Bupleurum Root (Chai Hu)
<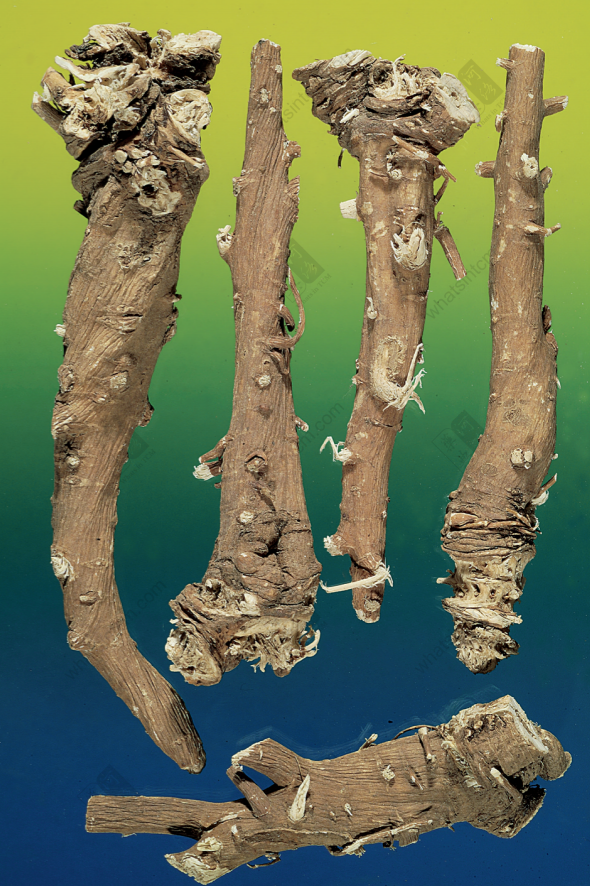

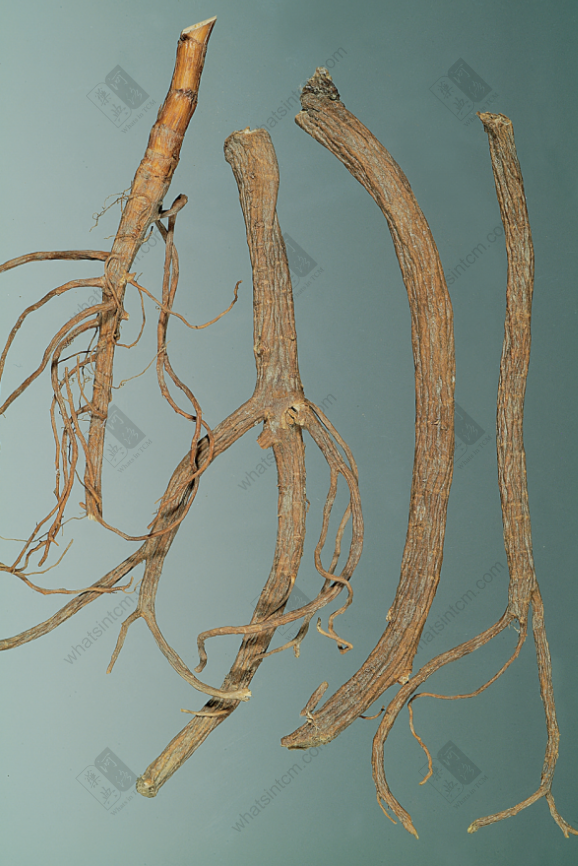
Top-Grade Northern Bupleurum Root (Hard and tough)

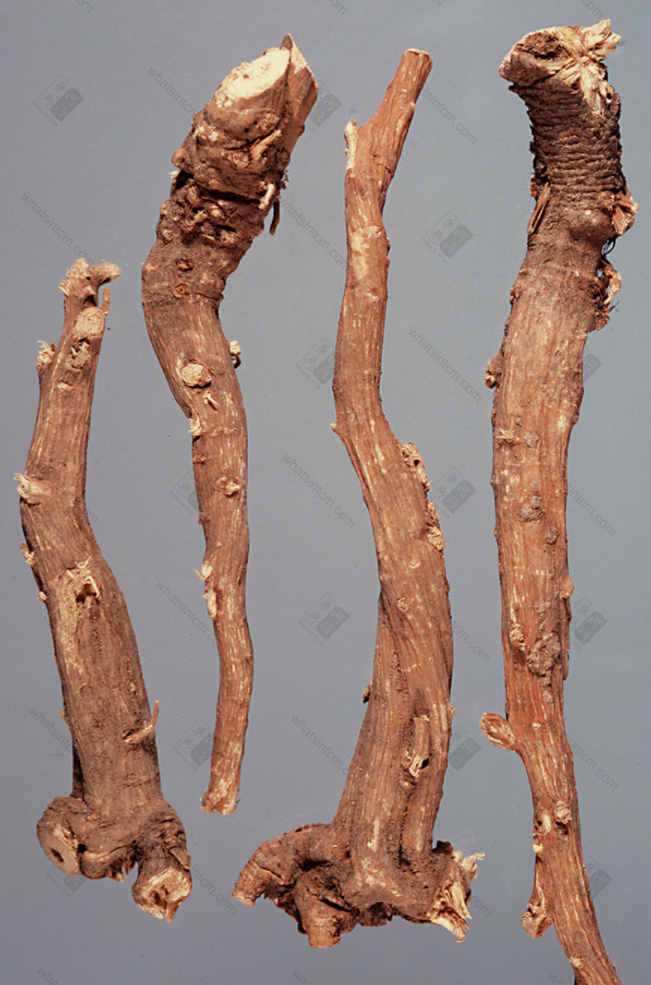
Northern Bupleurum Root (Left: 1st Grade, Right: 2nd Grade)
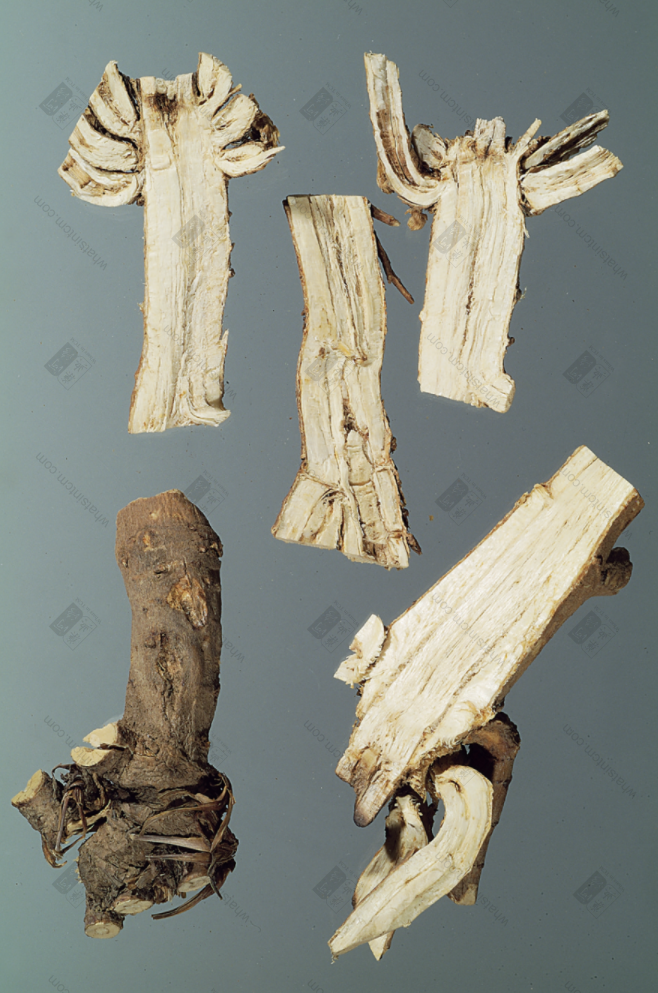

