Atractylodes Rhizome
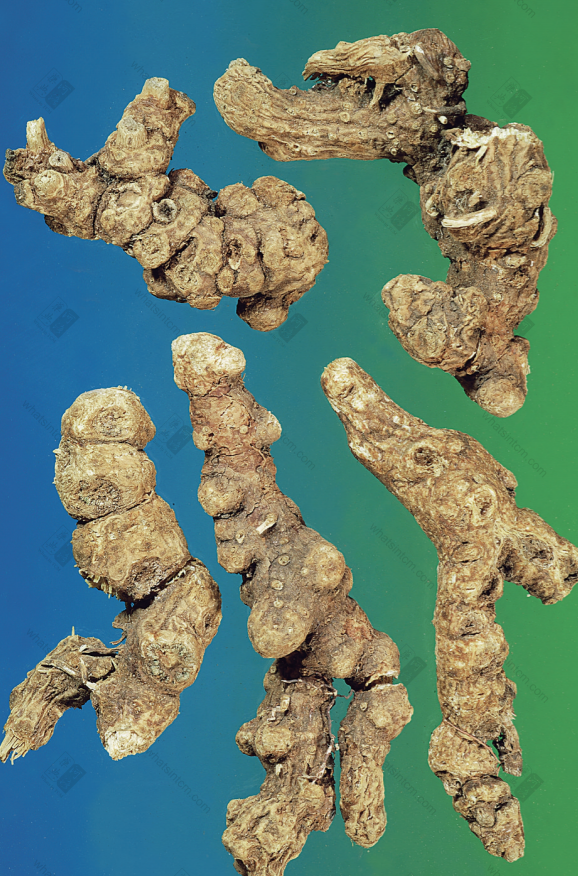 Tianjin Atractylodes Rhizome (Branching, knobby, fibrous roots, shrunken root scars, occasional residual stem)
Tianjin Atractylodes Rhizome (Branching, knobby, fibrous roots, shrunken root scars, occasional residual stem)
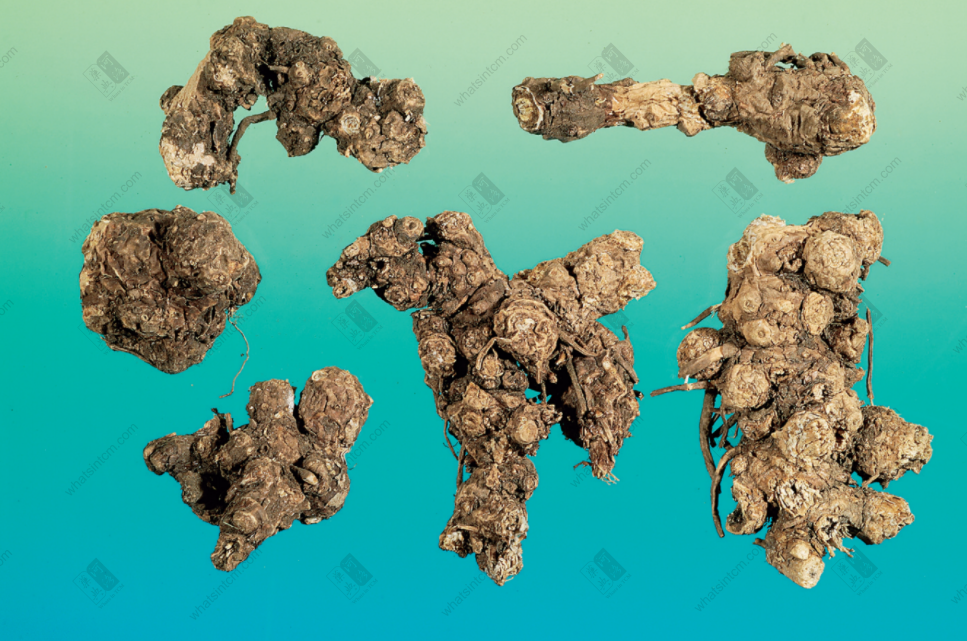 Northern Atractylodes Rhizome
Northern Atractylodes Rhizome
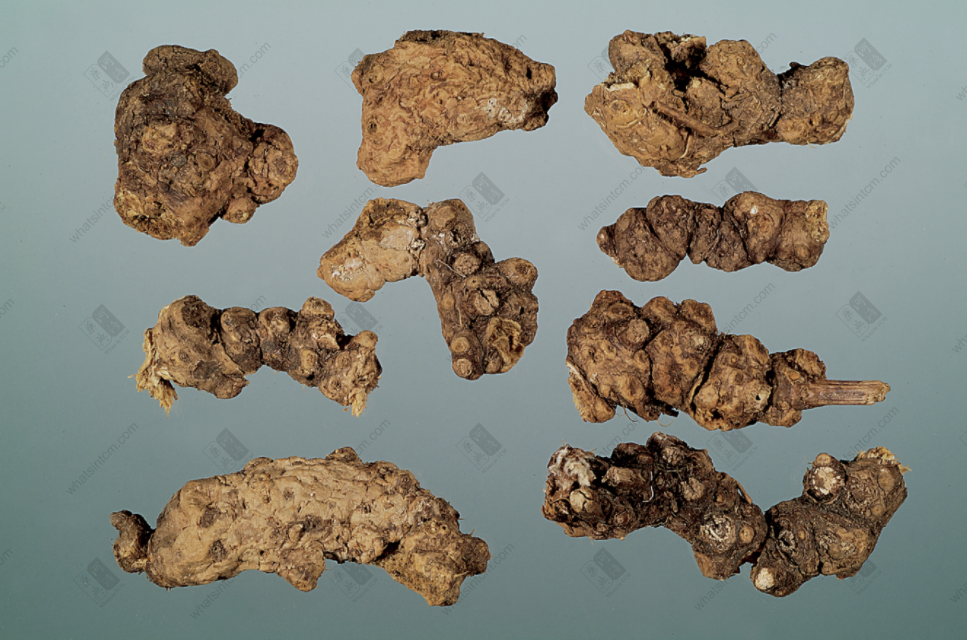 Northern Atractylodes Rhizome
Northern Atractylodes Rhizome
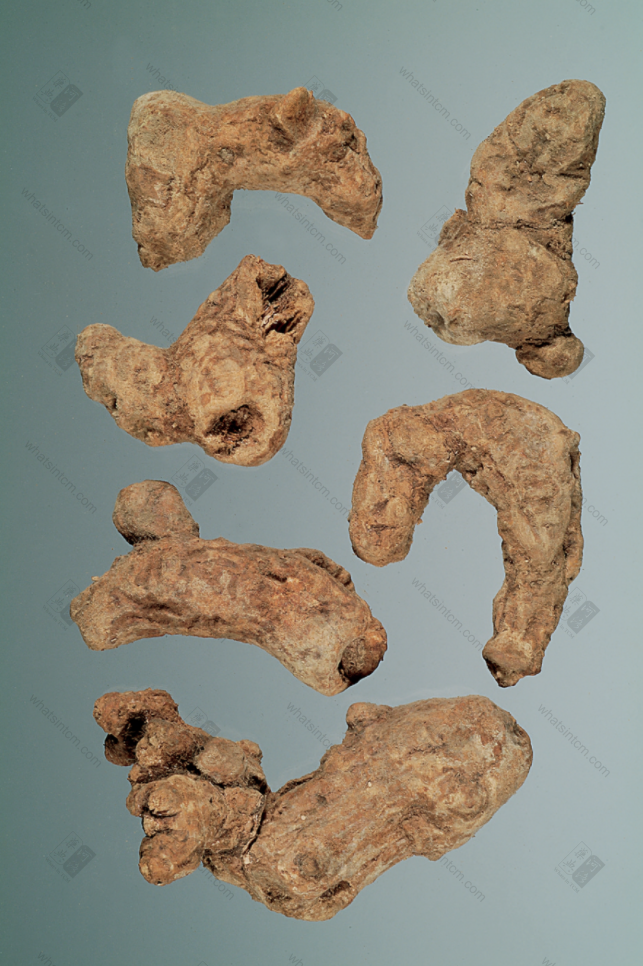 Southern Atractylodes Rhizome (Beaded, segmented, curved, gray-brown)
Southern Atractylodes Rhizome (Beaded, segmented, curved, gray-brown)
