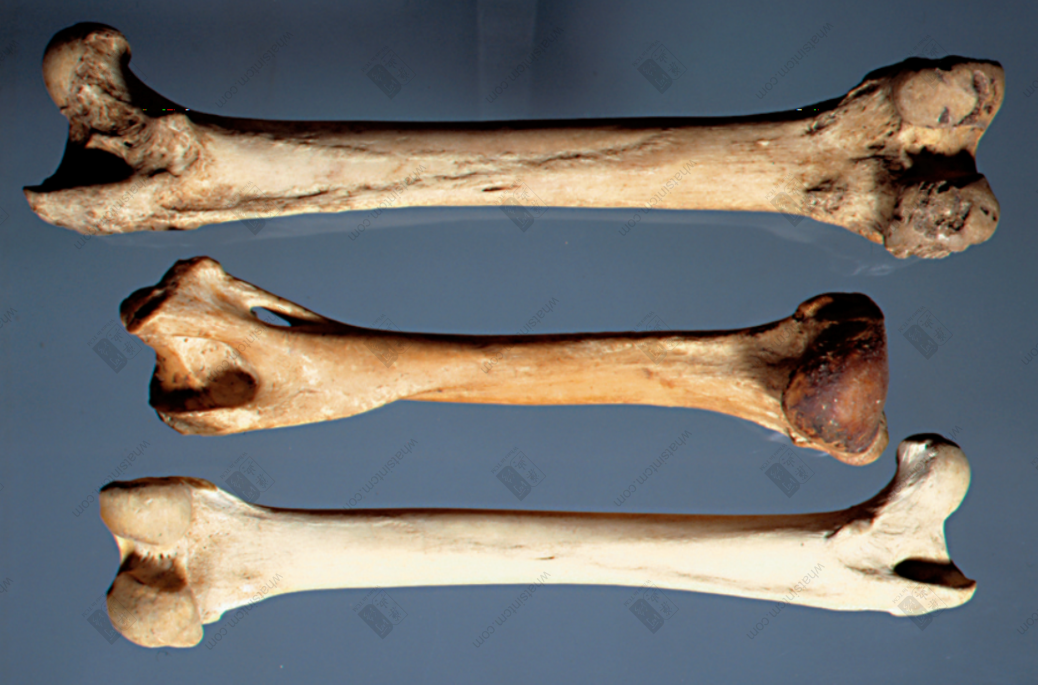 Tiger humerus (Tibia, phoenix eye) (Flat and elongated hole near the bone ring at the lower end of the upper section of the leg bone’s forelimb)
Tiger humerus (Tibia, phoenix eye) (Flat and elongated hole near the bone ring at the lower end of the upper section of the leg bone’s