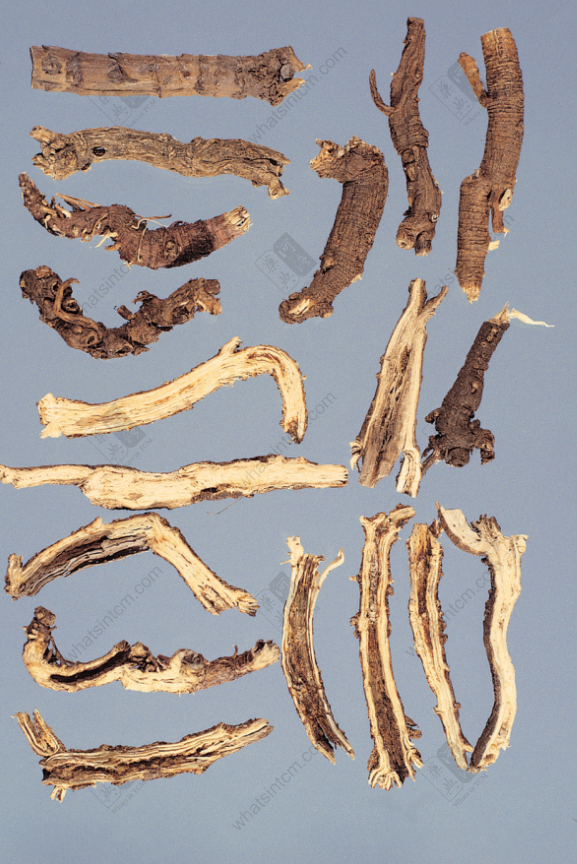
Top-Grade Northern Bupleurum Root Slices
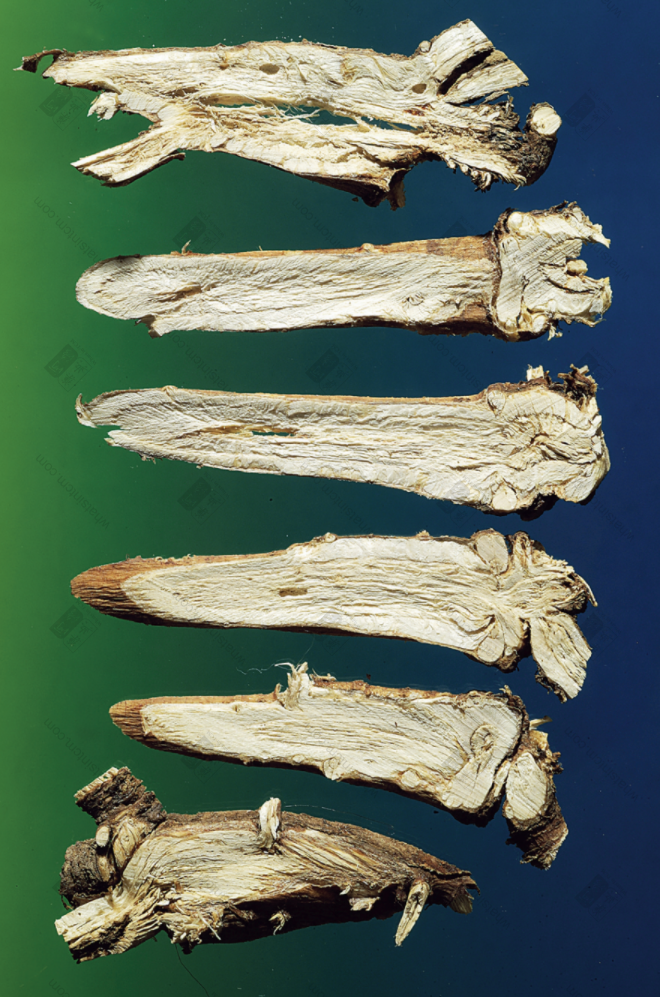
Top-Grade Northern Bupleurum Root Slices
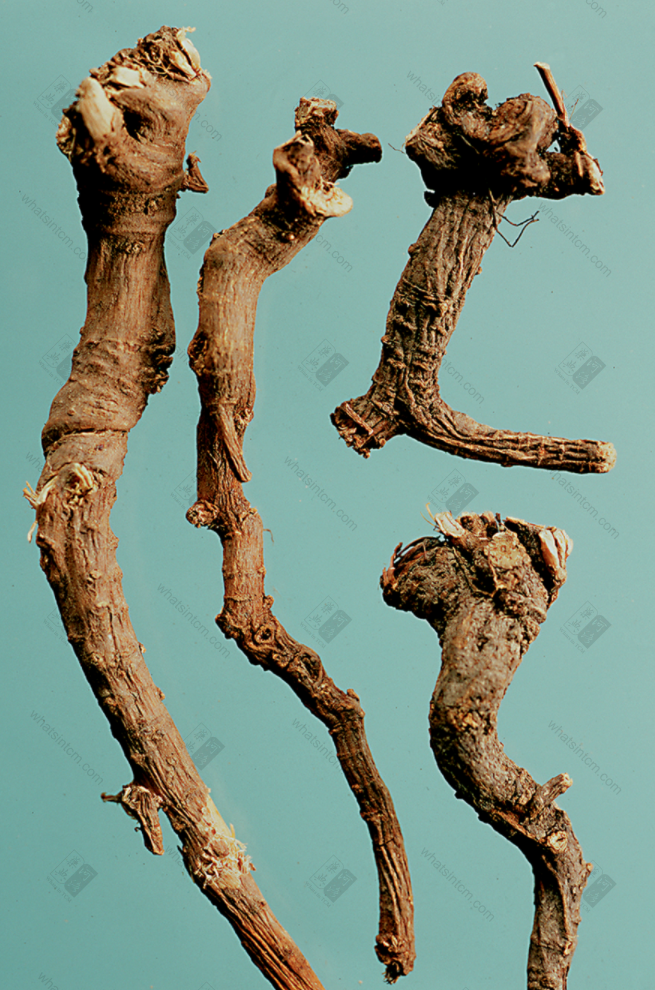

Northern Bupleurum Root
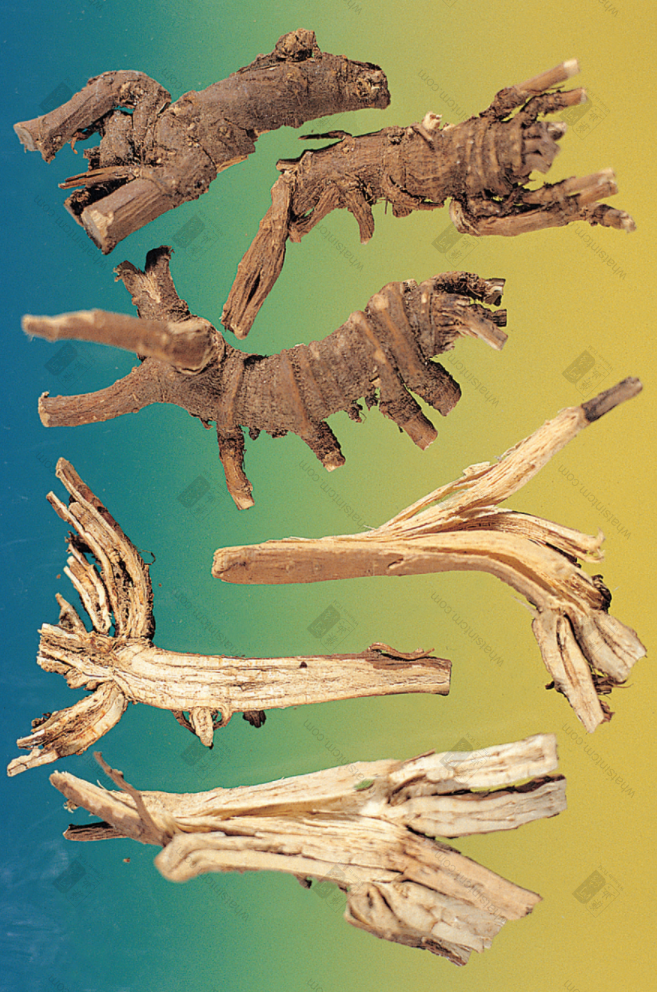

Northern Bupleurum Root Slices (Chicken meat floss)

