Yu Zhu (Solomon’s Seal Rhizome)
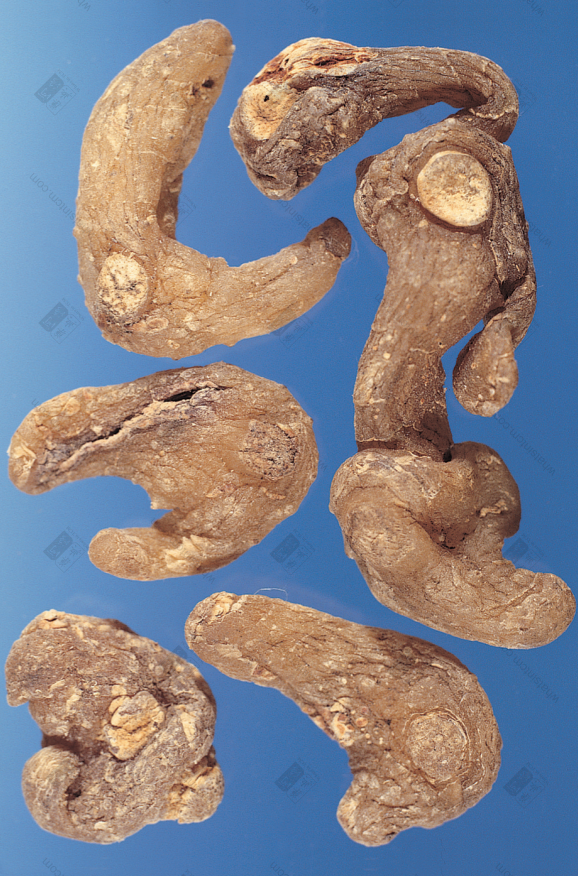 Jin Yu Zhu, first class (Long, cylindrical, flattened, yellowish-white, with wrinkled ridges and node marks)nn
Jin Yu Zhu, first class (Long, cylindrical, flattened, yellowish-white, with wrinkled ridges and node marks)nn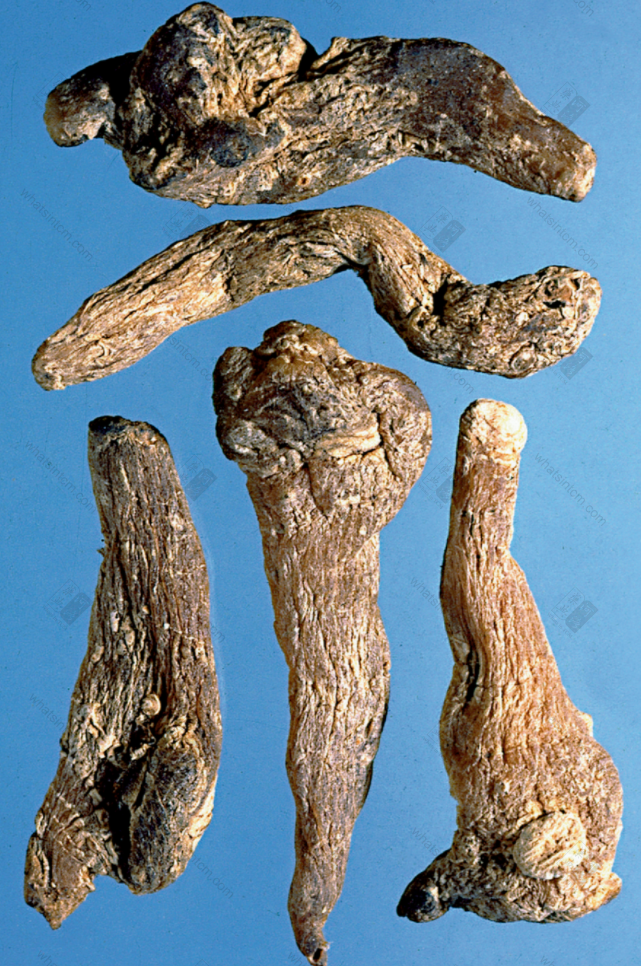 Jin Yu Zhu (Hard and brittle, softens when damp)nn
Jin Yu Zhu (Hard and brittle, softens when damp)nn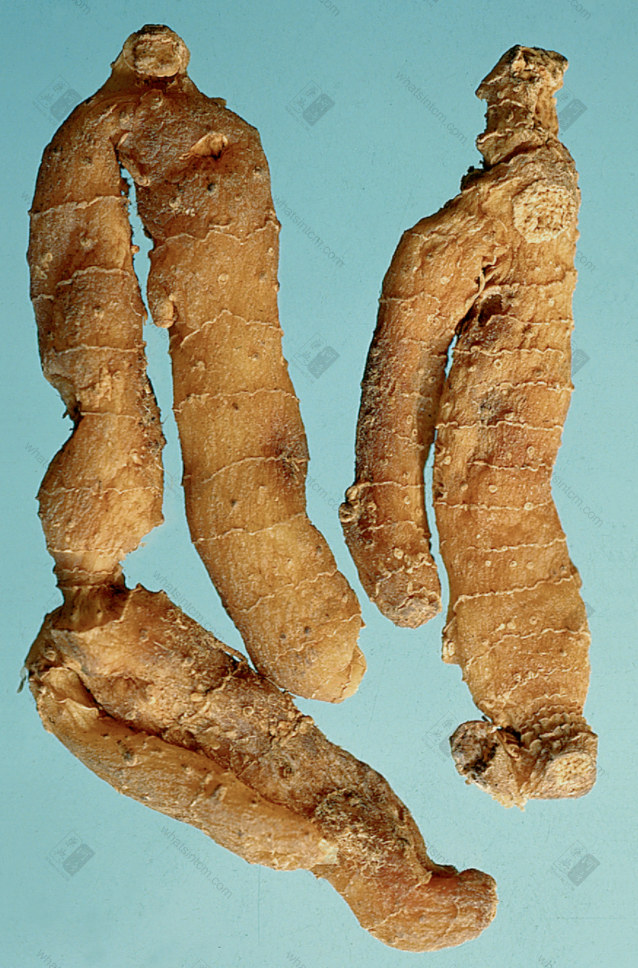 Guan Yu Zhu (Dalian Yu Zhu) (Transverse striations)(Clear nodes and internodes)nn