forelimb)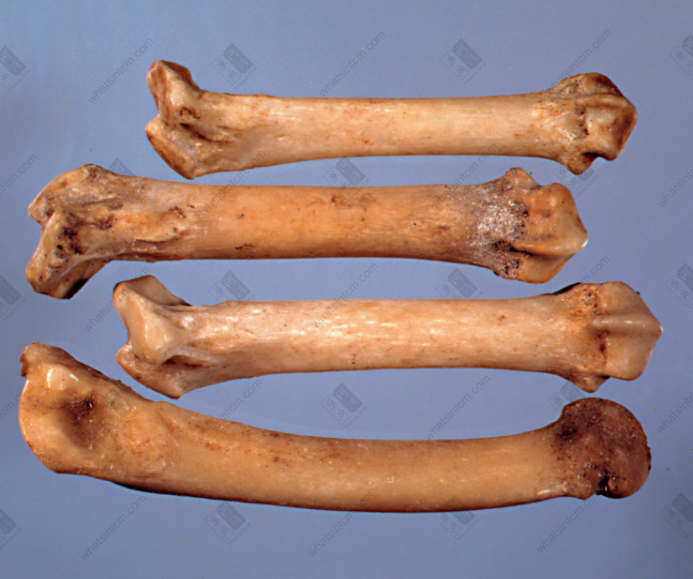
Tiger metacarpal bone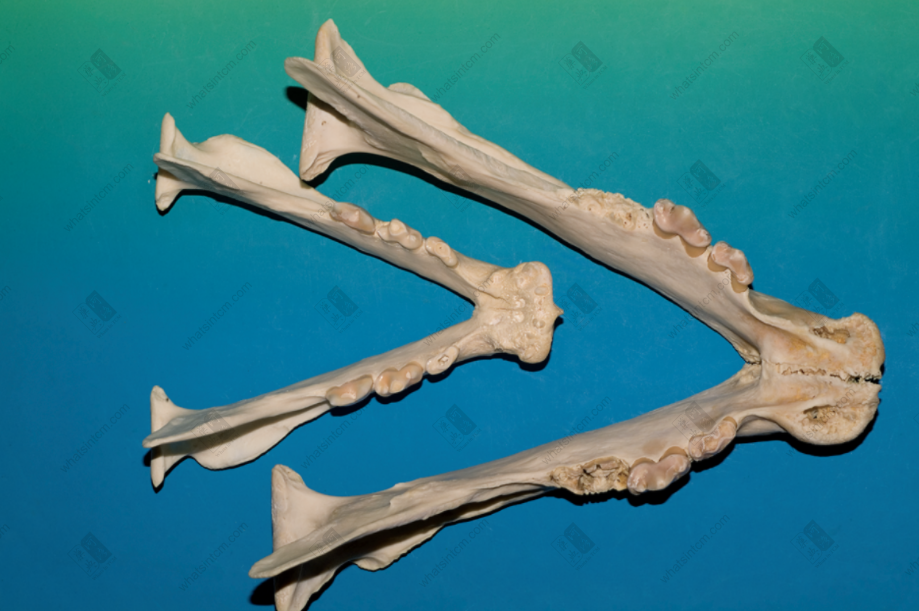 Mandible (Large tiger, small leopard)
Mandible (Large tiger, small leopard)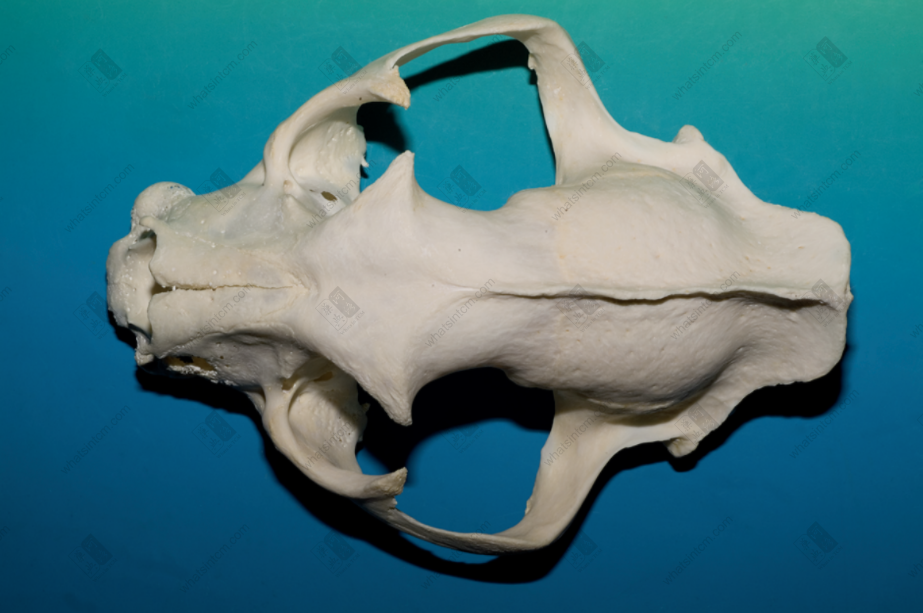 Leopard skull
Leopard skull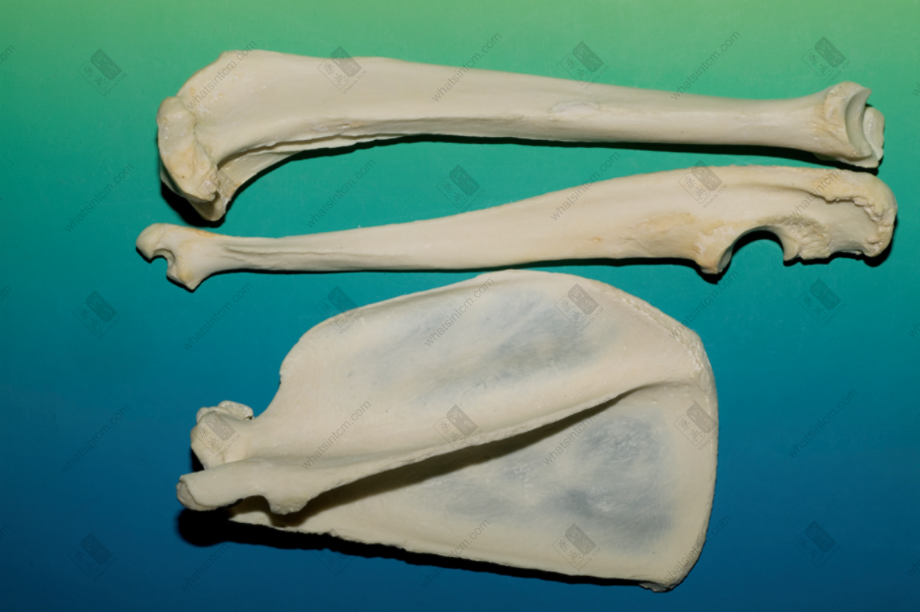 Leopard ulna, scapula