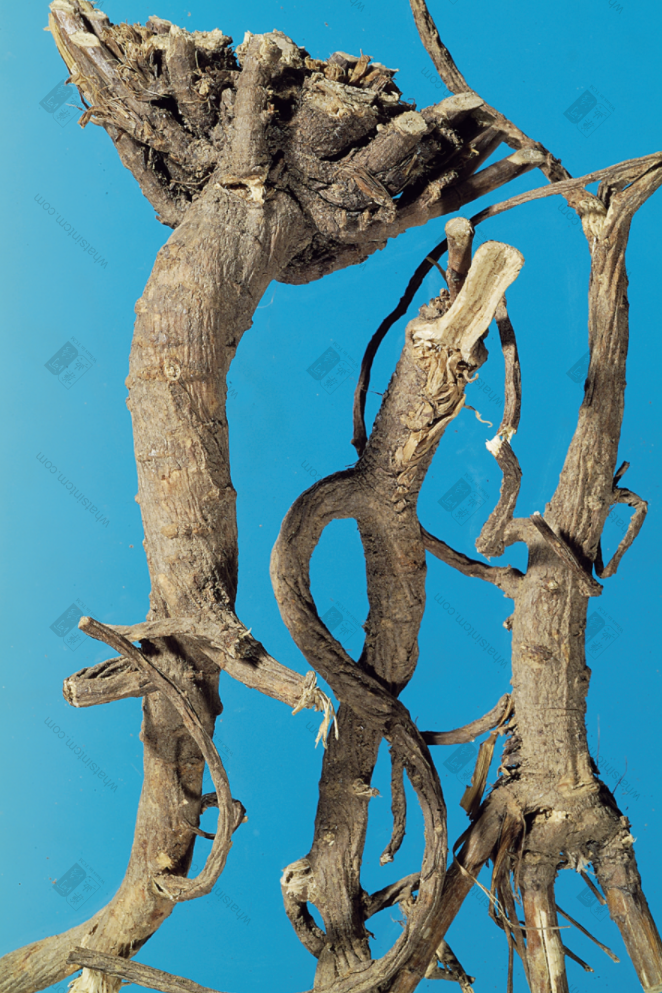
Wild Bupleurum Root
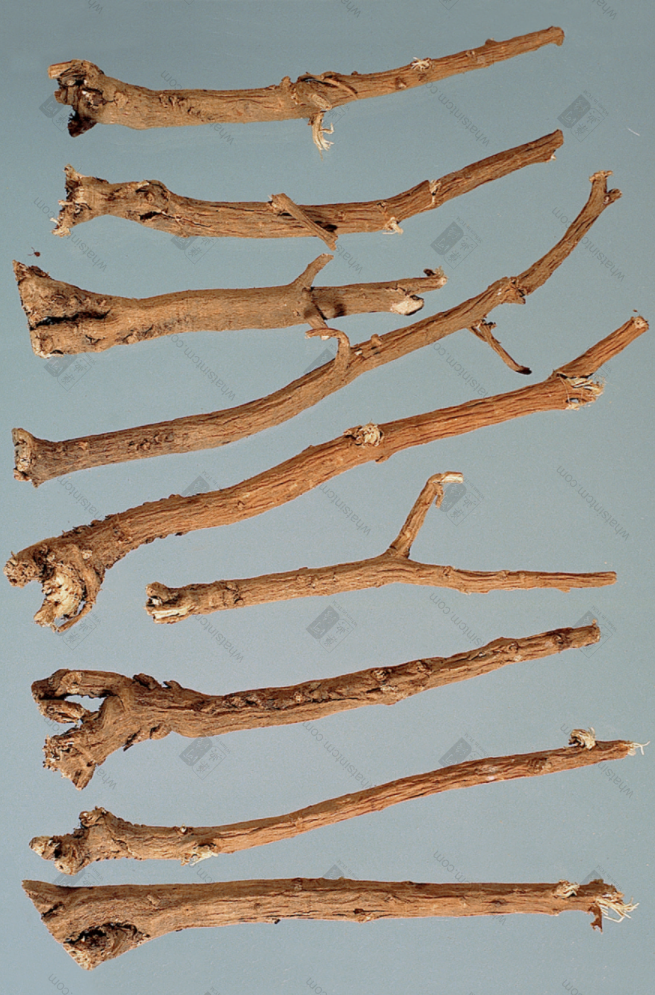