Guan Yu Zhu (Dalian Yu Zhu) (Transverse striations)(Clear nodes and internodes)nn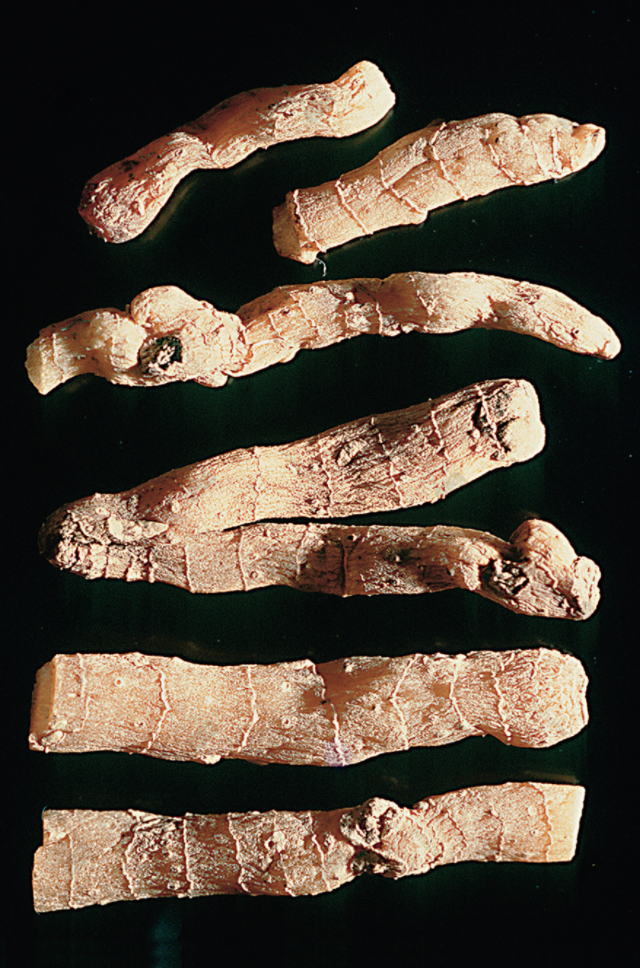 Yu Zhu (Western Yu Zhu)nn
Yu Zhu (Western Yu Zhu)nn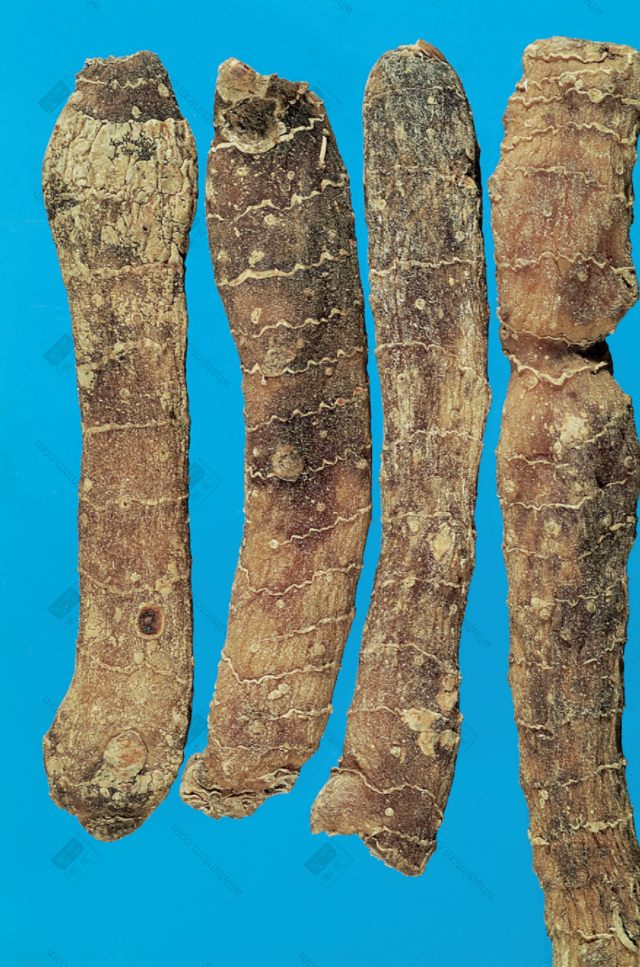 Substandard Yu Zhunn
Substandard Yu Zhunn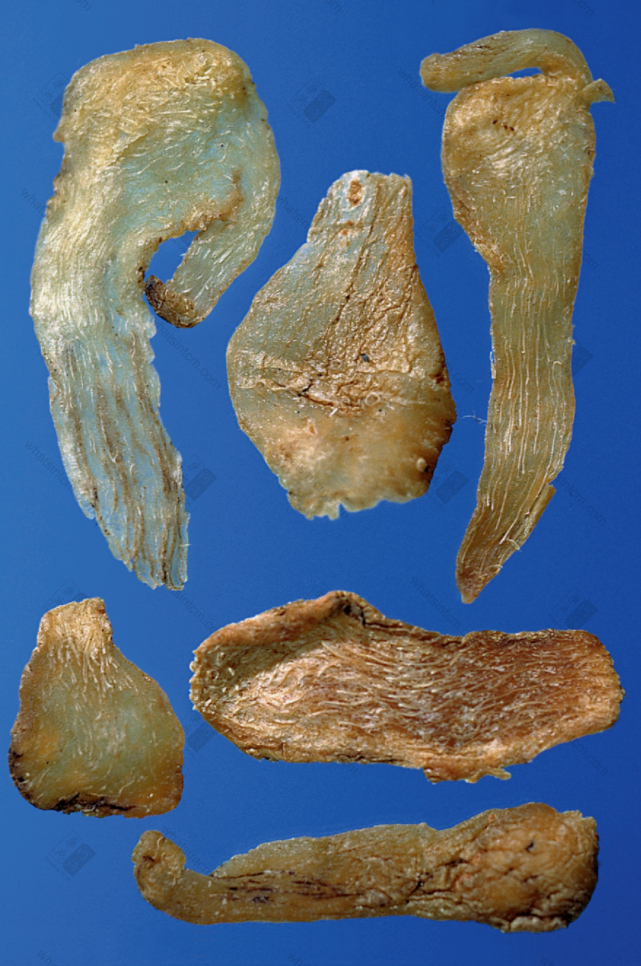 Jin Yu Zhu slices (Horny, translucent, soft, moist, and sticky)nn
Jin Yu Zhu slices (Horny, translucent, soft, moist, and sticky)nn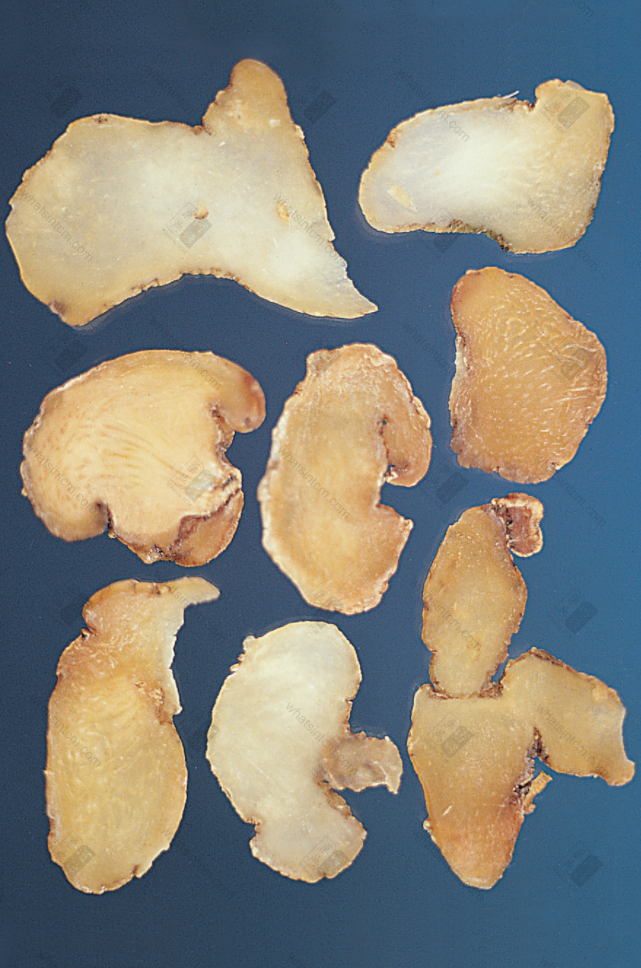 Jin Yu Zhu slicesnn
Jin Yu Zhu slicesnn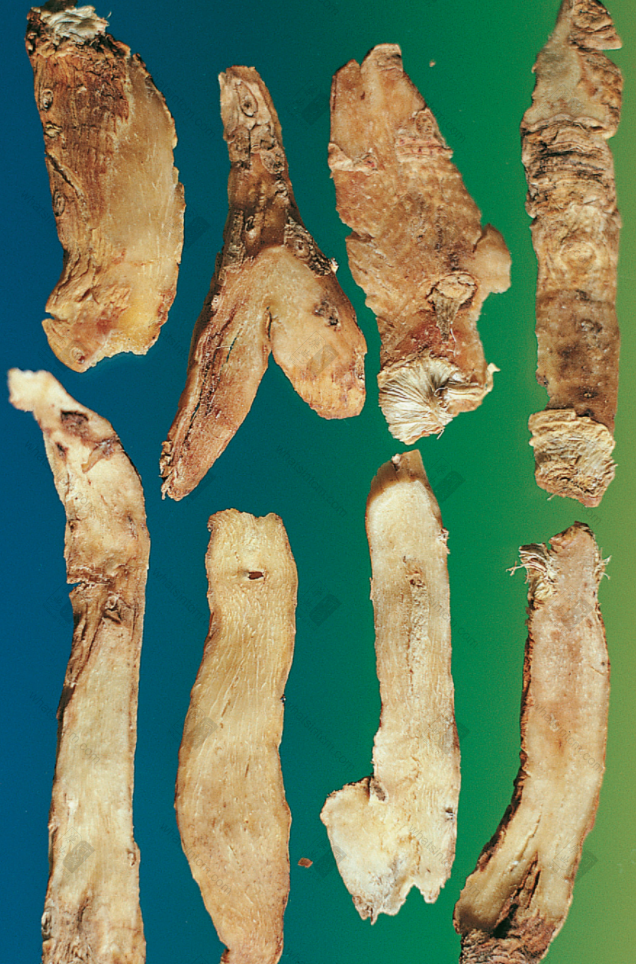 Hunan Yu Zhunn
Hunan Yu Zhunn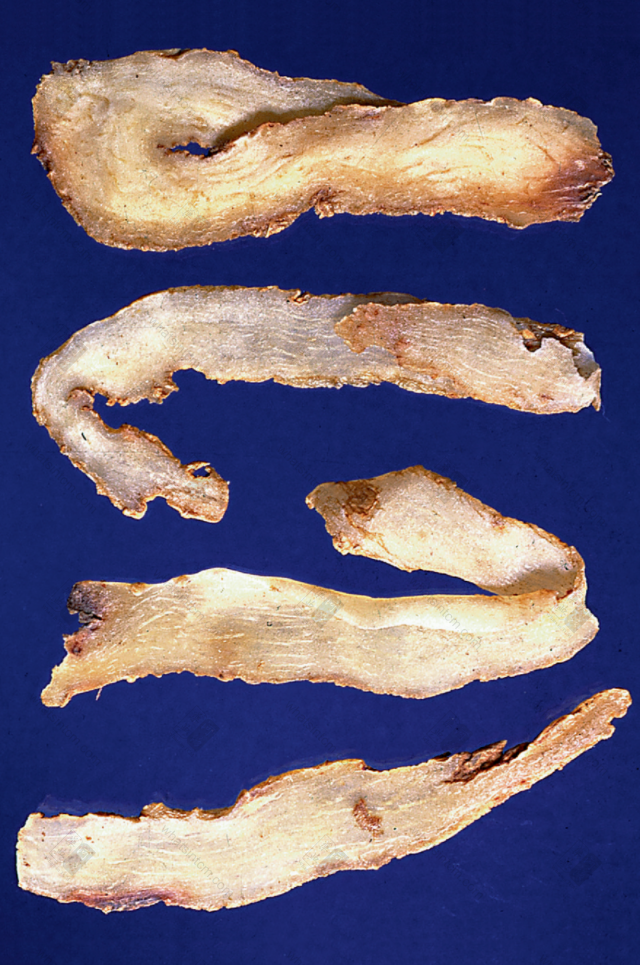 Long Guan Yu Zhu slicesnn