Leopard ulna, scapula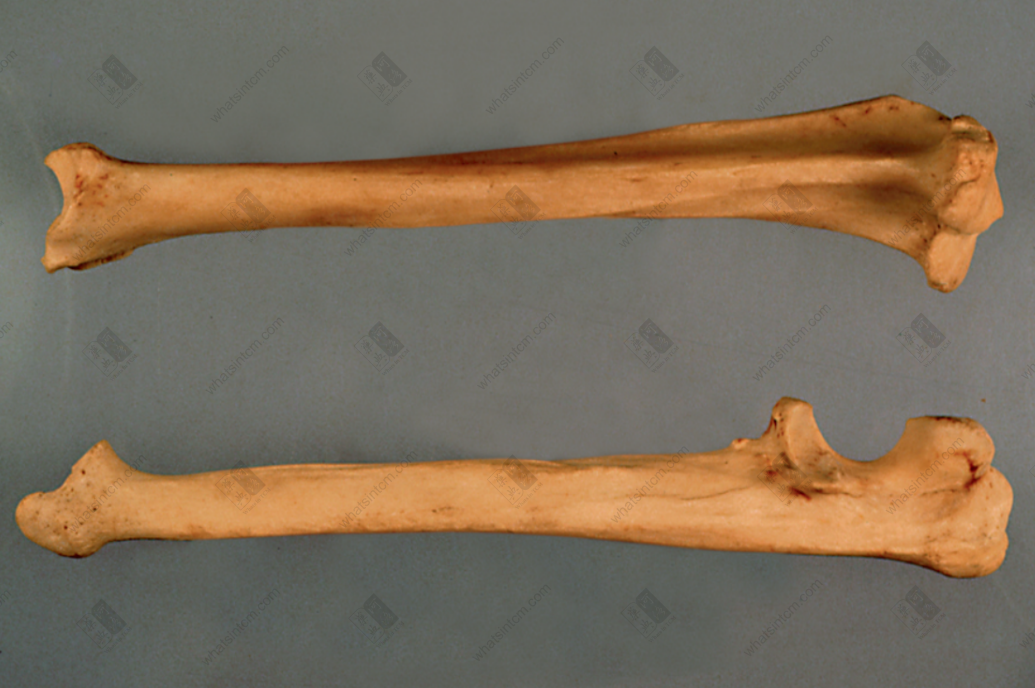 Leopard bone
Leopard bone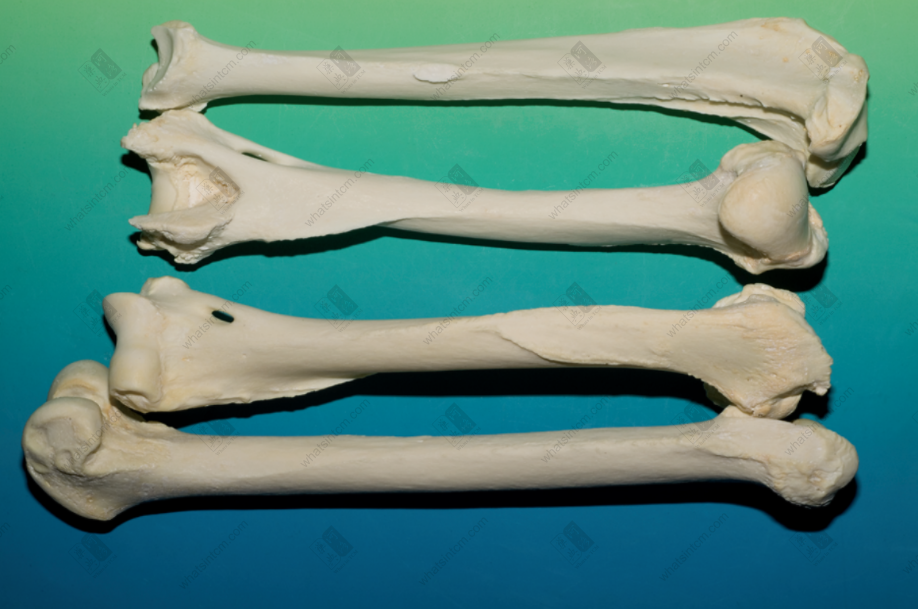 Leopard femur, humerus
Leopard femur, humerus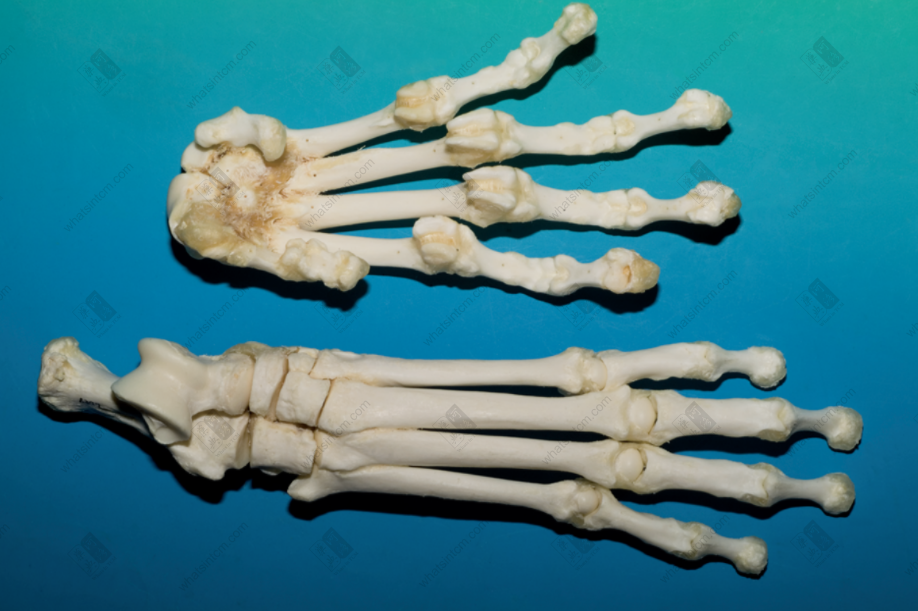 Leopard metacarpal bone
Leopard metacarpal bone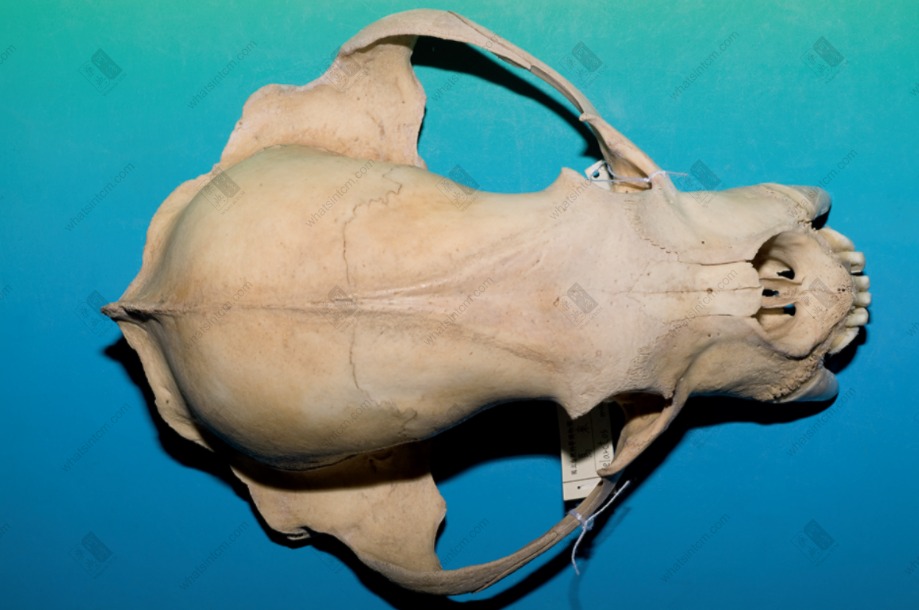 Bear skull