Jin Bupleurum Root (Root head coarse and forked)
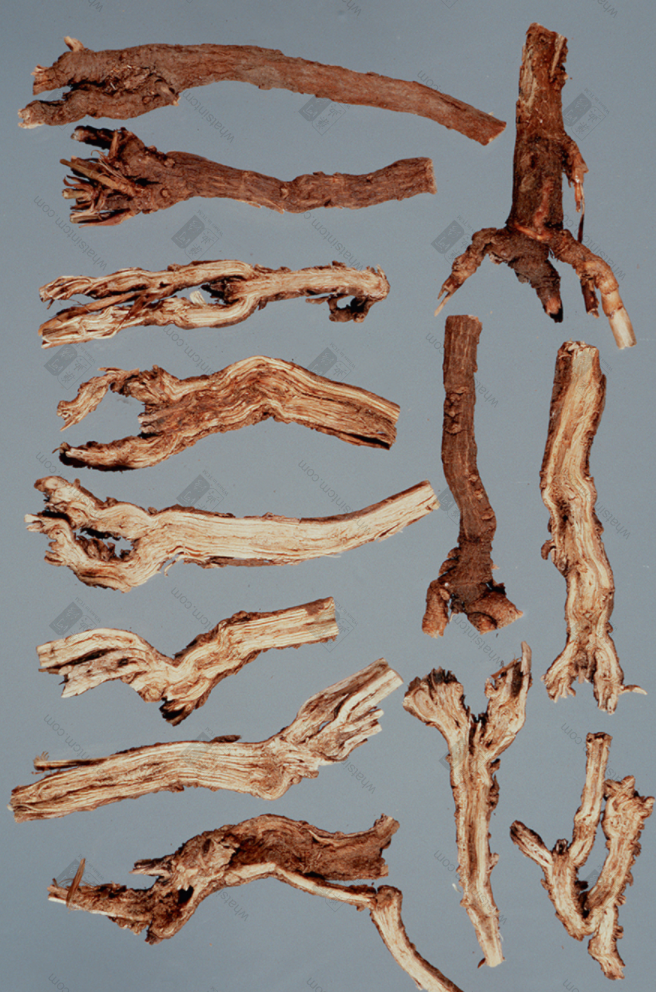
Jin Bupleurum Root Slices
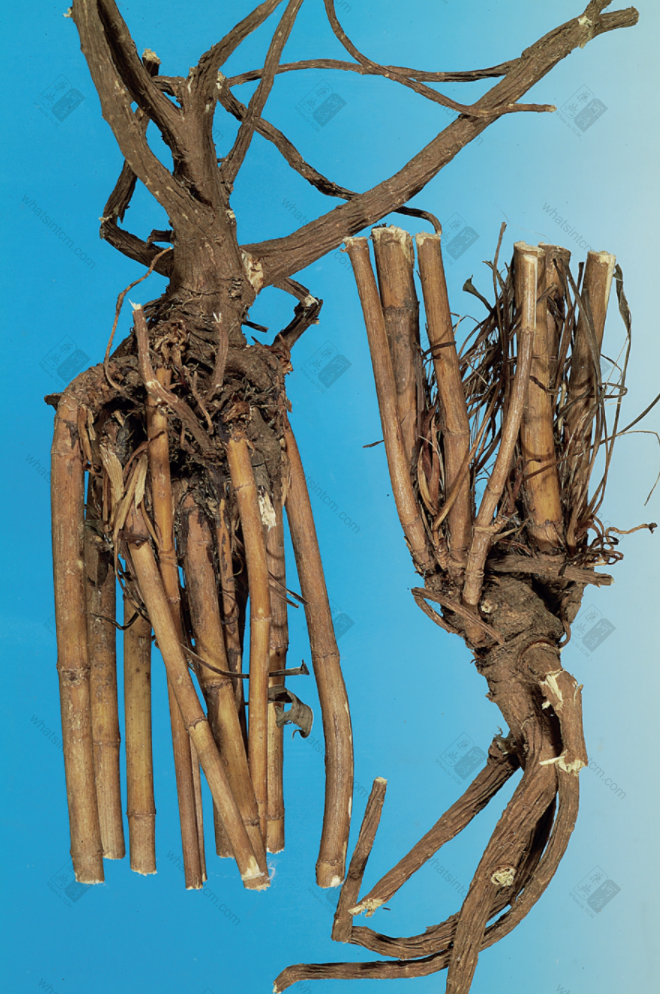

Hubei Bupleurum Root (Non-medicinal part exceeds 10%)
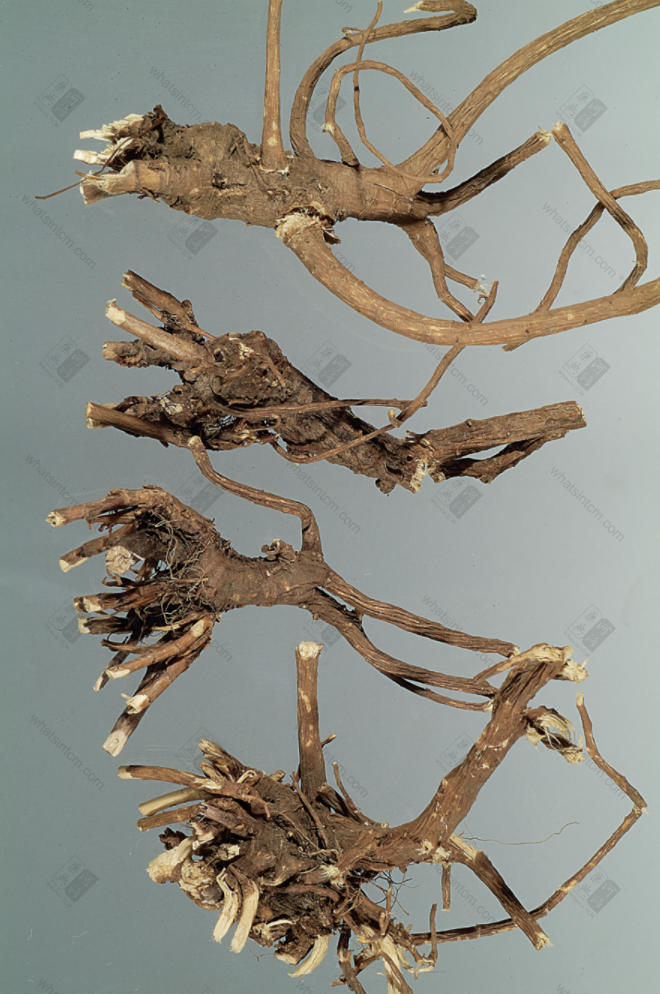

Hubei Bupleurum Root
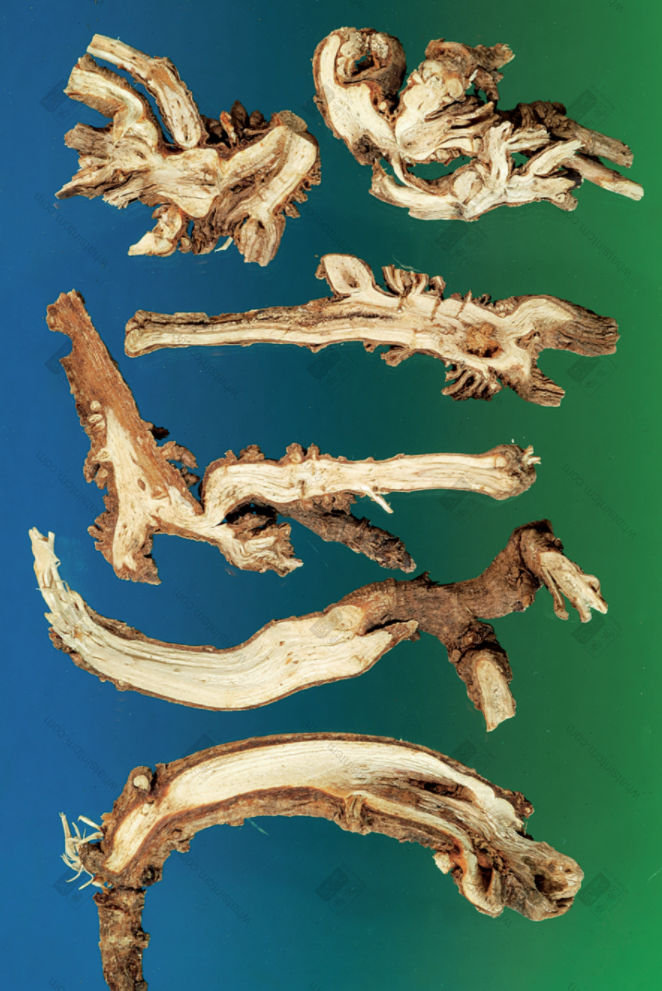
Hubei Bupleurum Root Slices
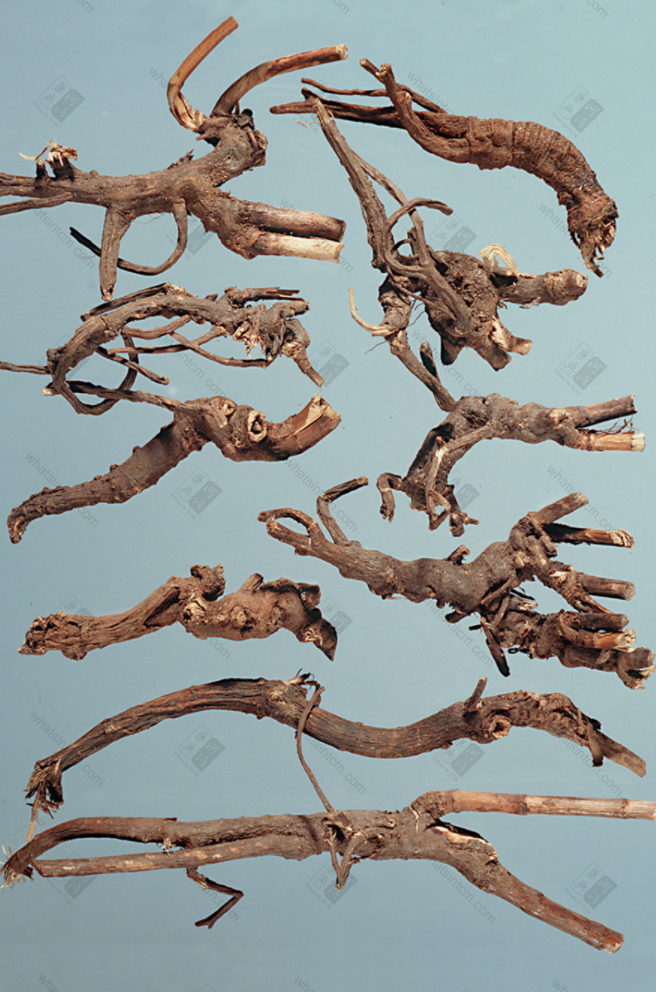