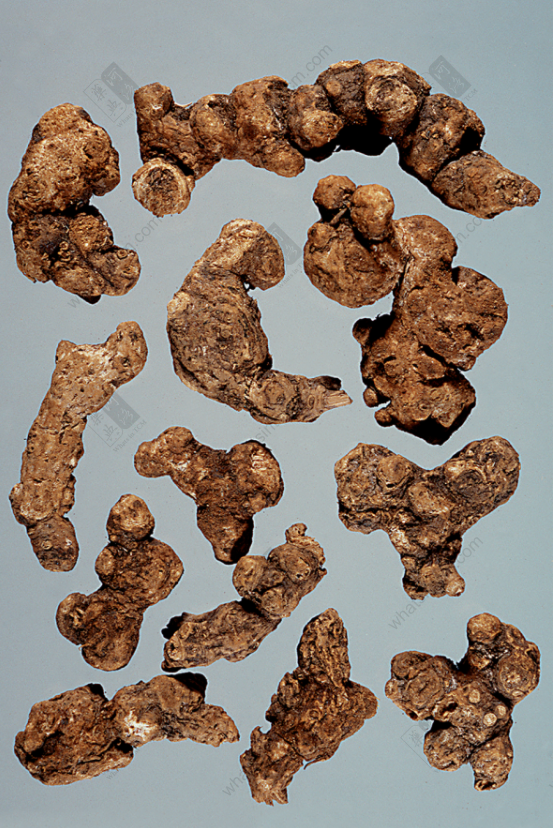 Atractylodes Rhizome (Southern Atractylodes Rhizome easily breaks, develops frost-like deposits when stored, Atractylodes Macrocephala Rhizome does not)
Atractylodes Rhizome (Southern Atractylodes Rhizome easily breaks, develops frost-like deposits when stored, Atractylodes Macrocephala Rhizome does not)
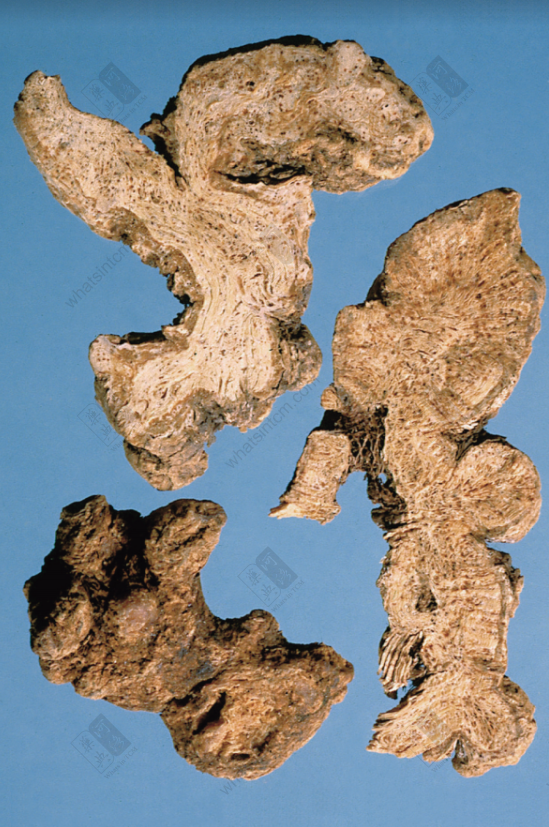 Atractylodes Rhizome Slice
Atractylodes Rhizome Slice
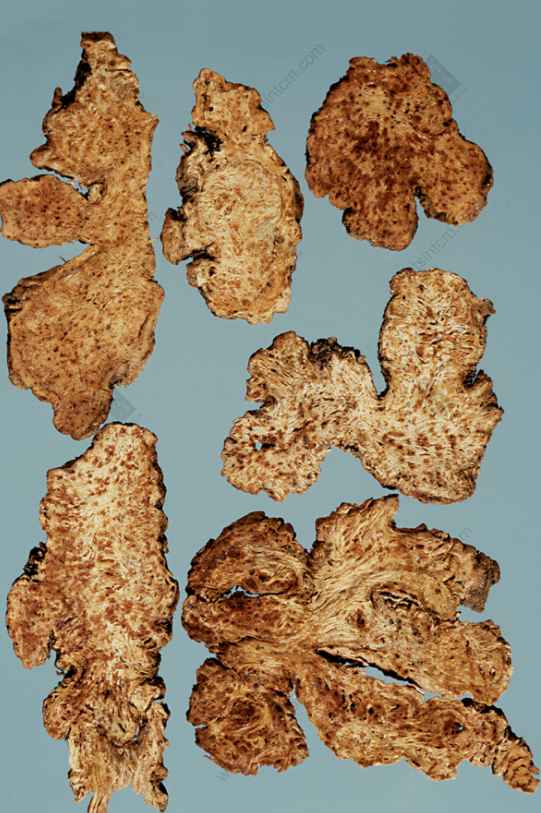 Rice Water Processed Atractylodes Rhizome Slice
Rice Water Processed Atractylodes Rhizome Slice
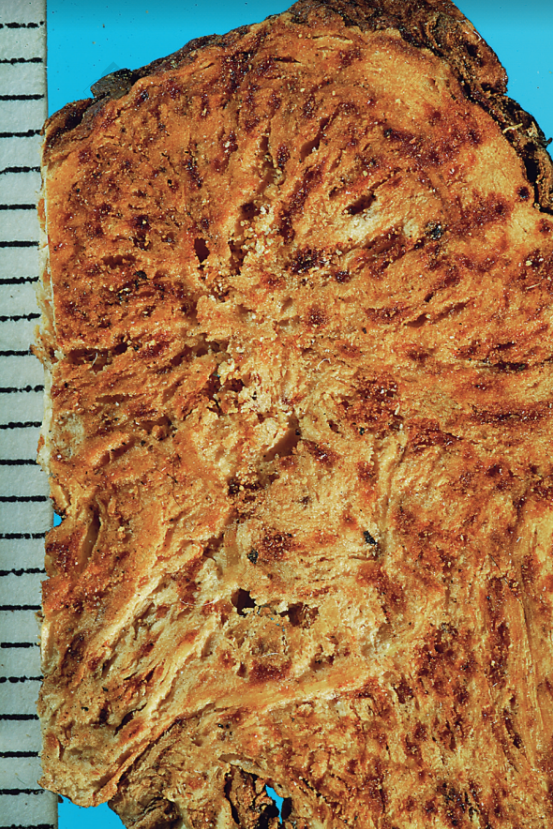 Atractylodes Rhizome (<a href='https://whatsintcm.com/dt_articles/硃砂/’>Cinnabar dots)