Bear skull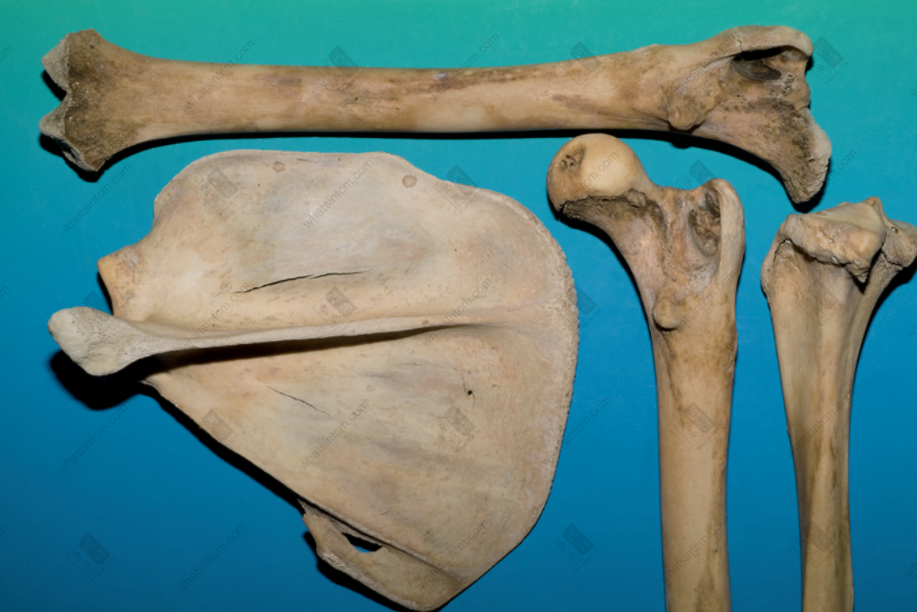 Bear ulna, scapula
Bear ulna, scapula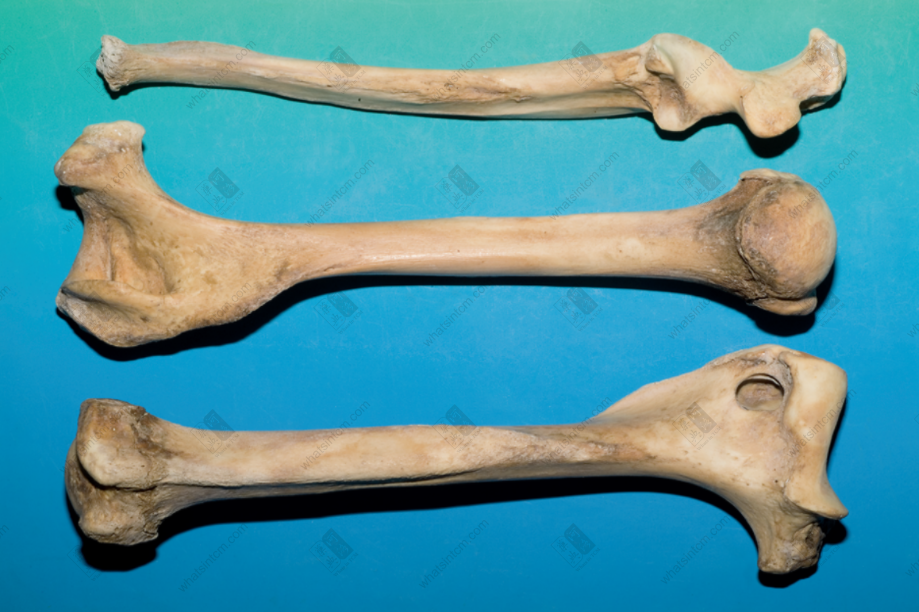 Bear fibula, femur, humerus
Bear fibula, femur, humerus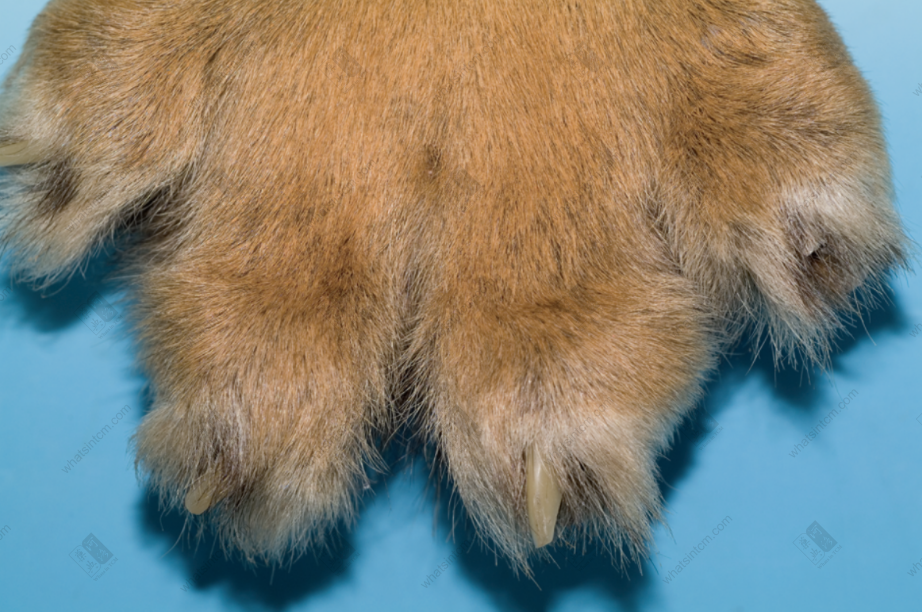 Tiger claw
Tiger claw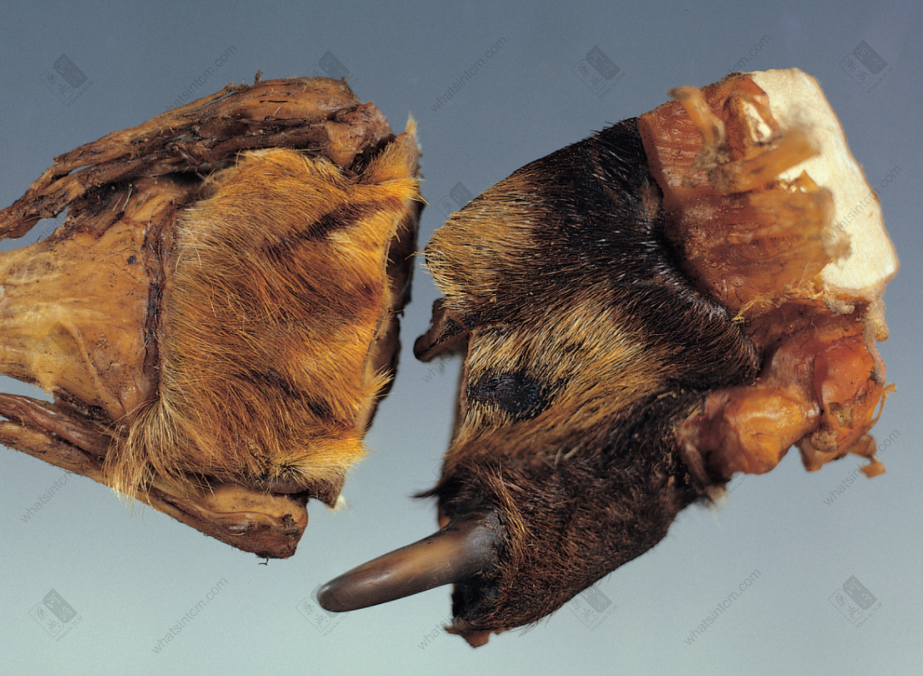 Fake tiger metacarpal bone