Hankou Bupleurum Root
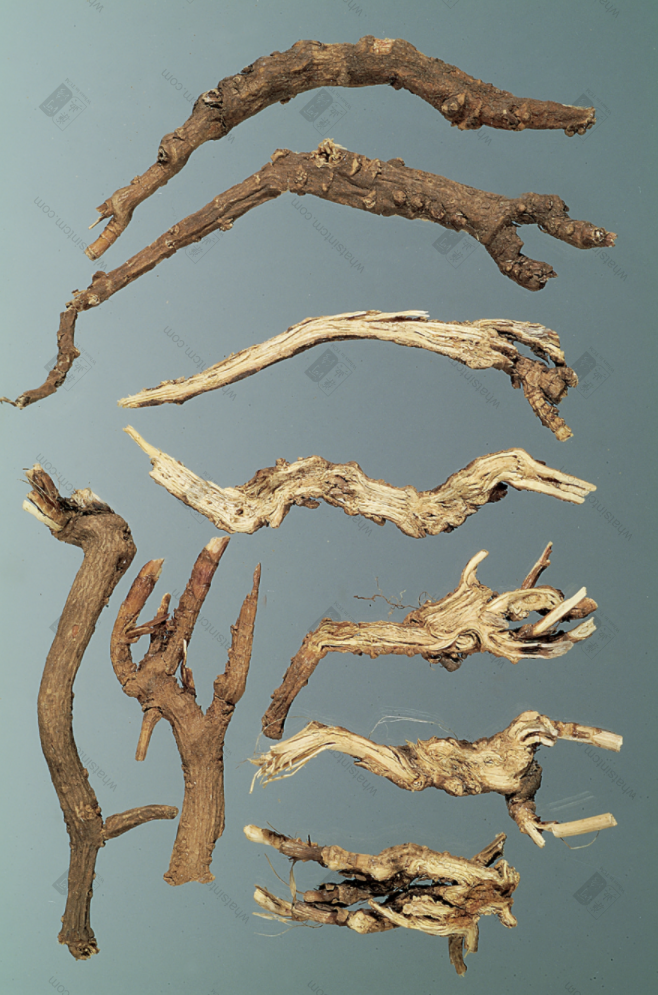

Hankou Bupleurum Root Slices
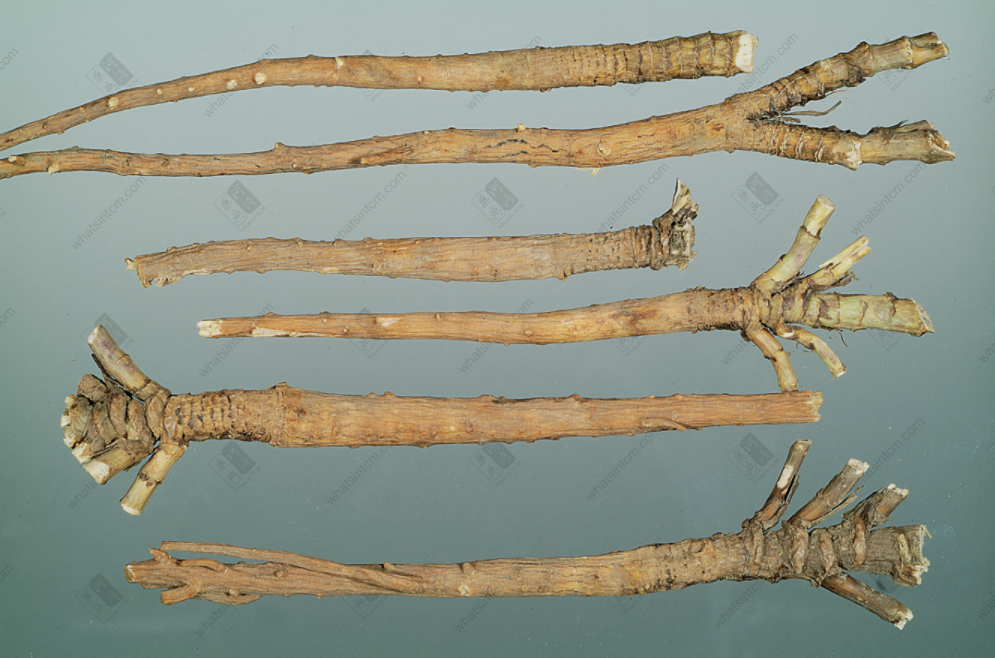

Cultivated Bupleurum Root
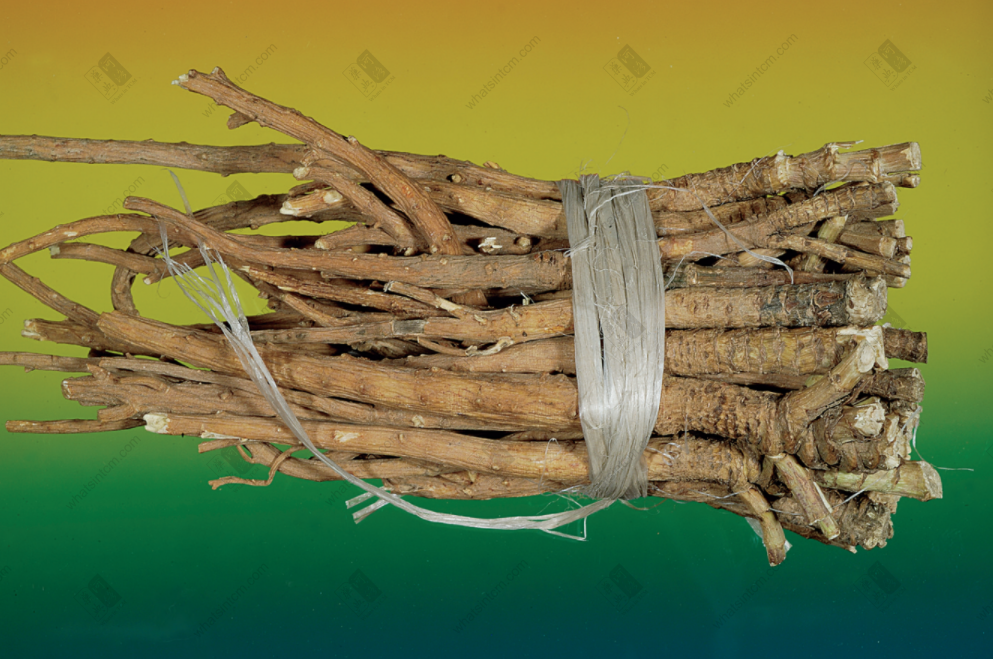

Cultivated Bupleurum Root