Atractylodes Rhizome (<a href='https://whatsintcm.com/dt_articles/硃砂/’>Cinnabar dots)
【Naming】
【Source】
Shen Nong’s Herbal Classic – Superior Grade
【Common Usage Level】
A
【Botanical Origin】
The above-ground rhizome of Atractylodes lancea (Thunb.) DC., or Atractylodes chinensis (DC.) Koidz., or Atractylodes japonica Koidz. ex Kitam., all belonging to the Compositae family. The former is commercially known as Southern Atractylodes Rhizome (茅朮, Maoshu), while the latter is known as Northern Atractylodes Rhizome.
【Characteristics】
(1) Southern Atractylodes Rhizome: Presents as a nearly cylindrical shape, beaded, segmented, curved and constricted, 3-10 cm long and 1-1.5 cm in diameter. The surface is grayish-brown, with longitudinal wrinkles, transverse curved lines, and residual short, thin roots. Root scars and remnants of stems are visible. It is firm and solid. The fracture surface is flat, yellowish-white, with obvious reddish-brown oil glands scattered throughout (commonly known as <a href='https://whatsintcm.com/dt_articles/硃砂/’>Cinnabar dots). After the fracture surface is exposed for a while, fine needle-shaped crystals resembling white mold may precipitate. It has an aromatic odor and a slightly sweet and bitter taste. This includes Maoshan Atractylodes Rhizome and Han Atractylodes Rhizome.