Fake tiger metacarpal bone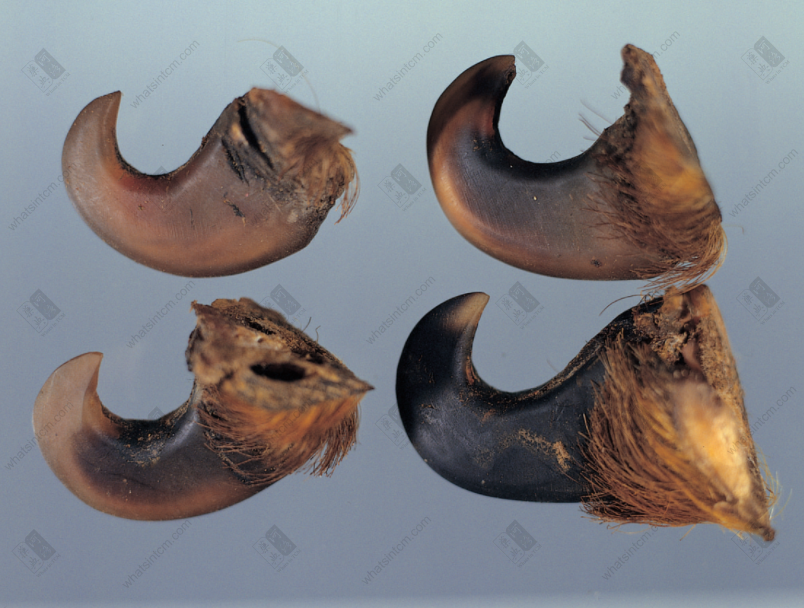 Fake tiger claw
Fake tiger claw
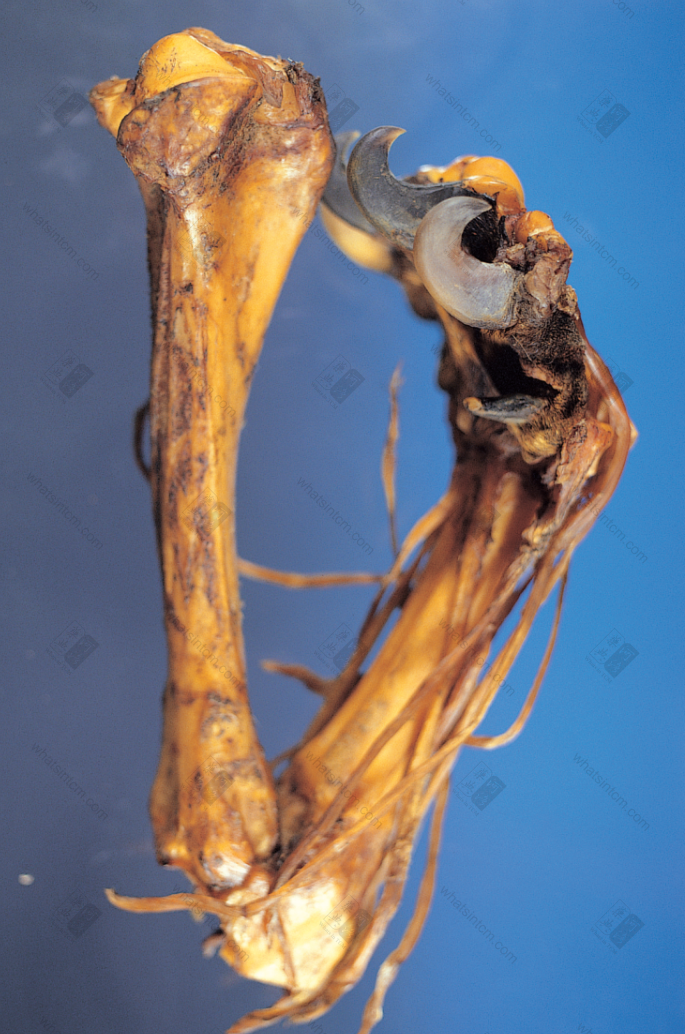
Fake tiger bone and tiger tendon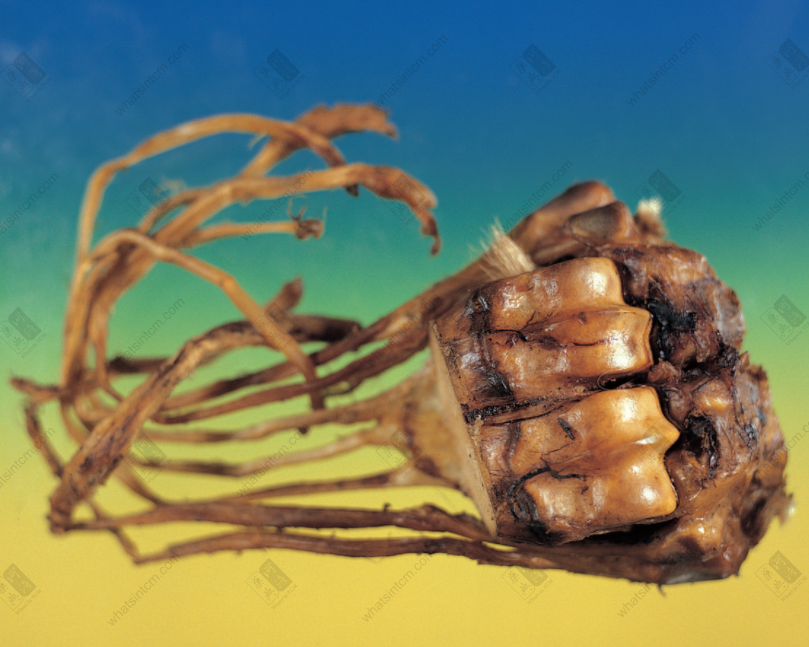 Fake tiger metacarpal bone and tiger tendon
Fake tiger metacarpal bone and tiger tendon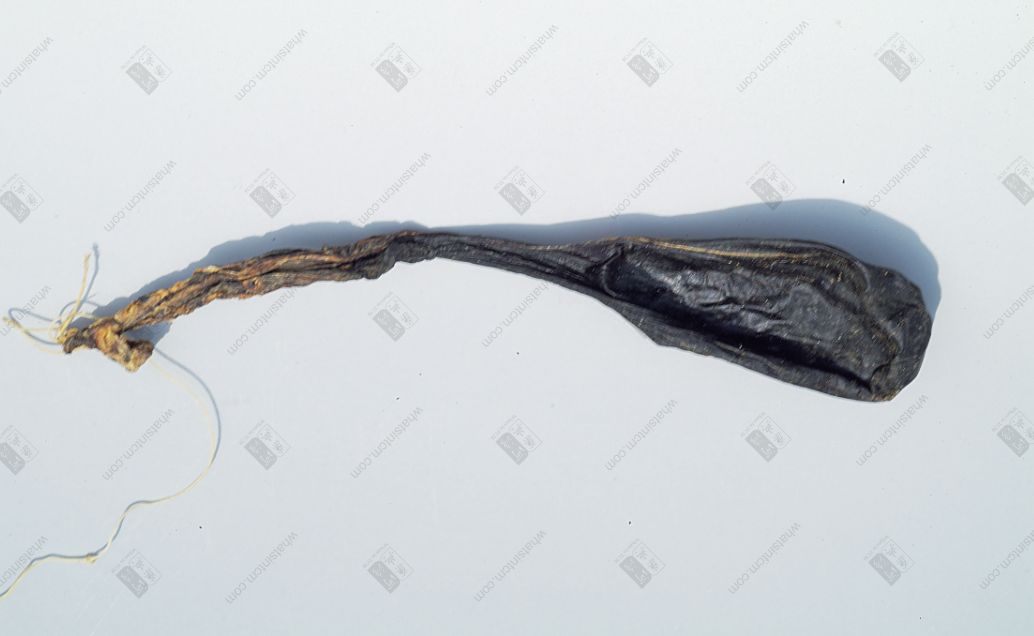 Tiger gallbladder