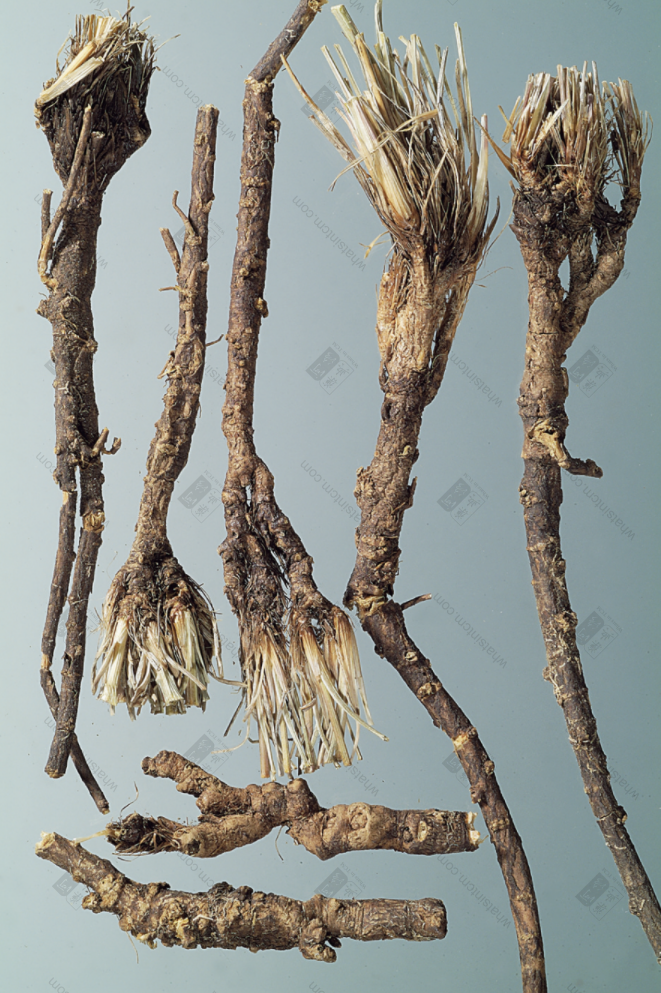

Southern Bupleurum Root (Broom head)
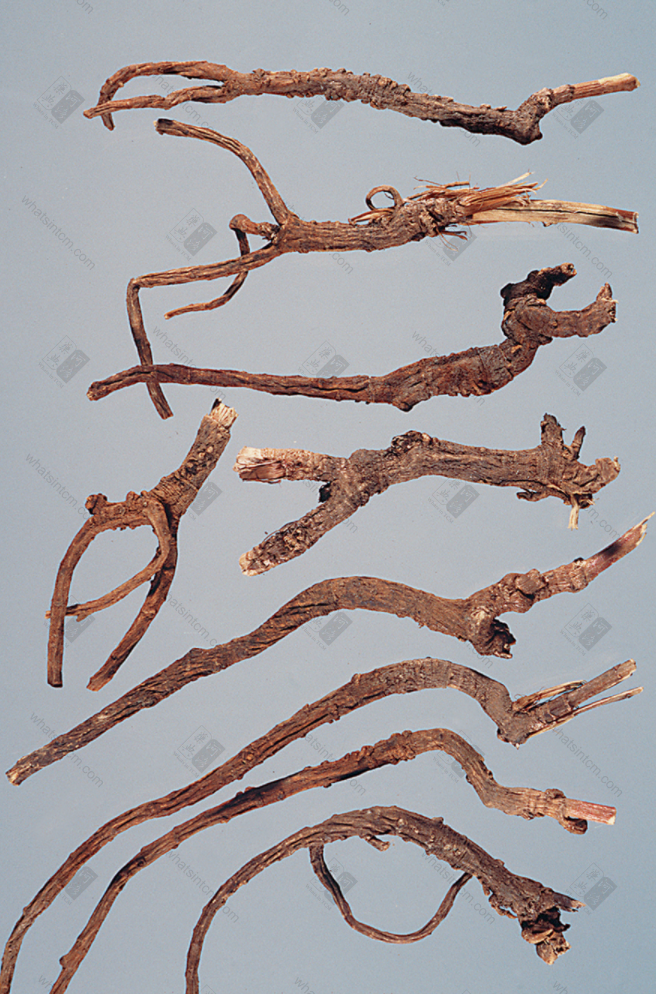

Southern Bupleurum Root
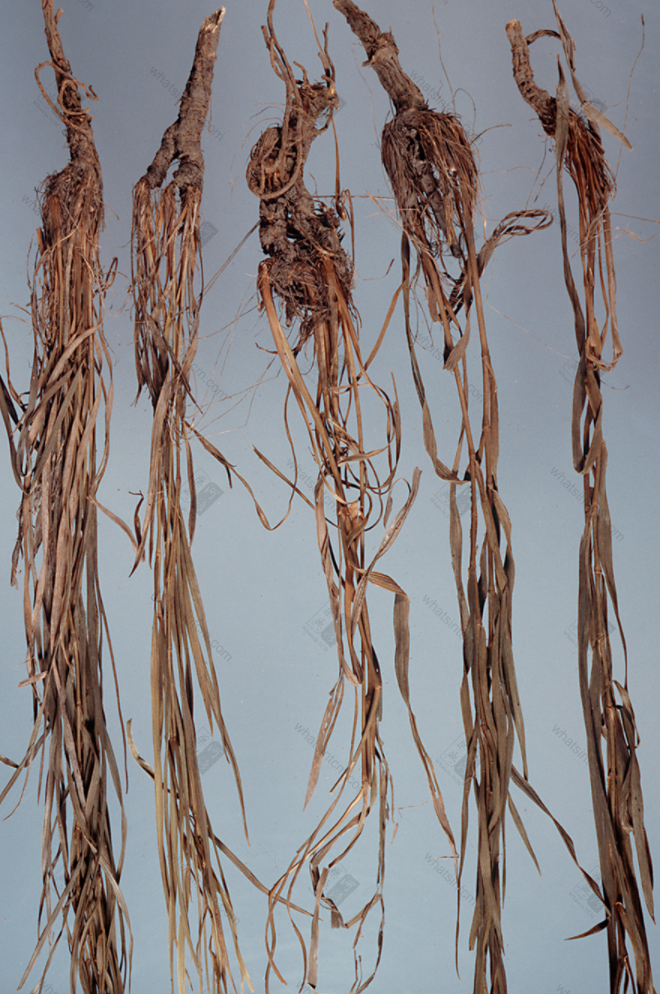

Bamboo Bupleurum Root (1980s)
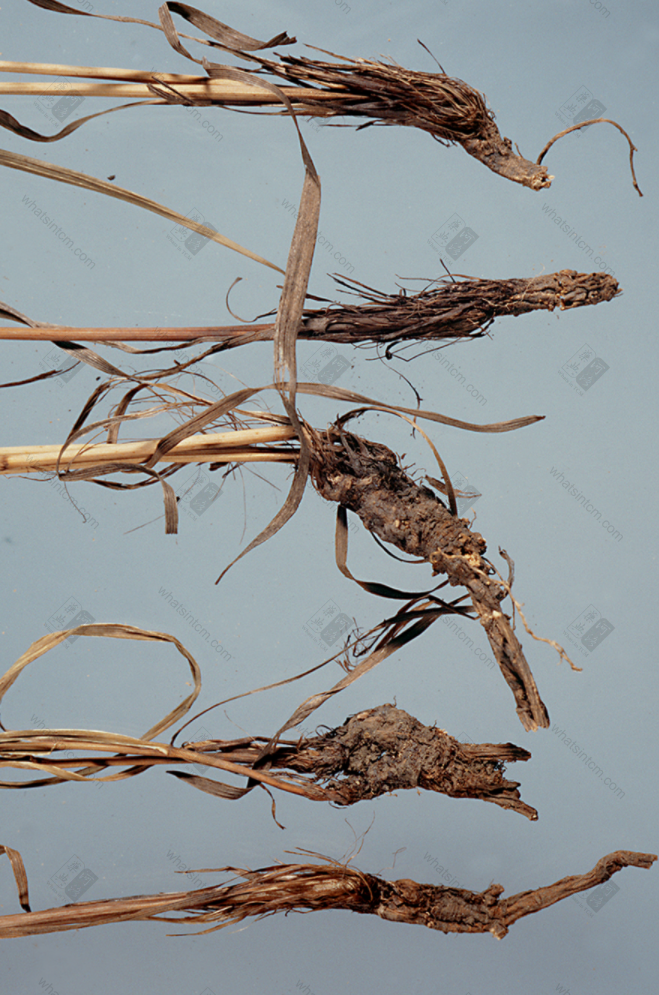