(2) Northern Atractylodes Rhizome: Presents as a nearly cylindrical shape, often branched or in knobby clumps or segmented, relatively short and thick, irregularly curved, 4-10 cm long and 1-4 cm in diameter. The cork layer is mostly removed, and it is yellowish-brown in color. Many circular stem bases or stem scars are visible, or hairy buds may be attached. There are traces of small roots falling off or short small roots attached at the bottom. The surface is brownish-yellow and rough. It is light in weight, relatively loose in texture, and easily broken, with a very uneven fibrous fracture surface. The fracture surface is yellowish-white, with scattered reddish-yellow or yellow oil glands and obvious wood fiber bundles. It has an aromatic odor, a weaker fragrance, and a slightly bitter taste. Compared with Southern Atractylodes Rhizome, this species is lighter and looser in texture, has fewer oil glands, does not precipitate white mold-like crystals on the cut surface, and has a weaker fragrance. The quality is second to Southern Atractylodes Rhizome. Most of the products produced in various parts of Hebei are collected and distributed in Tianjin, hence the name “Tianjin Atractylodes Rhizome.”
(3) Guan Atractylodes Rhizome: Mostly presents as a nodular cylindrical shape, relatively long, 4-12 cm long and 1-2.5 cm in diameter. The surface is dark brown, relatively smooth, and the texture is relatively light. The fracture surface is uneven, the interior is light yellow, fibrous, with a unique odor and a pungent, slightly bitter taste.
Prepared slices: Raw Atractylodes Rhizome: The surface is grayish-brown or dark brown, with wrinkles and transverse curved lines. The cut surface is yellowish-white or grayish-white, with obvious oil dots (<a href='https://whatsintcm.com/dt_articles/硃砂/’>Cinnabar dots). It has a strong and unique aroma and a slightly bitter and sweet taste. Processed Atractylodes Rhizome: The outer surface is charred black, the cut surface is yellowish-brown, the center shows oil dots, and it has a fragrant aroma.
【Processing】
1. Raw Atractylodes Rhizome 2. Processed Atractylodes Rhizome
【Identification】
《Zhenglei Bencao》: “The ones with large pieces and purple flowers are superior.” 《Puji Fang》: “Atractylodes Rhizome soaked in rice water to remove the skin, from Maoshan, is the best.” 《Bencao Beiyao》: “From Maoshan, firm, small, and with <a href='https://whatsintcm.com/dt_articles/硃砂/’>Cinnabar dots is good.” 《Benjing Fengyuan》: “Bitter, pungent, warm, non-toxic. The ones produced in Maoshan have a sweet taste, are thin, and have many hairs, which are the best.” 《Liang Lie Jianbie》: “The cross-section is yellowish-white, with reddish-brown oil dots everywhere, the odor is bitter, pungent, and strongly aromatic, fat and heavy, with much oil, is called Gu Cang, the top grade.”
It is best to have large pieces, shaped like beads, with few hairs, a yellow-black outer skin, a firm texture, obvious <a href='https://whatsintcm.com/dt_articles/硃砂/’>Cinnabar dots, sufficient oil content, a sweet and fragrant odor, and grow hair after being placed (white needle crystals precipitate like mold). It has a unique and strong aroma, with a sweet, pungent, and slightly bitter taste. The ones with wrinkled skin, hair, a loose texture, few <a href='https://whatsintcm.com/dt_articles/硃砂/’>Cinnabar dots, no oiliness, a bland taste, and a turbid odor are second best.
【Identification Terminology】
1. White Hair: Refers to the fine needle-like crystals that can precipitate from Atractylodes Rhizome after it is broken and left to stand (a mixture of Atractylodes alcohol and β-eucalyptol). It is generally believed that Atractylodes Rhizome that grows “white hair” is of good quality.
2. Cinnabar Dots: Refers to the scattered brown or yellow-orange oil dots (i.e., oil cells) visible on the flat cross-section of the medicinal material, such as in Atractylodes Rhizome, Notopterygium Root, Aucklandia Root, etc.
3. Frosting (Frost, Oozing Fat): Generally, white substances gradually precipitate on the surface of medicinal materials due to internal drying. For example, when Southern Atractylodes Rhizome is broken, white hair-like crystals precipitate on the fracture surface after a while. White crystals precipitate after drying Moutan Bark, Magnolia Bark, Dictamnus Root Bark, Cynanchum paniculatum, Asparagus Root, and Cynomorium Songaricum. This can also be called frosting.
【Chapter】
Rhizomes