Tiger gallbladder
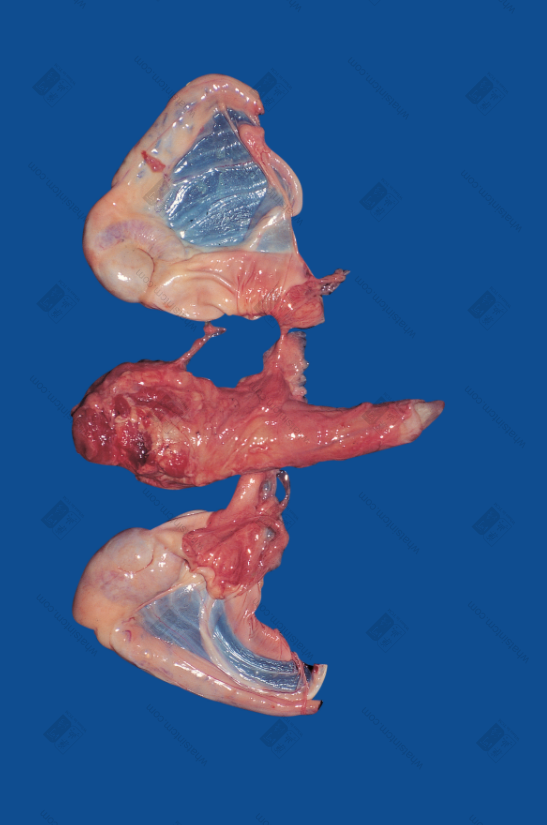
Tiger penis (Fresh)
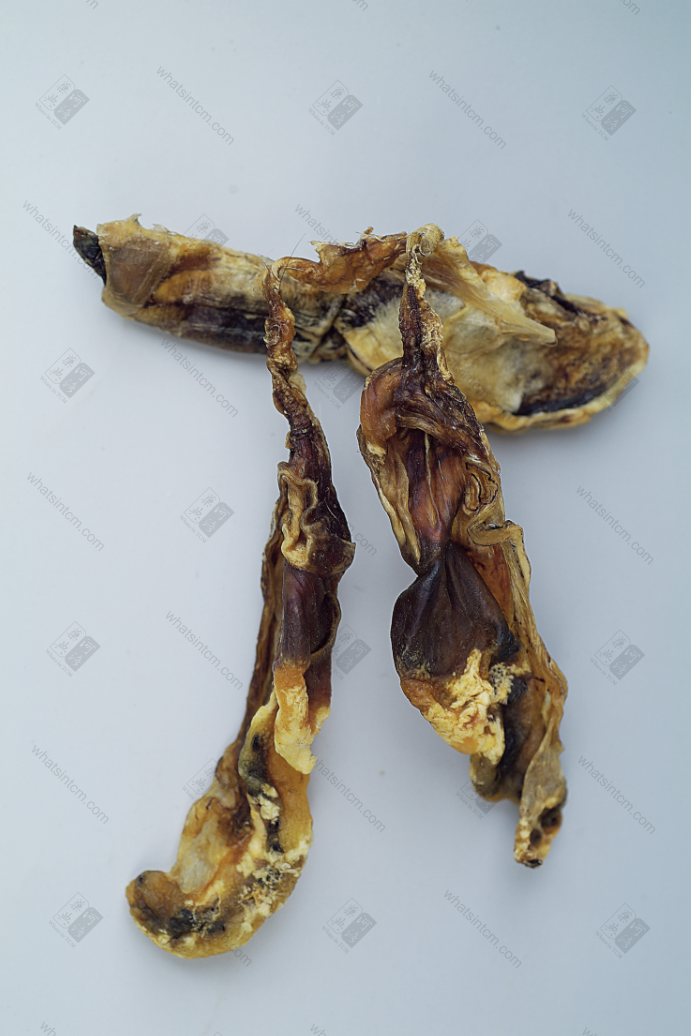
Tiger penis
Tiger penis (Without barbs)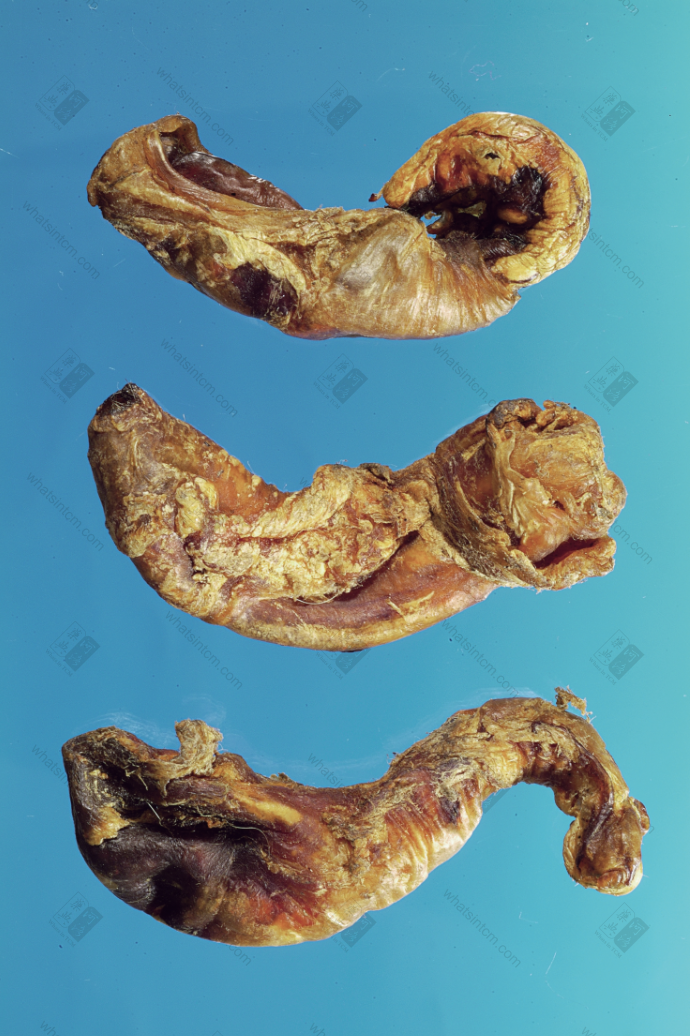
Tiger penis
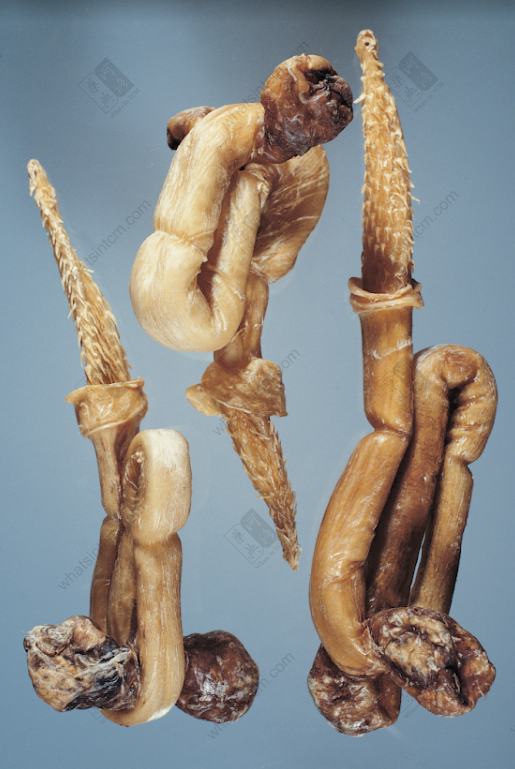

Fake tiger penis