Red Bupleurum Root (Spring bud Bupleurum Root, 1980s)
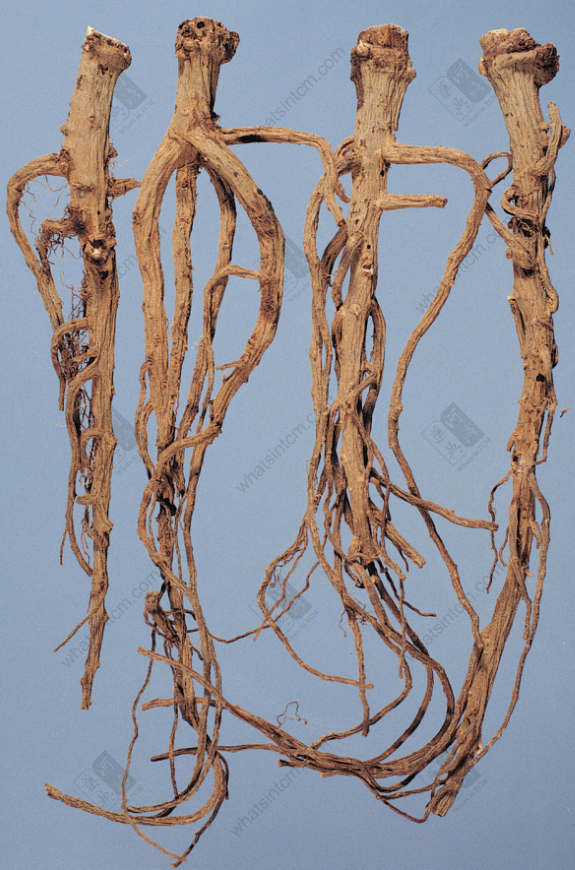

Mishima Bupleurum Root (Cultivated in Taiwan, 1985)
Gao’s Bupleurum Root (Cultivated in Taiwan)
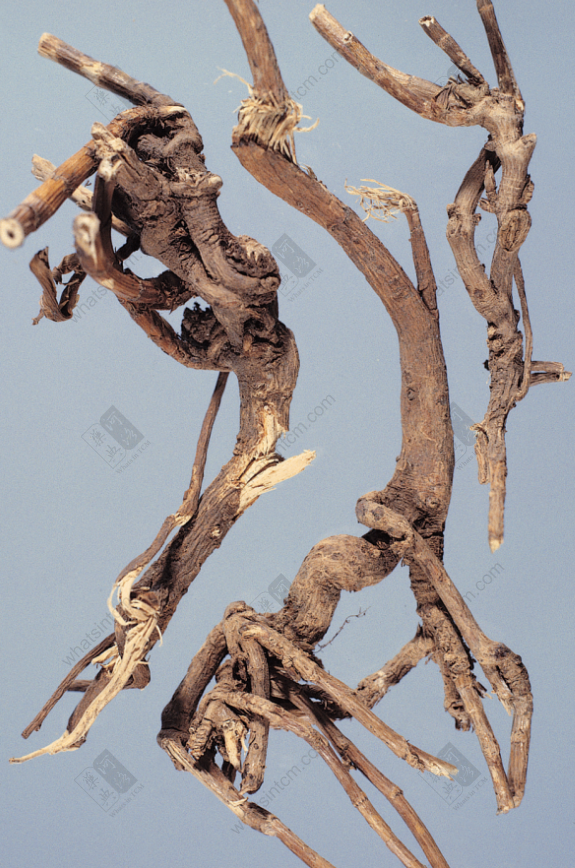