Long Guan Yu Zhu slicesnn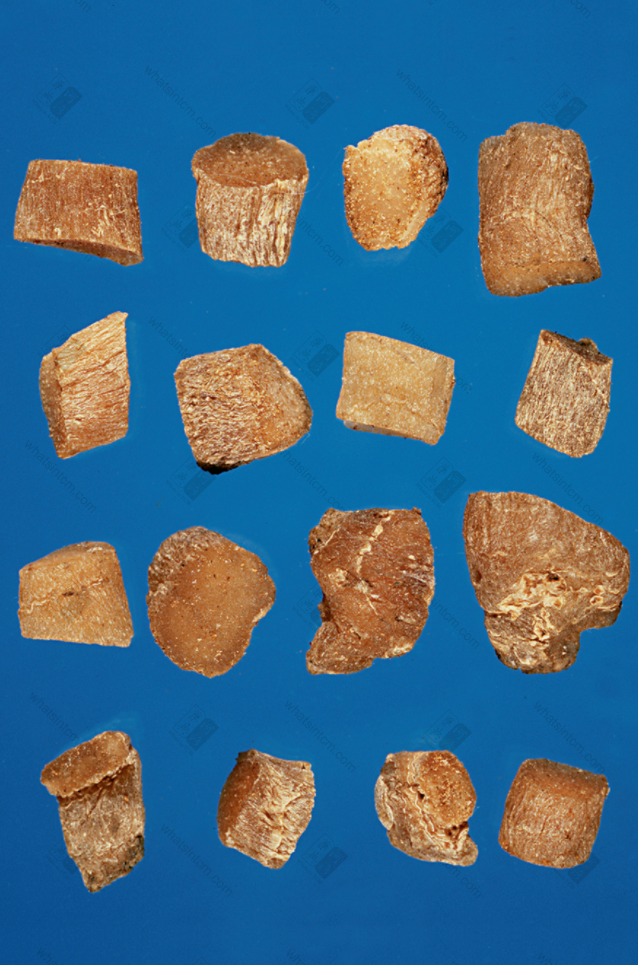 Small pieces of Yu Zhunn【Naming】n
Small pieces of Yu Zhunn【Naming】n
n 【Source】n
Shen Nong’s Classic of Materia Medica, Top Grade, *Wei Rui*
n 【Common Usage Level】n
C
n 【Botanical Origin】n
Rhizome of Polygonatum odoratum (Mill.) Druse of the Liliaceae family.
n 【Characteristics】n
This product is cylindrical, slightly flattened and shrunken, rarely branched, of varying lengths. Most commercial products are broken into segments of approximately 5-10-15 cm in length and about 1 cm in diameter, with multiple fibrous root scars throughout. One end of the rhizome may sometimes have buds. Every 3-6 cm, there are round, wavy, transverse ring segments. When dry, it is hard, but easily becomes soft and pliable when exposed to moisture. The fracture surface is horny, sweet, and sticky. Cultivated products are stout, while wild products are slender. The prepared slices are light yellow, with a cartilaginous, translucent appearance and are viscous. Odorless and sweet in taste.
n 【Identification】n
Illustrated Materia Medica: “Only the thin and cottony ones are good.” Complete Book of Processing: “People in the market call Rehmannia-like Huang Jing by this name, and those that are plump and large are considered best.” Those with long strips, thick and strong, yellow, bright, heavy, soft, and firm in texture, with sufficient sugar content and sweet taste are considered good. Those with wrinkled branches, dry and stiff skin, brown, dark yellow, dry and shriveled are considered second-rate.
n 【Identification Terminology】n
1. Transverse Striations: Refers generally to ring-like or spiral-shaped markings on root and rhizome-based medicinal materials. The transverse striations originate from nodes or stem scars, such as the transverse striations on Yu Zhu, which are nodes.
n 【Category】n
Rhizomes