Incriminating evidence (But it’s a fake tiger penis)
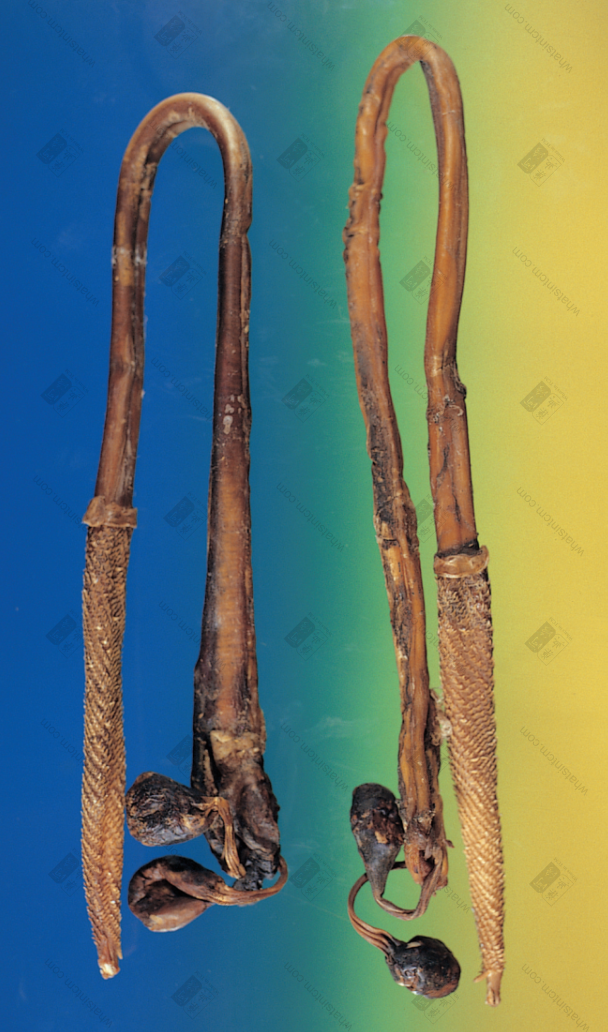

Fake tiger penis
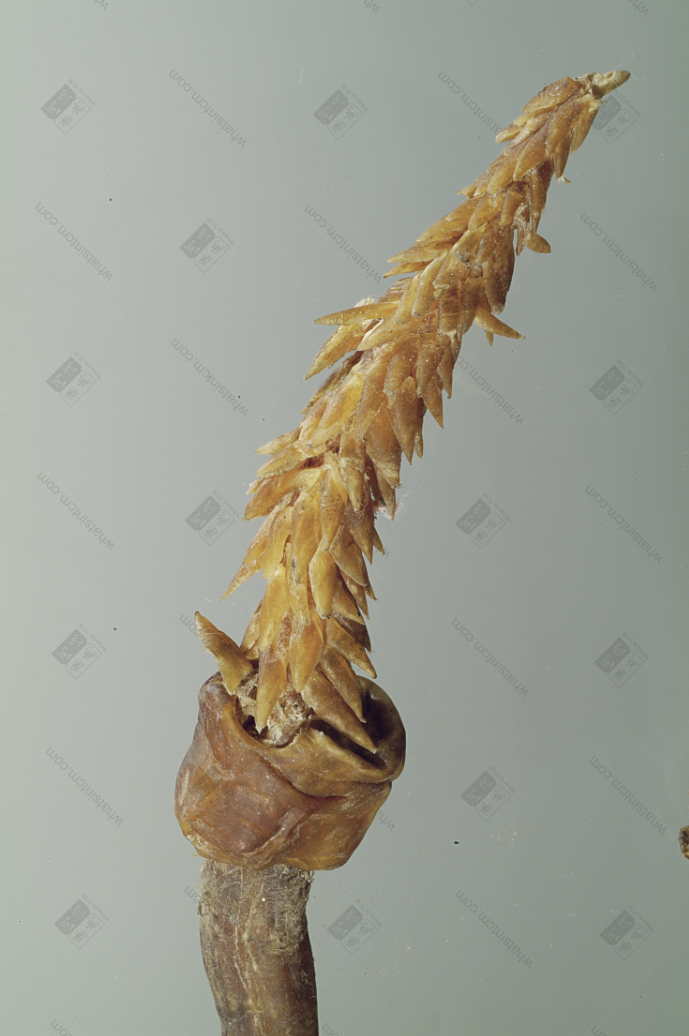

Fake tiger penis
【Naming】n
n 【Source】n
Mingyi Bielu, Middle Grade
n 【Frequency of Use】n
D
n 【Origin】n
The bones of the tiger Panthere tigris L. and other related animals in the same genus.