Fake Bupleurum Root
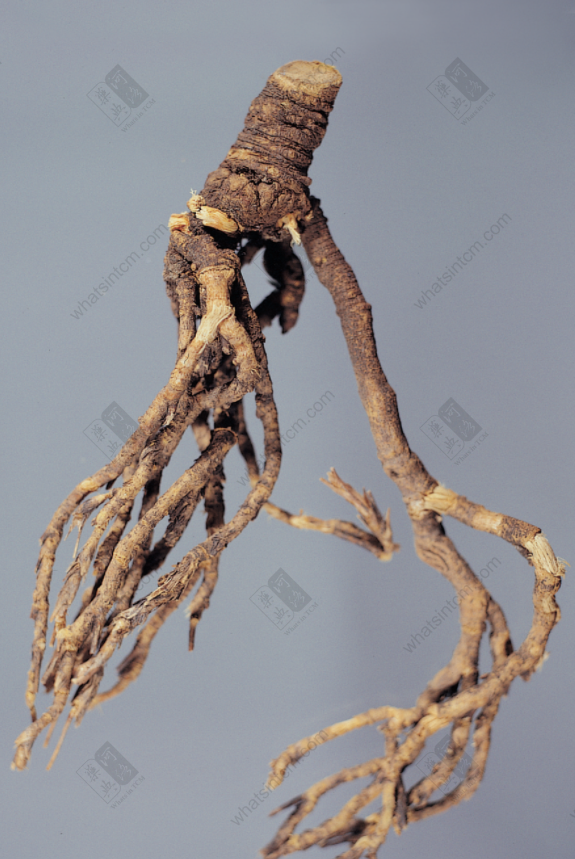

Fake Bupleurum Root
Fake Bupleurum Root Slices
【Naming】
【Source】
Shen Nong’s Classic of Materia Medica, Superior Class
【Common Usage Level】
A
【Botanical Origin】
The roots of various plants of the genus Bupleurum in the Umbelliferae family, mainly Bupleurum marginatum Wall. ex DC., Bupleurum chinense DC., and Buplurum scorzonerae-folium Willd.
【Characteristics】
(1) Northern Bupleurum Root: Also known as Hard Bupleurum Root. Hankou Bupleurum Root is the root of Bupleurum marginatum, and Jin Bupleurum Root is the root of Bupleurum chinense.
Hankou Bupleurum Root: The root is cylindrical or conical, with 3-6 hard, young-branch-like short stems remaining at the top (mostly residual stems), or with a small amount of stem base (leaf base present). The main root is straight or slightly curved, with branches in the lower part. The root head is enlarged and knotted, 6-20cm long and 0.6-1.5cm in diameter. Cultivated ones can reach 1-1.2cm. There are often 2-4 branch roots. The outer skin is grayish-brown or grayish-brown, while cultivated ones are mostly light yellowish-brown. The skin texture is fine and smooth, with few lenticels, and has longitudinal wrinkles and branch root scars. The texture is very hard, hard fibrous, almost lignified, light and tough, and not easy to break. The cross-section is woody and fibrous, the cortex is thin, brownish-yellow, and the xylem occupies most of the area, yellowish-white. It has a slightly fragrant odor and a slightly bitter taste.
Jin Bupleurum Root: The main root is conical, a few are cylindrical, 3-8cm long and 0.4-1cm in diameter, with 3-8 branches. The root head is thicker and forked, with multiple short stem bases remaining at the upper end. The stem base is surrounded by more fibrous leaf sheath remnants. The surface is yellowish-brown to brownish-brown, with obvious longitudinal wrinkles such as raised lenticels. The body is slightly light, the texture is slightly hard, but it is looser and softer than Northern Bupleurum Root. The cross-section is brownish-yellow, with an obvious rancid oil odor and a slightly bitter and pungent taste.
Sliced form: The outer skin is grayish-brown or grayish-brown, with longitudinal wrinkles and branch root scars. The cut surface is woody and fibrous, yellowish-white, and the xylem occupies most of the area. Rays are clearly visible, and there are slight cracks near the cambium. It has a slight aroma and a slightly bitter and pungent taste.
(2) Southern Bupleurum Root, also known as Soft Bupleurum Root or Fragrant Bupleurum Root, is the root of Bupleurum scorzoneraefolium. The root is thinner, mostly single-branched, with fewer branches, mostly curved and not straight, 4-10cm long and 0.3-0.5cm in diameter. The upper end is slightly larger, with no knotted head. There are residual brownish fibrous leaf sheaths, or hair-like fibers left after the stems and leaves have withered. The lower end is smooth and thin. The surface is reddish-brown or brownish-brown. There are obvious ring patterns near the root, and the whole body has longitudinal wrinkles and fibrous root scars and obvious lenticels. The texture is slightly soft, fleshy, and easy to break. The cross-section is flat, light brown, unclear fibrous, with a slight aroma, rancid oil odor, and a slightly bitter and pungent taste.
Bamboo Leaf Bupleurum Root: The root is mostly fusiform, with obvious nodes at the base of the rhizome, green stems and leaves, clear fragrance, and a light taste.
Sliced form: The outer skin is reddish-brown, the cut surface is flat, light yellow, with a flower heart remaining. High-quality Northern Bupleurum Root twists like chicken meat floss, has a slight aroma, and a bitter and pungent taste. After being processed (炙), the color becomes darker.
Poisonous Large Leaf Bupleurum Root: The roots and rhizomes are cylindrical, often with 3-5cm long residual stems at the top, and a few fibrous roots growing at the lower end. The surface is yellowish-brown or grayish-brown, rough and wrinkled, with nodes and internodes, especially obvious near the reed stem. The texture is hard, the center of the cross-section is hollow, and some can see cambium layers and pith. The odor is unique and the taste is slightly bitter.
【Processing】
1. Soft Bupleurum Root 2. Hard Bupleurum Root 3. Vinegar-Bupleurum Root 4. Honey-fried Bupleurum Root 5. Stir-fried Bupleurum Root
【Identification】
Zheng Lei Ben Cao: “The one with a single nest and long root is good.” Ben Cao Yan Yi Bu Yi: “Bupleurum Root grown in Yinzhou is the best.” Ben Cao Pin Hui Jing Yao: “The root that is soft is good,” “The one with a strong reed head, red hairs like a rat’s tail, a single nest, and long root is excellent,” “The ones from Yinzhou, Shouzhou, and Lanzhou are the best.” Ben Cao Gang Mu: “[Ji said] Northern Bupleurum Root is used for dispersing, and Haiyang Soft Bupleurum Root is good for deficiency heat,” “The bamboo leaf one is the best,” “The root resembles a reed head, with red hairs like a rat’s tail, a single nest, and long root is good.” Ben Cao Bei Yao: “The northern one is like Qian Hu but soft and good, the southern one is hard and cannot be used.” Yao Xing Qie Yong: “The dry and long, slightly white one is good.” Liang Lie Jian Bie: “The one with a light brownish color inside and a bitter taste with a slight good aroma is excellent.”
1. Northern Bupleurum Root is best with thick and long roots, neat, fine skin, few branch roots, and no residual stems or fibrous roots. Hankou Bupleurum Root is best with a hard texture and a smooth body, and Jin Bupleurum Root is best with a hard and tough texture, slightly soft, and a strong rancid oil odor. High-quality slices twist into a chicken meat floss shape.
2. Southern Bupleurum Root is best with a single branch, thick and long roots, no fibrous roots, a soft and fleshy texture, and a strong rancid oil odor.
【Identification Terms】
1. Miao (苗): Generally refers to the above-ground stem part of root or rhizome medicinal materials, also known as “lu miao” (蘆苗). For example, Bupleurum Root is called Hard Miao Bupleurum Root and Soft Miao Bupleurum Root.
2. Sao Zhou Tou (掃帚頭): Refers to the fibrous hair-like material at the top of root and rhizome medicinal materials, shaped like a broom. Such as Southern Bupleurum Root.
3. Ji Rou Si (雞肉絲): High-quality Northern Bupleurum slices twist into a chicken meat floss shape.
Comparison of the characteristics of four types of Bupleurum Root
Name
Item Northern Bupleurum Root Southern Bupleurum Root Small Leaf Black Bupleurum Root Large Leaf Bupleurum Root
Source Dried root of Bupleurum chinense DC Dried root of Bupleurum scorzonrifolitum Wild Dried root of Bupleurum smithii Wolffvar.parvifolia Shanetn Y Li Dried root of Bupleurum longiratum Turcz
Root Head Conical, often with several stem bases or short fibrous leaf bases remaining at the top Not enlarged, long conical, mostly single root, few branches, often single head, with many brown fibrous leaf bases at the top called brown head Not enlarged, often single head, with black-brown leaf bases or fibers at the top Not enlarged, with 1-2 stem bases at the top, stem large and hollow, thicker than genuine Bupleurum Root
Main Root Cylindrical or long conical, many branches Conical, small, slightly curved, few branches Long conical, with branches in the lower part Root and rhizome cylindrical, with branches, internodes obvious
Residual Stem Base 3~5 1~2 Several 1~3
Residual Leaf Base 3~15 Numerous fibrous None None or few
Surface Gray-black or gray-brown or earthy-brown, light brown, light brown, relatively smooth Reddish-brown, with ring patterns near the root head Gray-yellow, light black-brown, rough with transverse raised lenticels Yellow-brown, rhizome brown, rough, with ring patterns, rhizome with obvious segments, growing a few fine roots
Cross-section Light brown on the outside, yellow in the middle, hard, fibrous cross-section Light brown, oily spots in the middle, rougher, with wart-like raised lenticels, cross-section not fibrous, slightly flat Light brown, cortex and xylem easily separated, fibrous Yellow-white, hollow
Texture Hard, fibrous cross-section Soft Soft and brittle Tough
Odor Slightly fragrant, slightly bitter and pungent taste, no rancid oil odor Slightly bitter and pungent, with rancid oil odor Slightly fragrant, light taste, slightly bitter and pungent taste Slightly bitter, stronger pungent taste, with rancid oil odor, poisonous
【Category】
Roots
 >