n 【Characteristics】n
The commodity is available as a whole skeleton or individual bones. The whole skeleton of tiger bone retains some muscle and connective tissue, and is rich in oil. A complete skeleton, after removing the muscle and tissue, including the head, tail, and limbs, is called “Whole Tiger Bone.” Removing the limbs yields “Tiger Body Bone,” while the limbs alone are called “Four Leg Bones.” The “Four Leg Bones” may retain the skin and fur of the feet, along with the claws, which is called “Hairy Legs.”nnThe skull is relatively round, laterally compressed dorsoventrally, with a short snout and a flat frontal bone. The upper part of the forehead has a shallow groove, and the back of the parietal bone often has a ridge. The zygomatic bone is large and protrudes outward. Each eye socket has an oval translucent hole below, with the hole surface sloping. The maxilla has 3 pairs of incisors, 1 pair of canines, and 4 pairs of molars. The mandible has 3 pairs of incisors, 1 pair of canines, and 3 pairs of molars, for a total of 30 teeth. The incisors are small, the canines are conical, strong, sharp, and slightly curved inward. The molars are shaped like the Chinese character “山” (mountain), with serrated edges. The last pair of molars in the maxilla may not be prominent in young tigers. All teeth are white or light yellowish-white with a luster. The tooth base is deeply embedded within the jawbone, hence the common saying “sitting bone growing teeth.”nnThere are 7 cervical vertebrae. The 1st cervical vertebra is butterfly-shaped, and the 3rd to 7th cervical vertebrae are saddle-shaped. There are 13 thoracic vertebrae, each with a relatively long spinous process on top. There are 3 sacral vertebrae, which are often fused into one piece, with 3 spinous processes visible on top. There are 22-28 caudal vertebrae, mostly in even numbers, with a slight protrusion in the middle of each vertebra. There is 1 ischium, which is rectangular and symmetrical on both sides. There are two scapulae, which are fan-shaped and semi-circular. The central part is very thin, and there is a ridge-like protrusion on the outside.nnThe leg bones of the tiger (tiger tibia) have obvious ridges. The upper section is a single bone, while the lower section is composed of two fused bones. The lower end of the upper section of the forelimb, near the bone ring, has a flat and elongated hole on the lateral side, commonly known as the “Phoenix Eye.” The two bones of the lower section are similar and stand side-by-side, slightly flattened and twisted, but one is longer. The upper section of the hind limb is cylindrical and can be placed flat on all sides without wobbling. The upper inner side has a round axis, and the lower end has a long oval groove, which is where the kneecap is located. The kneecap (i.e., tiger knee) is elongated oval in shape, like a saddle, with a smooth inner surface, thick and heavy, often with a tongue-shaped tendon. The main bone of the lower section is thick and large, presenting a triangular prism shape, while the other bone is very thin, commonly known as the “Bladder Bone.”nnThe forefoot has 5 toes, and the hind foot has 4 toes, all with short claws at the ends.nnThe surface of the tiger bone is yellowish-white or grayish-white, delicate, and oily. It is relatively heavy and solid in texture. The cross-section reveals that the central space accounts for about one-third of the bone, with the bone marrow forming a silken network, which is grayish-yellow.
n 【Preparation】n
1. Oiled Tiger Bone 2. Vinegar Tiger Bone
n 【Identification】n
“Zhenglei Bencao”: “The skull and tibia are used, and the ones with yellow color are the best.” “Yifang Leiju”: “The whole tiger tibia is used, and the lower section of the front leg is excellent, especially the ones with marrow.” “Bencao Mengquan”: “The yellow and male ones are the best.” “Bencao Gangmu”: “Therefore, the tibia is considered superior.” “Ren Shu Bian Lan”: “The tiger bone from the front leg tibia with full marrow is the best.” “Bencao Chengya Banji”: “The bone in the wrist of the forepaw, which is round and flat like a chess piece, is the most potent.” “Bencao Beiyao”: “The skull and tibia are considered good.” “Jingyan Danfang Huibian”: “Tiger bone, it should be long and flattened to be genuine.”nnThe characteristics of tiger bone: the whole skeleton is unusually heavy. The skull is round and wide, with a flat zygomatic bone. There are 26 ribs, which are flat and round without ridges. The leg bone, also known as the tiger tibia, is round, thick, and short, with very thick bone quality, solid and heavy, and a yellow luster on the surface. The forelimb has a bladder bone, and the hind limb has a “Phoenix Eye” (lion bone and leopard bone also have the Phoenix Eye, while other animal bones do not). When the leg bone is broken, the inner wall has loofah-like yellow-white oily residue (bone marrow) with a distinctive odor. The hind limb has a pair of kneecaps, called “Tiger Knee,” shaped like a saddle. See the description of the medicinal material characteristics for detailed features of other bones.nnThe leg bones of other animals are mostly triangular in shape, with thin and light bone quality, which is very different from tiger bone.nnThe best ones are large, heavy, solid, yellowish-white, and without residual meat. Smaller ones, lighter, grayish-white, and with residual meat are inferior. If the tiger bone is grayish-white and without luster, it is “dead bone.” If the bone color has turned green, it means the tiger died from a poisoned arrow wound, and the bone contains toxic substances. The above two should not be used in medicine.
n 【Identification Terminology】n
1. Sitting bone growing teeth (mountain-shaped teeth): The molars of tigers and leopards are shaped like the Chinese character “山” (mountain), with serrated edges. The tooth bone is deeply embedded within the jawbone, commonly known as “sitting bone growing teeth.”n2. Bang bone: Refers to the lower leg bone of the hind limb of the feline tiger, which is composed of two bones. Its characteristic is that the main bone is thick and large, presenting a triangular prism shape, and the other bone is very thin, which is called the fibula in zoology.n3. Scapular spine: Refers to the inner surface of the tiger’s scapula, which is slightly flat, and there is a raised ridge on the outside. Commonly known as the scapular spine.n4. Tiger’s might: Refers to the clavicle (2 pieces) of the tiger bone, which is small and curved in shape, commonly known as the tiger’s might.n5. Tiger shin: The common name for the tiger’s kneecap.n6. Rod bone: The thick and strong long bone of the upper part of the tiger’s hind limb, which is the femur, is cylindrical and can be placed flat on all sides without wobbling, commonly known as the rod bone.n7. Loofah sponge: A vivid description of the tiger bone‘s bone marrow.n8. Phoenix eye: Specifically refers to the unique flat, narrow, and elongated round translucent hole on the inner side of the lower end of the upper section of the tiger bone‘s forelimb, near the humeral ring.n9. Nasal void: Refers to the long, longitudinal groove in the middle of the tiger’s nasal bone, commonly known as the nasal void.n10. Butterfly bone: The atlas of the tiger, which is butterfly-shaped on the back, commonly known as the “butterfly bone.”n11. Supporting bone (bladder bone): Refers to the thinner and longer one of the parallel bones in the lower section of the tiger bone‘s hind limb, called the supporting bone. That is, the above-mentioned bang bone, the thin bone called the fibula in zoology.
n 【Chapter】n
Vertebrates

